Breeders take quantum leap

Wheat breeders from across the globe took a big step towards modernizing their molecular breeding skills at a recent workshop sponsored by the Wheat Initiative, with the CGIAR Excellence in Breeding Platform (EiB) and the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT).
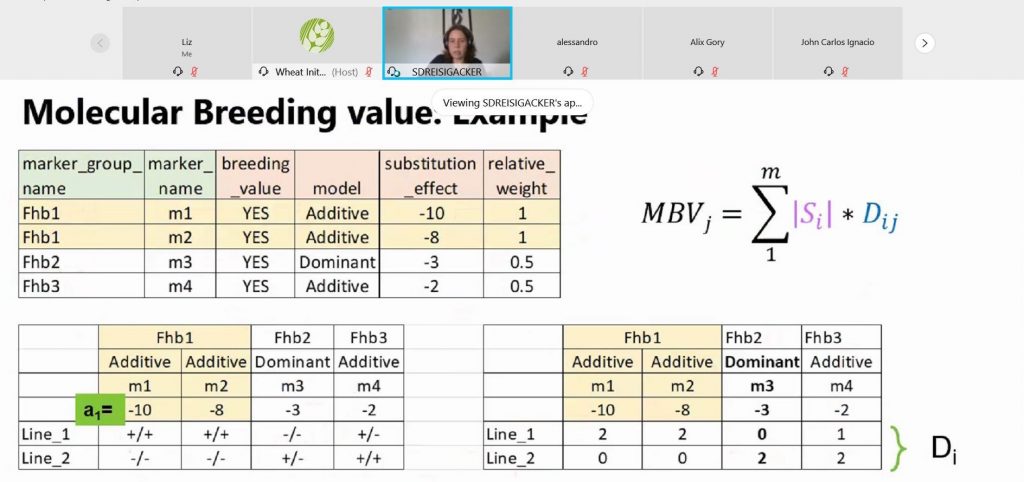
The workshop focused on three open-source tools used in molecular breeding: GOBii-GDM for genomic data management, Flapjack for data visualization and breeding analysis, and Galaxy for Genomic Selection. These tools help breeders make selections more quickly and precisely, and ultimately lead to more cost effective and efficient improvement of varieties.
The Wheat Initiative — a global scientific collaboration whose goals are to create improved wheat varieties and disseminate better agronomic practices worldwide — and its Breeding Methods and Strategies expert working group had planned to host these trainings during the 2020 Borlaug Global Rust Initiative Technical Workshop in the United Kingdom. After it became obvious that in-person trainings were not possible, the course organizers — including CIMMYT molecular wheat breeder Susanne Dreisigacker and EiB Adoption Lead and former GOBii project director Elizabeth Jones — decided to come together to host online workshops.
Many of the tools will be incorporated into EiB’s Enterprise Breeding System (EBS), a new integrated data management system being developed for CGIAR breeders. Jones plans to also design training modules for these molecular breeding tools that will be accessible to anyone through the EiB Toolbox.
In the meantime, the tools used in the workshop are all freely available: DArTView, Flapjack (training videos), GOBii-GDM (request access through the web form or by email), and Galaxy Genomic Selection.

Powering data analysis around the world
The workshop series, “Transforming Wheat Breeding Through Integrated Data Management with GOBii and Analysis in Flapjack,” aimed to benefit breeders from wheat producing countries all over the world, with sessions over two different time zones spread out over three days to reduce “Zoom fatigue.” Participants joined the first session from Australia, Canada, Ethiopia, France, India, Ireland, Italy, Morocco, Pakistan, Switzerland, Tunisia, the United Kingdom and the United States.
“It was wonderful to see the diversity of participants that we were able to train through an online workshop, many of whom otherwise might not have been able to travel to the UK for the original meeting,” said Jones. “Participants were very engaged, making the workshop so rewarding.”
The workshop was guided by Teresa Saavedra, Wheat Initiative coordinator. Apart from Dreisigacker and Jones, other trainers explained specific tools and approaches. Iain Milne from the James Hutton Institute in Scotland gave more details about the Flapjack genotyping visualization tool, which includes analysis for pedigree verification, marker assisted backcrossing and forward breeding. Andrew Kowalczyk, developer at Diversity Arrays Technology, spoke about the genotyping data QC tool DArTView.
Clay Sneller, wheat breeder at Ohio State University, contributed training materials for important molecular breeding tools. Carlos Ignacio, previously based at the International Rice Research Center (IRRI) and now working on a PhD in Genomic Selection at Ohio State University, contributed his experience as a GOBii team member and a major contributor towards the design of Flapjack tools. Star Gao, application specialist with GOBii and now a requirements analyst for the Enterprise Breeding System, also facilitated the sessions.
Gilles Charmet, research director at the France’s National Research Institute for Agriculture, Food and Environment (INRAE), introduced the sessions in the Americas/Europe time zone with welcome remarks and overview of the goals of the Wheat Initiative. Alison Bentley, director of the CIMMYT Global Wheat Program, briefed on the achievements and goals of the CIMMYT Wheat program and the Accelerating Genetic Gains in Maize and Wheat for Improved Livelihoods (AGG) project.
“This training will contribute towards us reaching our AGG goals of accelerating gains in wheat, by sharing technical knowledge, and allowing our beneficiary partners to have state-of-the-art know-how in the use of genetic and genomic data,” Bentley said.
Participant Stéphane Boury from Caussade Semences, France commented, “This was a very effective way to learn about new tools in wheat breeding.”
The sessions continue in Australasia next week, and will be introduced by Peter Langridge, chair of the Scientific Board for the Wheat Initiative, and EiB director Michael Quinn. Sanjay Kumar Singh, incoming chair of the Breeding expert working group for the Wheat Initiative, will close the event.