New generation of farmers lead the way in making farming more productive and profitable
In the Indo-Gangetic Plains of northern India, nearly 70% of the population is involved in agriculture and extension services. Despite the abundantly fertile soil and farmers’ resilience, the adoption of agricultural innovations and productivity in the region has been slow.
This slow progress is often attributed to comparatively low levels of agricultural mechanization in the region and small land holdings of individual farmers, which often makes them risk averse to new technologies. However, times are changing.

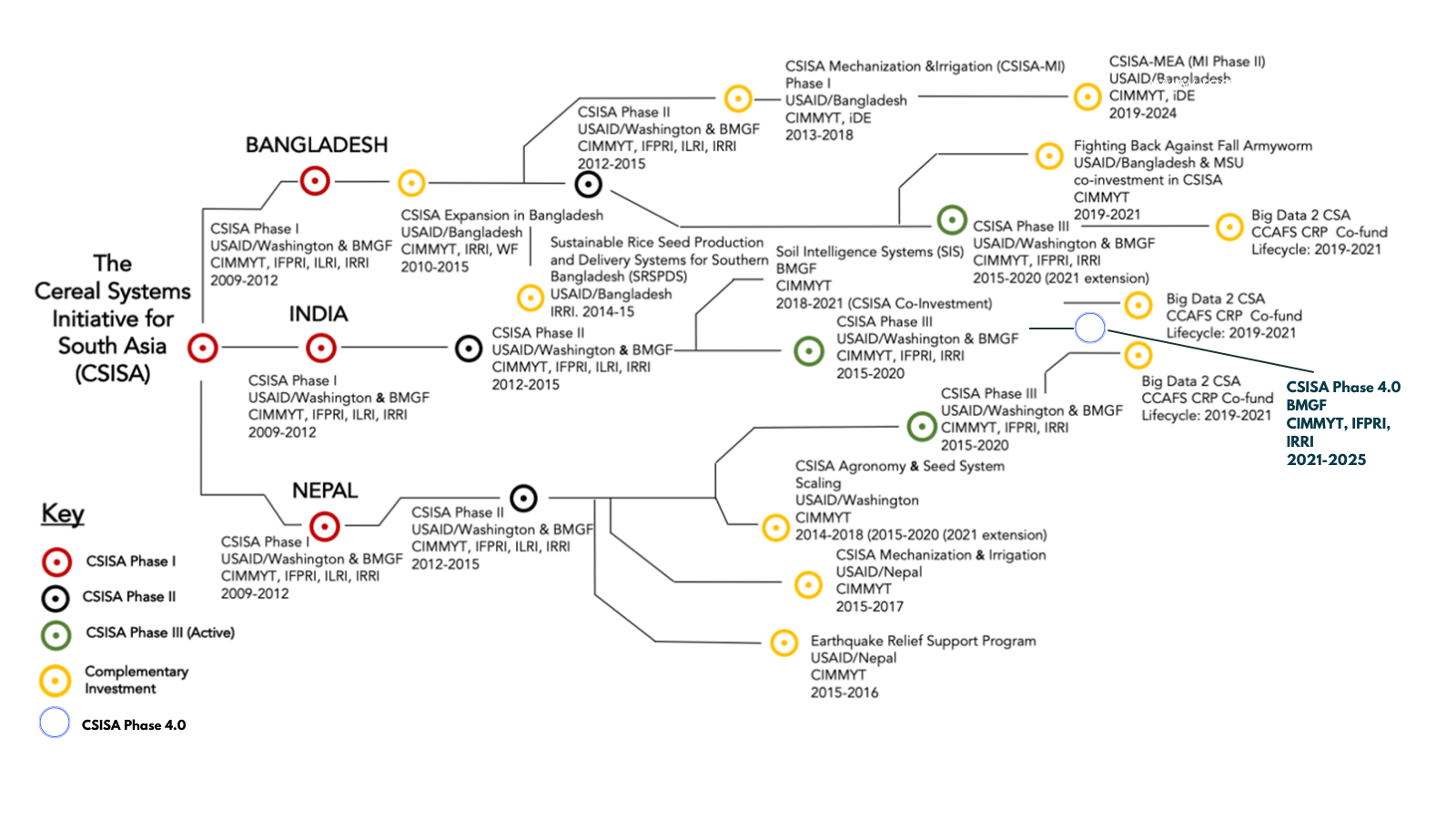
Through the Cereal Systems Initiative for South Asia (CSISA) project, researchers from the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), working closely with the local Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK) and partners, have led the transition from traditional farming to sustainable intensification agricultural practices in the region, helping the region slowly but steadily realize its full potential. Over the years, working extensively with progressive farmers, CSISA scientists have helped optimize the cost of inputs and increase productivity through new technology adoption and capacity building for these farmers.
Krishnamohan Pathak, a farmer in his early sixties from the village of Patkhaoli, first learned about conservation agriculture practices when he attended a field event in Nonkhar village in Deoria district, Uttar Pradesh. CSISA researchers invited farmers from Nonkhar and neighbouring villages to attend a field day event, an exposure activity, on zero tillage wheat and direct seeded rice (DSR) technologies. Zero tillage allows farmers to plant directly without plowing or preparing the soil, minimizing soil movement. Pathak was one of the farmers who got to see first-hand the advantages of these sustainable agricultural practices.
Seeing merit in these practices, Pathak continued to engage with CSISA scientists and in 2013-2014, adopted zero tillage, and directly seeded rice in his family-owned fields.
“The CSISA field team encouraged me to buy a rice planter which has helped manage paddy transplantation on time, and wheat after that through zero till,” Pathak said.
Pathak later participated in other agri-technology events and CSISA field trial activities. In 2018, he joined other progressive farmers from the region who attended a training at ISARC (IRRI South Asia Regional Centre) in Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh on direct seeded rice, organized by CSISA researchers to build capacity and raise awareness of the conservation agriculture method.
The next generation leads the way
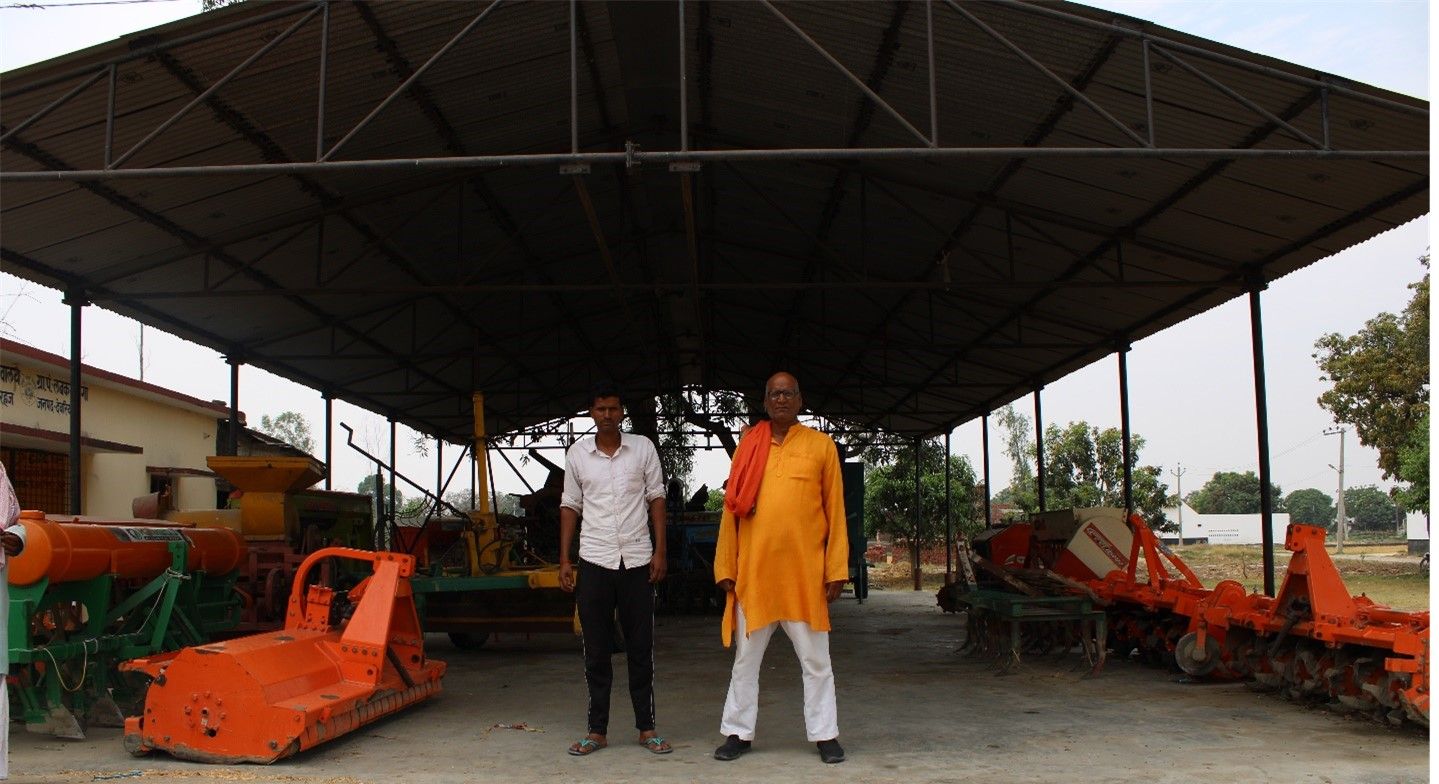
Today, Pathak is one of the key influential farming members in the region. He has now, however, passed the baton to his 37-year-old son Gangesh Pathak. “I have occupied myself with other local leadership activities after my son has been active in the fields. I am not so skilled at using these machines, their maintenance and their services. The younger generation seems much better at adapting,” he said.
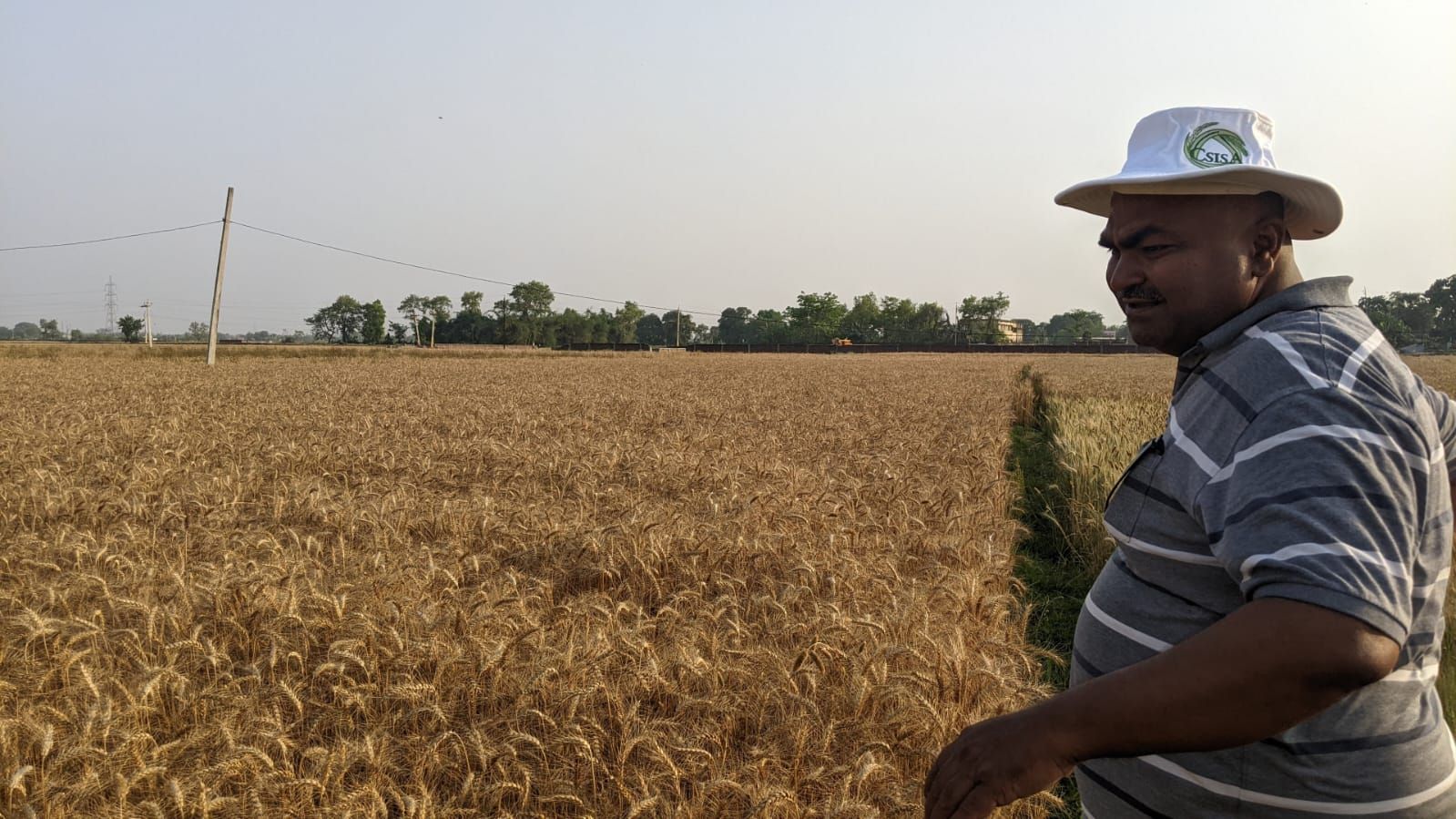
Gangesh has been involved actively in farming ever since he finished his graduation, trying to make it lucrative. He has enjoyed recent success growing wheat and rice through new technology and practices. Standing in the fields recently harvested with the new improved wheat variety DBW 187, grown through early sowing – a method which goes against the traditional practice of planting after November – and zero tillage, he is happy with his 5.5 ton per hectare yield.
He spoke enthusiastically about the farming machinery he has procured to reduce drudgery in his farms and the hiring services provided to smallholder farmers in the region. After his father bought the transplanter in 2014, the family added larger machines such as the Happy Seeder, Super Seeder, Laser Land Leveller, Straw Reaper, and Direct Seeded Rice machine.

According to Gangesh, this has been possible thanks to the support from the local agriculture authorities and guidance from the CSISA team, who told his father about the various schemes offered by the central and state government to support farmers to adopt more productive and sustainable agricultural technologies.
Ajay Kumar Pundir, CIMMYT agronomist, based in Uttar Pradesh and leading CSISA’s efforts, stressed the importance of access to agricultural mechanization and support.
“Our job just does not end at informing and training farmers about better-bet agricultural practices. Along with other public and private stakeholders, we must support and ensure their availability and access – machines, quality seeds, timely information – for farmers to adopt it,” he said.
Custom hiring center help scale mechanization
With so much farm machinery, the Pathaks soon began extending hiring services. Custom hiring is a promising enterprise opportunity for farmers as they can use the machinery on their farms and earn extra income by extending services to other farmers at a reasonable cost, which helps cover diesel and maintenance costs. Gangesh made about 2.5 lakhs (USD $3,033.76) in profit during the 2022-2023 Rabi (winter crops) through hay machine hiring services, where around 250 farmers used these services.
Once the word spread, demand for hiring services by smallholder farmers, challenged by scarce labor for sowing and harvesting, started growing. Gangesh was encouraged by the good profits and was keen to share the benefits of such hiring services to as many farmers as possible, and he helped establish a Farmer Producer Organization (FPO) with his father, Krishnamohan. FPO is a group made up of farmer-producers who are entitled to a host of benefits, including quality seeds, technical support, market access, under the Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare (DA&FW).
The FPO, started by the Pathaks in 2020, with 75 members (farmers) initially, currently boasts of around 300 farmers. Almost all FPO members have availed the custom hiring services for all farming purposes and various crops. Farmers, “particularly smallholders who cannot afford to purchase these machines for less than a few acres of land, are happy with the custom hiring services. It helps reduce their input cost by almost 50% along with other FPO member benefits,” Gangesh said.
Community-based technology demonstrations by CSISA and KVK and partners are ongoing to scale-out proven technologies and practices like early wheat sowing, zero tillage, and direct seeded rice. Gangesh is hopeful that farmers in the region, despite the emerging climate crisis concerns – already being felt in the region – can produce more and improve their income. He reckons that diversifying between rice-wheat cropping systems, mechanizing and system optimization through better advisories, and improved access to technologies as recommended by agronomists, will help farmers stay ahead of the curve.
About CSISA
Established in 2009, the Cereal Systems Initiative for South Asia (CSISA) is a science-driven and impacts-oriented regional initiative for increasing the productivity of cereal-based cropping systems. CSISA works in Bangladesh, India, and Nepal. CSISA activities in India focus on the eastern Indo-Gangetic Plains, dominated by small farm sizes, low incomes, and comparatively low agricultural mechanization, irrigation, and productivity levels. Learn about CSISA (India) Phase 4.0