Research, innovation, partnerships, impact
On May 15, 2019, as part of the CGIAR System Council meeting held at the ILRI campus in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, around 200 Ethiopian and international research and development stakeholders convened for the CGIAR Agriculture Research for Development Knowledge Share Fair. This exhibition offered a rare opportunity to bring the country’s major development investors together to learn and exchange about how CGIAR investments in Ethiopia help farmers and food systems be more productive, sustainable, climate resilient, nutritious, and inclusive.

Under the title One CGIAR — greater than the sum of its parts — the event offered the opportunity to highlight close partnerships between CGIAR centers, the Ethiopian government and key partners including private companies, civil society organizations and funding partners. The fair was organized around the five global challenges from CGIAR’s business plan: planetary boundaries, sustaining food availability, promoting equality of opportunity, securing public health, and creating jobs and growth. CGIAR and its partners exhibited collaborative work documenting the successes and lessons in working through an integrated approach.
There were 36 displays in total, 5 of which were presented by CIMMYT team members. Below are the five posters presented.
How can the data revolution help deliver better agronomy to African smallholder farmers?
This sustainability display showed scalable approaches and tools to generate site-specific agronomic advice, developed through the Taking Maize Agronomy to Scale in Africa (TAMASA) project in Nigeria, Tanzania and Ethiopia.
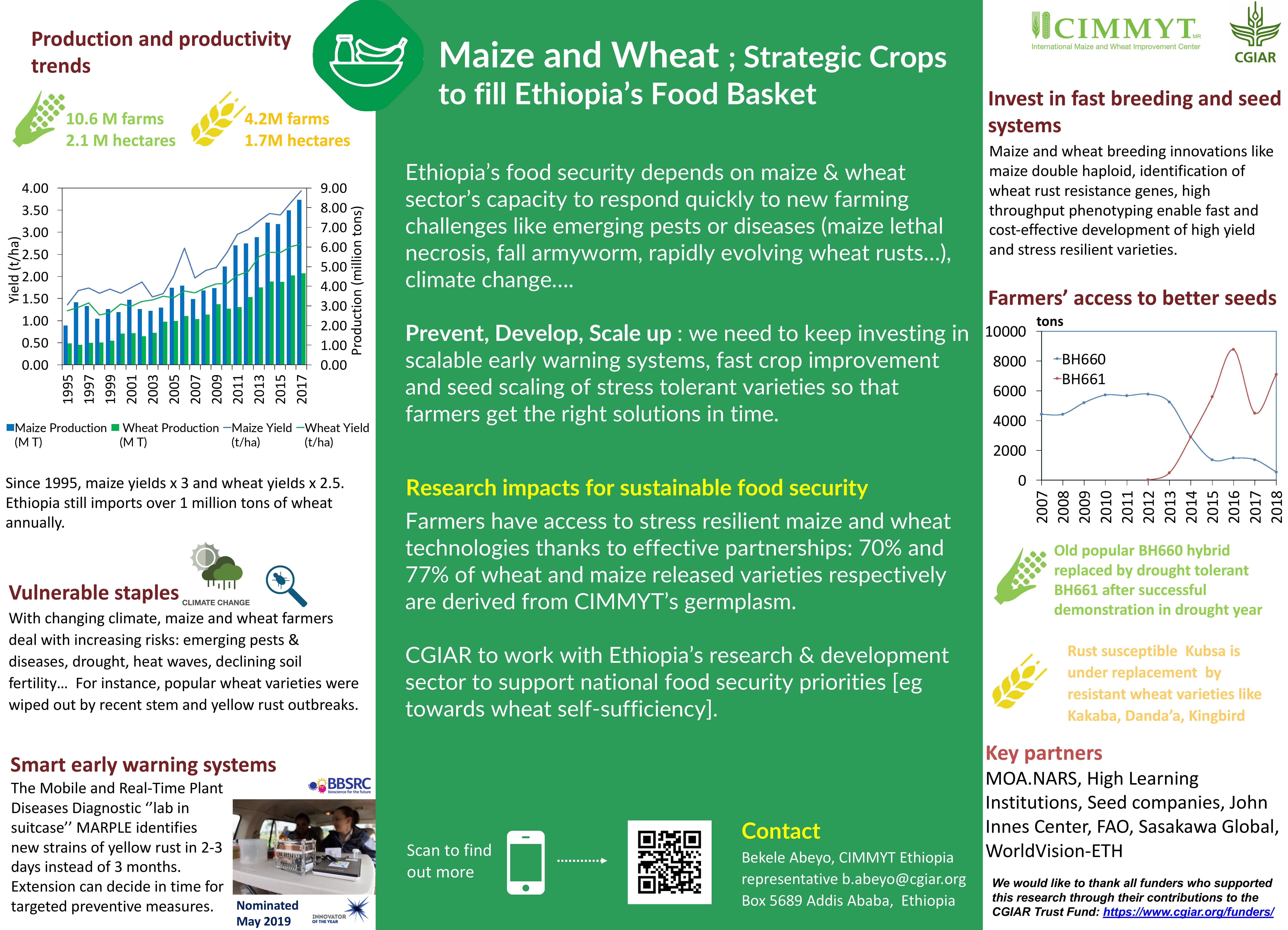
Maize and wheat: Strategic crops to fill Ethiopia’s food basket
This poster describes how CGIAR works with Ethiopia’s research & development sector to support national food security priorities.
Addressing gender norms in Ethiopia’s wheat sector
Research shows that restrictive gender norms prevent women’s ability to innovate and become productive. This significantly impacts Ethiopia’s economy (over 1% GDP) and family welfare and food security.
Quality Protein Maize (QPM) for better nutrition in Ethiopia
With the financial support of the government of Canada, CIMMYT together with national partners tested and validated Quality Protein Maize as an alternative to protein intake among poor consumers.
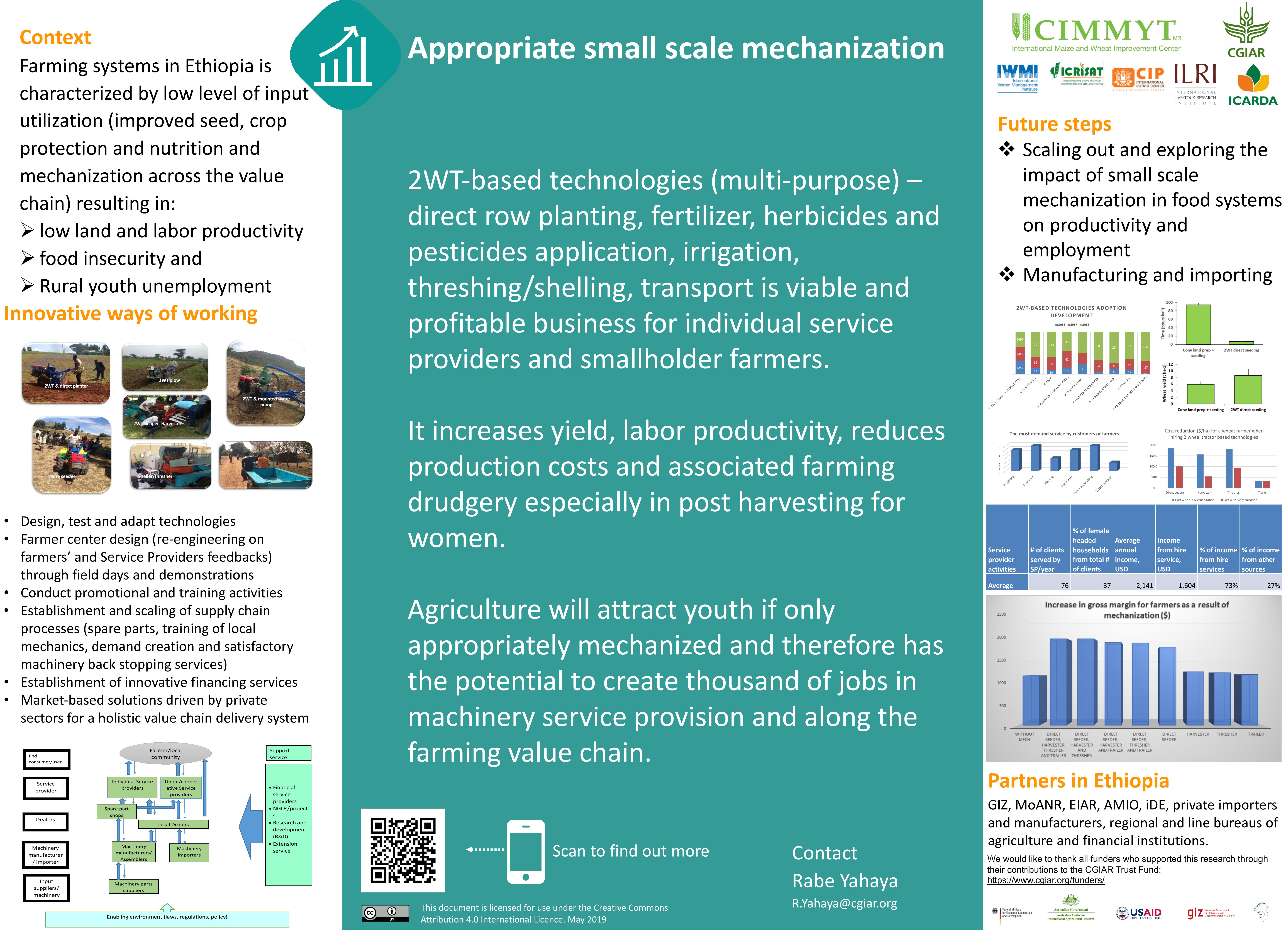
Appropriate small-scale mechanization
The introduction of small-scale mechanization into the Ethiopian agriculture sector has the potential to create thousands of jobs in machinery service provision along the farming value chain.
About the CGIAR System Council
The CGIAR System Council is the strategic decision-making body of the CGIAR System that keeps under review the strategy, mission, impact and continued relevancy of the System as a whole. The Council meets face-to-face not less than twice per year and conducts business electronically between sessions. Additional meetings can be held if necessary.
Related outputs from the Share Fair 2019
- https://www.ilri.org/news/greater-sum-its-parts-%E2%80%93-highlighting-how-cgiar-working-one
- https://paepard.blogspot.com/2019/05/agriculture-knowledge-share-fair-for.html
- https://www.cgiar.org/news-events/all-news/cgiar-system-council-share-fair/
- https://www.flickr.com/photos/ilri/sets/72157680428999578/