New publications: Voicing demand for farm power
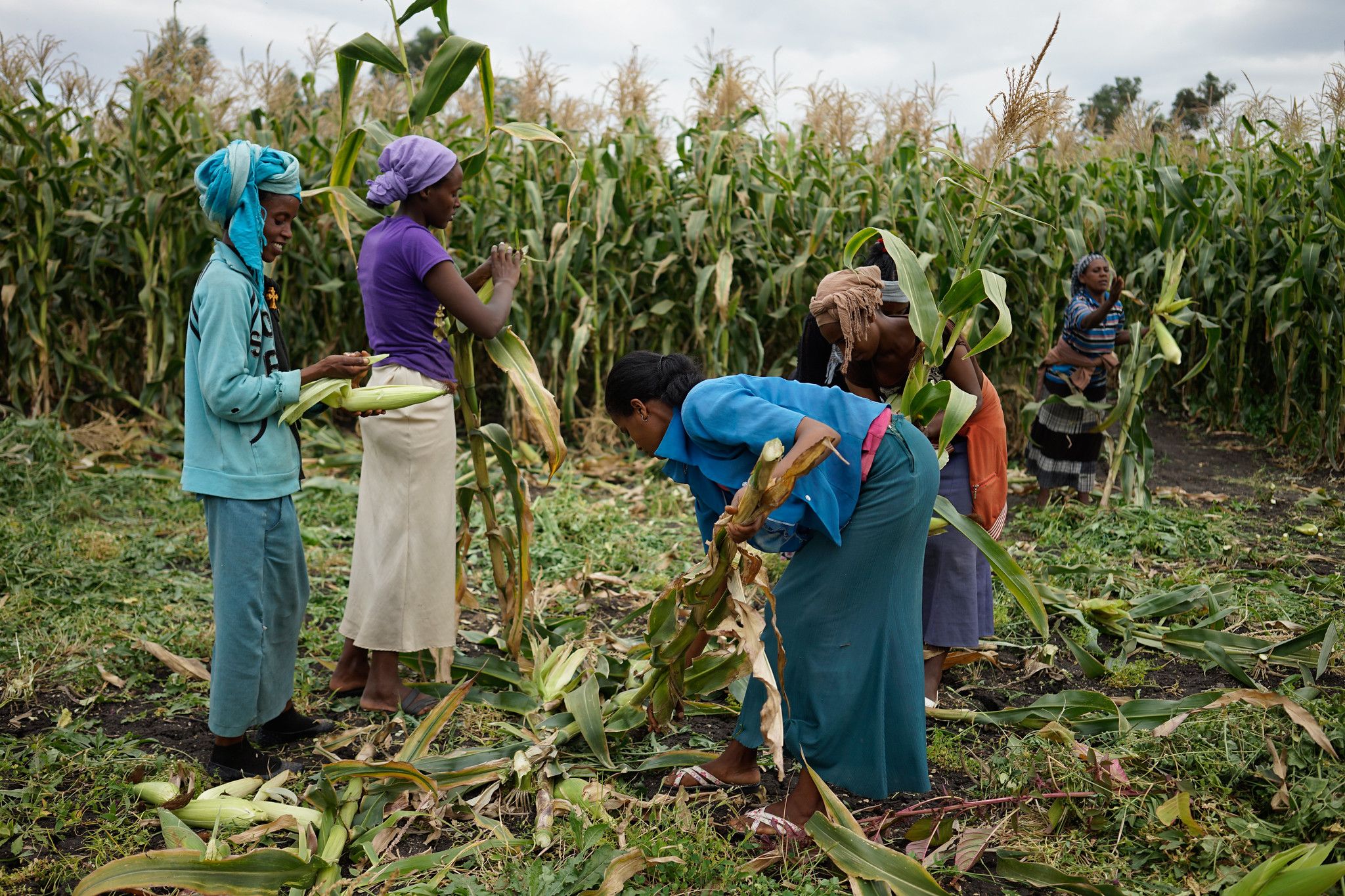
A new study examines how intra-household gender dynamics affect women’s articulation of demand for and adoption of labor-saving technologies in maize-based systems, drawing on empirical data from diverse household categories in Ethiopia and Kenya, where both women and men play important roles in agriculture.
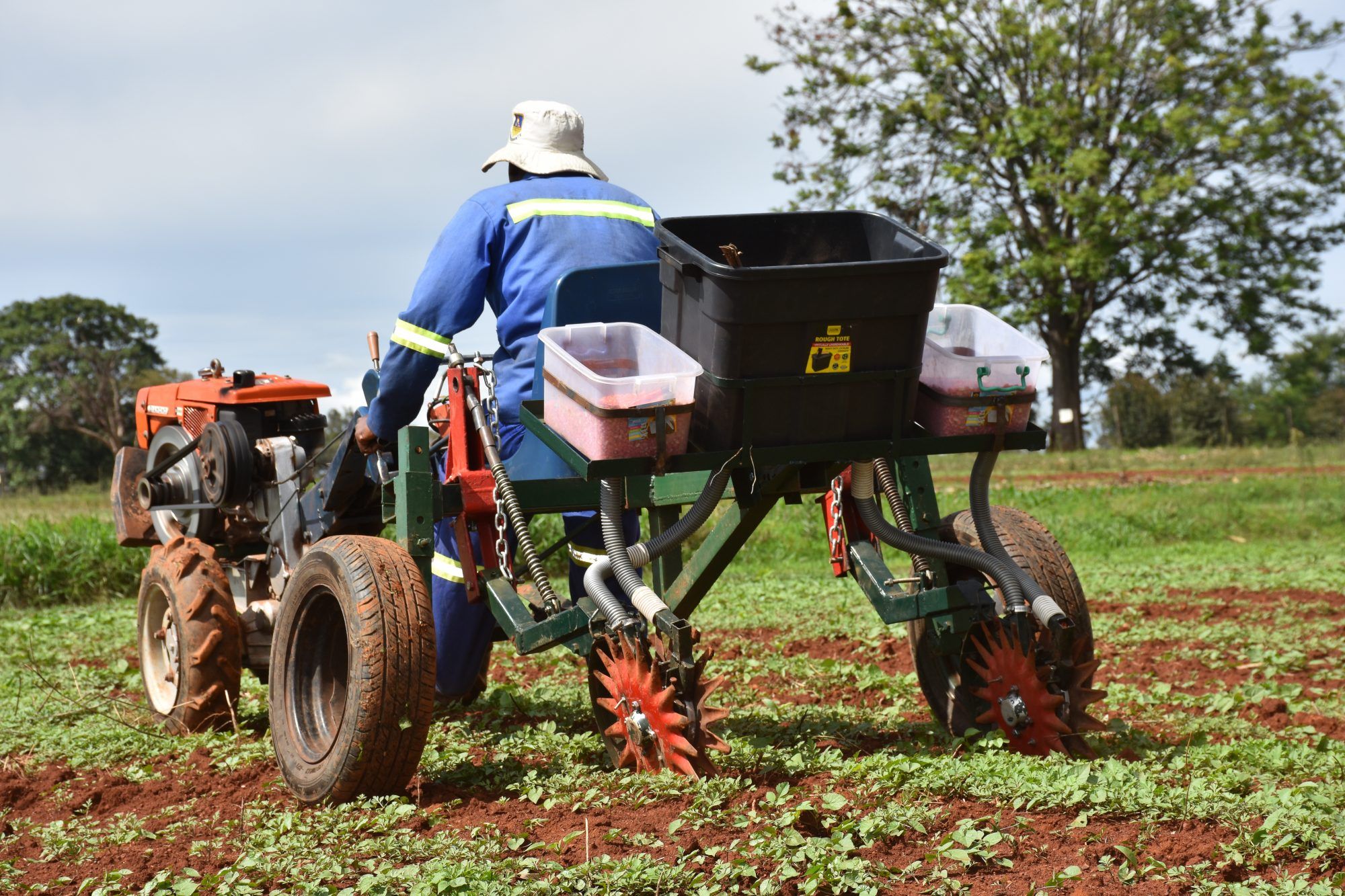
Where agriculture relies heavily on manual labor, small-scale mechanization can reduce labor constraints and contribute to higher yields and food security. However, demand for and adoption of labor-saving machinery remains weak in many areas. Paradoxically, this includes areas where women face a particularly high labor burden.
“How do we make sense of this?” asks Lone Badstue, a rural development sociologist at the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT). “What factors influence women’s articulation of demand for and use of farm power mechanization?”
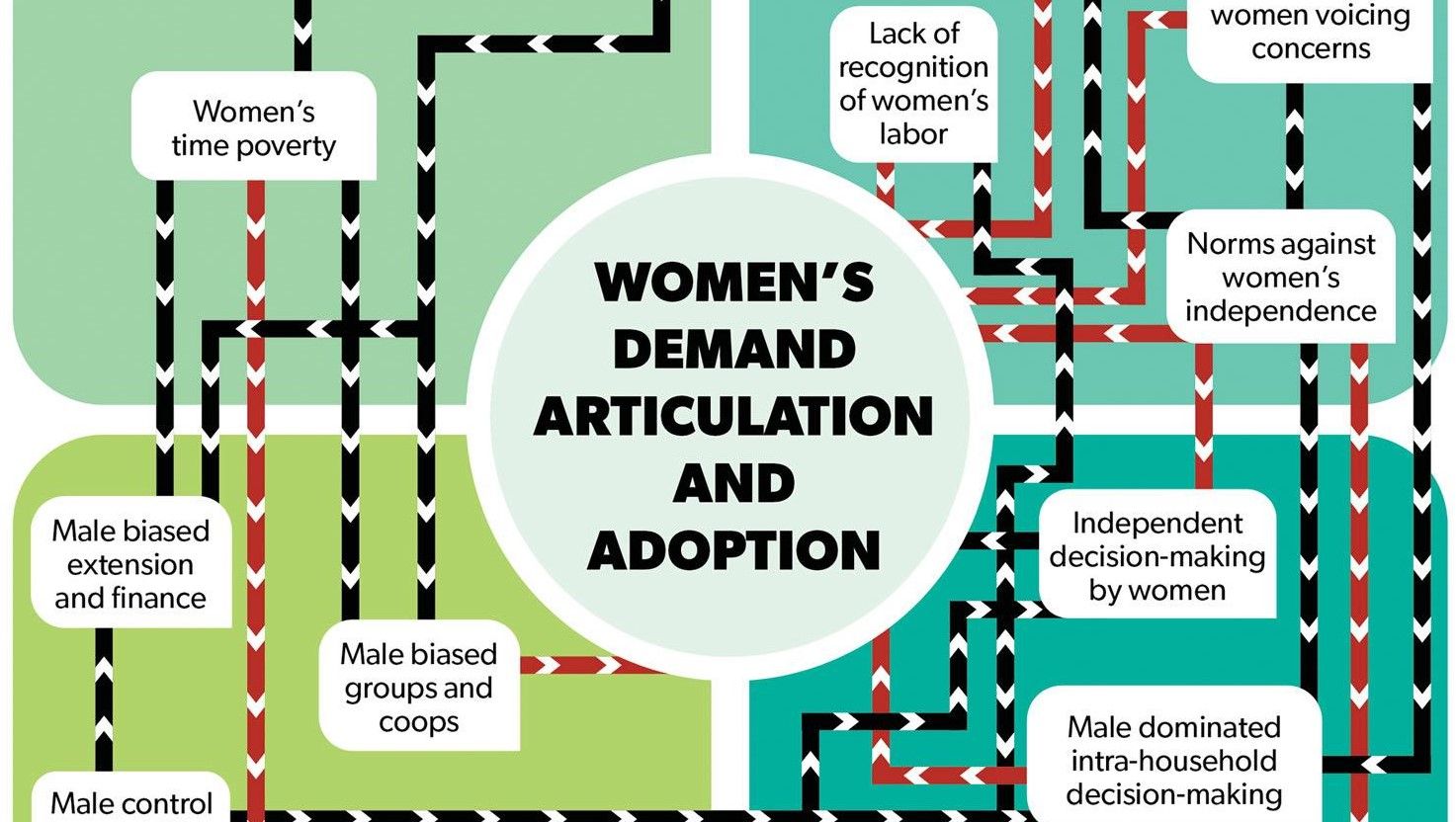
To answer this question, an international team of researchers analyzed data from four analytical dimensions — gender division of labor; gender norms; gendered access to and control over resources like land and income; and intra-household decision-making — to show how interactions between these influence women’s demand for and use of mechanization.
“Overall, a combination of forces seems to work against women’s demand articulation and adoption of labor-saving technologies,” says Badstue. Firstly, women’s labor often goes unrecognized, and they are typically expected to work hard and not voice their concerns. Additionally, women generally lack access to and control over a range of resources, including land, income, and extension services.
This is exacerbated by the gendered division of labor, as women’s time poverty negatively affects their access to resources and information. Furthermore, decision-making is primarily seen as men’s domain, and women are often excluded from discussions on the allocation of labor and other aspects of farm management. Crucially, many of these factors interlink across all four dimensions of the authors’ analytical framework to shape women’s demand for and adoption of labor-saving technologies.
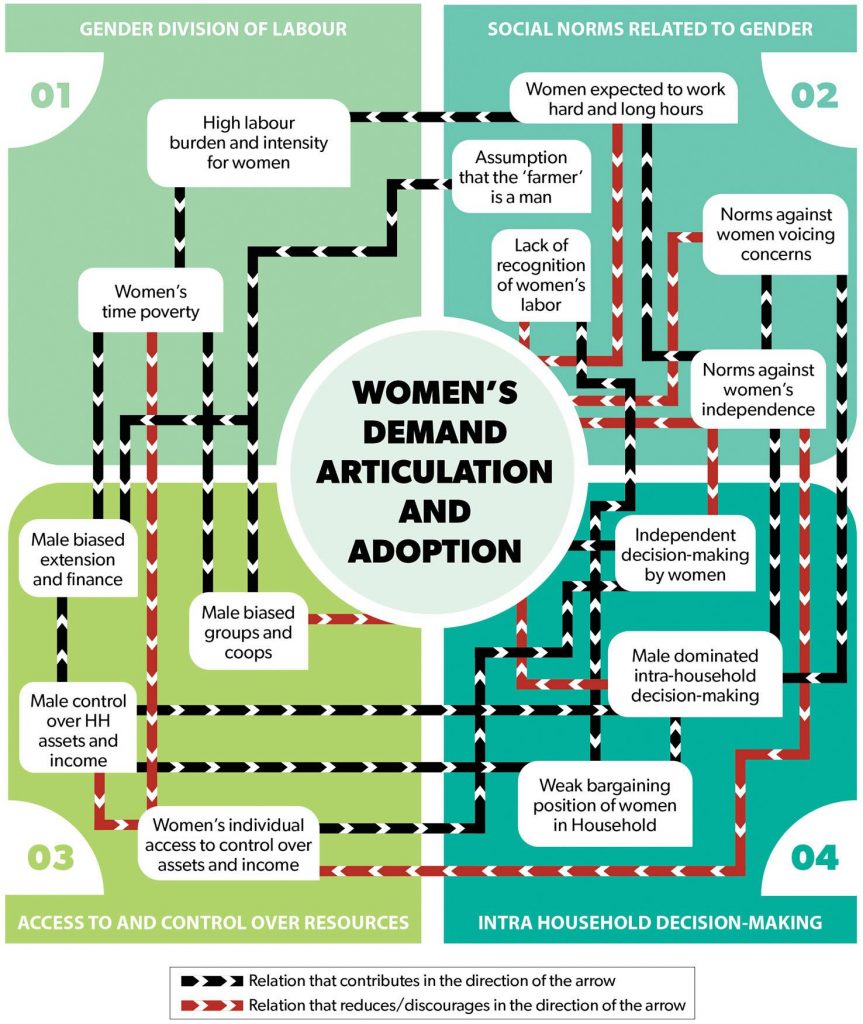
Demand articulation and adoption of labor-saving technologies in the study sites are shown to be stimulated when women have control over resources, and where more permissive or inclusive norms influence gender relations. “Women’s independent control over resources is a game changer,” explains Badstue. “Adoption of mechanized farm power is practically only observed when women have direct and sole control over land and on- or off-farm income. They rarely articulate demand or adopt mechanization through joint decision-making with male relatives.”
The study shows that independent decision-making by women on labor reduction or adoption of mechanization is often confronted with social disapproval and can come at the cost of losing social capital, both within the household and in the community. As such, the authors stress the importance of interventions which engage with these issues and call for the recognition of technological change as shaped by the complex interplay of gender norms, gendered access to and control over resources, and decision-making.
Read the full article ‘How local gender norms and intra-household dynamics shape women’s demand for labor-saving technologies: insights from maize-based livelihoods in Ethiopia and Kenya’ in Gender, Technology and Development.
Read more recent publications by CIMMYT researchers:
1. Activity profiling of barley vacuolar processing enzymes provides new insights into the plant and cyst nematode interaction. 2020. Labudda, M., Rozanska, E., Prabucka, B., Muszynska, E., Marecka, D, Kozak, M, Dababat, A.A, Sobczak, M. In: Molecular Plant Pathology v. 21, no, 1, pg. 38-52.
2. Heteromorphic seeds of wheat wild relatives show germination niche differentiation. 2020. Gianella, M., Balestrazzi, A., Pagano, A., Müller, J.V., Kyratzis, A.C., Kikodze, D., Canella, M., Mondoni, A., Rossi, G., Guzzon, F. In: Plant Biology v. 22, no. 2, pg. 191-202.
3. Genetic dissection of maternal influence on in vivo haploid induction in maize. 2020. Nair, S.K., Chaikam, V., Gowda, M., Hindu, V., Melchinger, A.E., Prasanna, B.M. In: The Crop Journal v. 8 no. 2, pg. 287-298.
4. Genome-wide analyses and prediction of resistance to MLN in large tropical maize germplasm. 2020. Nyaga, C., Gowda, M., Beyene, Y., Muriithi, W.T., Makumbi, D., Olsen, M., Mahabaleswara, S.L., Jumbo, M.B., Das, B., Prasanna, B.M. In: Genes v. 11, no. 1, art. 16.
5. Performance and yield stability of maize hybrids in stress-prone environments in eastern Africa. 2020. Rezende, W.S., Beyene, Y., Mugo, S.N., Ndou, E., Gowda, M., Julius Pyton Sserumaga, Asea, G., Ismail Ngolinda, Jumbo, M.B., Oikeh, S.O., Olsen, M., Borém, A., Cruz, C.D., Prasanna, B.M. In: The Crop Journal v. 8, no. 1, pg. 107-118.
6. Genetic analysis of QTL for resistance to maize lethal necrosis in multiple mapping populations. 2020. Awata, L.A.O., Beyene, Y., Gowda, M., Mahabaleswara, S.L., Jumbo, M.B., Tongoona, P., Danquah, E., Ifie, B.E., Marchelo-D’ragga, P.W., Olsen, M., Ogugo, V., Mugo, S.N., Prasanna, B.M. In: Genes v. 11, no. 1, art. 32.
7. Variation in occurrence and aflatoxigenicity of Aspergillus flavus from two climatically varied regions in Kenya. 2020. Monda, E., Masanga, J., Alakonya, A. In: Toxins v. 12, no. 1, art. 34.
8. A detached leaf assay to rapidly screen for resistance of maize to Bipolaris maydis, the causal agent of southern corn leaf blight. 2020. Aregbesola, E., Ortega Beltran, A., Falade, T. D. O., Gbolagade Jonathan, Hearne, S., Bandyopadhyay, R. In: European Journal of Plant Pathology v. 156, no. 1, pg. 133-145.
9. Spread and impact of fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda J.E. Smith) in maize production areas of Kenya. 2020. De Groote, H., Kimenju, S.C., Munyua, B., Palmas, S., Kassie, M., Bruce, A.Y. In: Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment v. 292, art. 106804.
10. Genetic dissection of grain yield and agronomic traits in maize under optimum and low-nitrogen stressed environments. 2020. Berhanu Tadesse Ertiro, Olsen, M., Das, B., Gowda, M., Labuschagne, M. In: International Journal of Molecular Sciences v. 21, no. 2, art. 543.
11. ToxA-Tsn1 interaction for spot blotch susceptibility in Indian wheat: an example of inverse gene-for-gene relationship. 2020. Sudhir Navathe, Punam S. Yadav., Chand, R., Vinod Kumar Mishra, Vasistha, N.K., Prabina Kumar Meher, Joshi, A.K., Pushpendra Kumar Gupta In: Plant Disease v. 104, no. 1, pg. 71-81.
12. Novel sources of wheat head blast resistance in modern breeding lines and wheat wild relatives. 2020. Cruppe, G., Cruz, C.D., Peterson, G.L., Pedley, K.F., Asif, M., Fritz, A.K., Calderon Daza, L., Lemes da Silva, C., Todd, T.C., Kuhnem, P., Singh, P.K., Singh, R.P., Braun, H.J., Barma, N.C.D., Valent, B. In: Plant Disease v. 104, no. 1, pg. 35-43.
13. Stripe rust resistance genes in a set of Ethiopian bread wheat cultivars and breeding lines. 2020. Gebreslasie Zeray Siyoum, Huang, S., Gangming Zhan, Badebo, A., Qingdong Zeng, Jianhui Wu, Qilin Wang, Shengjie Liu, Lili Huang, Xiaojing Wang, Zhensheng Kang, Dejun Han In: Euphytica v. 216, no. 2, art. 17.
14. Appraisal of wheat genomics for gene discovery and breeding applications: a special emphasis on advances in Asia. 2020. Rasheed, A., Takumi, S., Hassan, M.A., Imtiaz, M., Ali, M., Morgounov, A.I., Mahmood, T., He Zhonghu In: Theoretical and Applied Genetics v. 113, pg. 1503–1520.
15. Diversity and incidence of plant-parasitic nematodes associated with saffron (Crocus sativus L.) in Morocco and their relationship with soil physicochemical properties. 2020. Mokrini, F., Salah-Eddine Laasli, Karra, Y., El Aissami, A., Dababat, A.A. In: Nematology v. 22, no. 1, pg. 87-102.
16. Maya gene variants related to the risk of type 2 diabetes in a family-based association study. 2020. Domínguez-Cruz, M.G., Muñoz, M. de L., Totomoch-Serra, A., García-Escalante, M.G., Burgueño, J., Valadez-González, N., Pinto-Escalantes, D., Diaz-Badillo, A. In: Gene v. 730, art. 144259.
17. Effect of allele combinations at Ppd-1 loci on durum wheat grain filling at contrasting latitudes. 2020. Arjona, J.M., Royo, C., Dreisigacker, S., Ammar, K., Subira, J., Villegas, D. In: Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science, v. 206, no. 1, pg. 64-75.
18. Yield and quality in purple-grained wheat isogenic lines. 2020. Morgounov, A.I., Karaduman, Y., Akin, B., Aydogan, S., Baenziger, P.S., Bhatta, M.R., Chudinov, V., Dreisigacker, S., Velu, G., Güler, S., Guzman, C., Nehe, A., Poudel, R., Rose, D., Gordeeva, E., Shamanin, V., Subasi, K., Zelenskiy, Y., Khlestkina, E. In: Agronomy v. 10, no. 1, art. 86.
19. Anther extrusion and its association with Fusarium head blight in CIMMYT wheat germplasm. 2020. Kaijie Xu, Xinyao He, Dreisigacker, S., He Zhonghu, Singh, P.K. In: Agronomy v. 10, no. 1 art. 47.
20. Does farm structure affect rural household incomes? Evidence from Tanzania. 2020. Chamberlin, J., Jayne, T.S. In: Food Policy v. 90, art. 101805.
21. GAR dwarf gene Rht14 reduced plant height and affected agronomic traits in durum wheat (Triticum durum). 2020. Shan Duan, Zhangchen Zhao, Yue Qiao, Chunge Cui, Morgounov, A.I., Condon, A.G., Liang Chen, Yin-Gang Hu In: Field Crops Research v. 248, art. 107721.
22. Ex-ante and ex-post coping strategies for climatic shocks and adaptation determinants in rural Malawi. 2020. Abid, M., Ali, A., Rahut, D.B., Raza, M., Mehdi, M. In: Climate Risk Management v. 27, art. 100200.
23. Management of spot blotch and heat stress in spring wheat through azoxystrobin-mediated redox balance. 2020. Sudhir Navathe, Chand, R., Vinod Kumar Mishra, Pandey, S.P., Kumar, U., Joshi, A.K. In: Agricultural Research v. 9, pg. 169–178.
24. Spatial variation in fertilizer prices in Sub-Saharan Africa. 2020. Bonilla Cedrez, C., Chamberlin, J., Guo, Z., Hijmans, R.J. In: PLoS One v. 115, no. 1, art. e0227764.
25. Unravelling the variability and causes of smallholder maize yield gaps in Ethiopia. 2020. Banchayehu Tessema Assefa, Chamberlin, J., Reidsma, P., Silva, J.V., Ittersum, M.K. van. In: Food Security v. 12, pg. 83-103.
26. Linking land distribution with food security: empirical evidence from Pakistan. 2020. Mahmood, H.Z., Ali, A., Rahut, D.B., Pervaiz, B., Siddiqui, F. In: Journal of Animal and Plant Sciences v. 30, no.1, pg. 175-184.
27. Agricultural growth and sex-disaggregated employment in Africa: future perspectives under different investment scenarios. 2020. Frija, A., Chebil, A., Mottaleb, K.A., Mason-D’Croz, D., Dhehibi, B. In: Global Food Security v. 24, art. 100353.
28. Genetic diversity analysis using DArTseq and SNP markers in populations of Aegilops species from Azerbaijan. 2020. Abbasov, M., Sansaloni, C.P., Burgueño, J., Petroli, C.D., Akparov, Z., Aminov, N., Babayeva, S., Izzatullayeva, V., Hajiyev, E., Rustamov, K., Mammadova, S.A., Amri, A., Payne, T.S. In: Genetic Resources and Crop Evolution v. 67, no. 2, pg. 281-291.
29. Bridging the disciplinary gap in conservation agriculture research, in Malawi. A review. 2020. Hermans, T.D.G., Whitfield, S., Dougill, A.J., Thierfelder, C. In: Agronomy for Sustainable Development v. 40, no. 1, art. 3.
30. Scaling agricultural mechanization services in smallholder farming systems: case studies from sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, and Latin America. 2020. Van Loon, J., Woltering, L., Krupnik, T.J., Baudron, F., Boa, M., Govaerts, B. In: Agricultural Systems v. 180, art. 102792.