Breaking Ground: Sudha Nair helps bridge gap between maize breeding and genetics
Sudha Nair is inspired every day by her passion for biology and genetics. The senior scientist at the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) based in Hyderabad, India, works to define and practice the best strategies for applying genomics in agriculture.
“I always knew that science is what I would love to pursue,” said Sudha, an alumnus of both the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) in New Delhi and the National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences in Japan.
Originally from Kerala, India, Sudha did not expect a career in agriculture. “I studied for engineering after my high school as I was selected for that course before I was selected for the biology stream. It didn’t take me even a single moment to decide to leave the course six months later when I was selected for the undergraduate program in agriculture,” Sudha said. “I can’t say that it is love for agriculture that forced me to choose the field I am in, but it is the fascination for biological science. I love genetics and I love research; as long as I get to do this as part of my job, I am happy.”
Sudha’s first experience working with CIMMYT involved her PhD dissertation at IARI, which was a part of research conducted for the Asian Maize Biotechnology Network (AMBIONET), led by CIMMYT. “I had always looked at CIMMYT as an organization doing high quality applied science,” she said.
Starting in 2010 as a consultant for the Drought Tolerant Maize for Africa (DTMA) project, Sudha then interviewed for the position of maize fine-mapping specialist in 2011 and was selected as a scientist. Her career at CIMMYT has now spanned close to a decade.
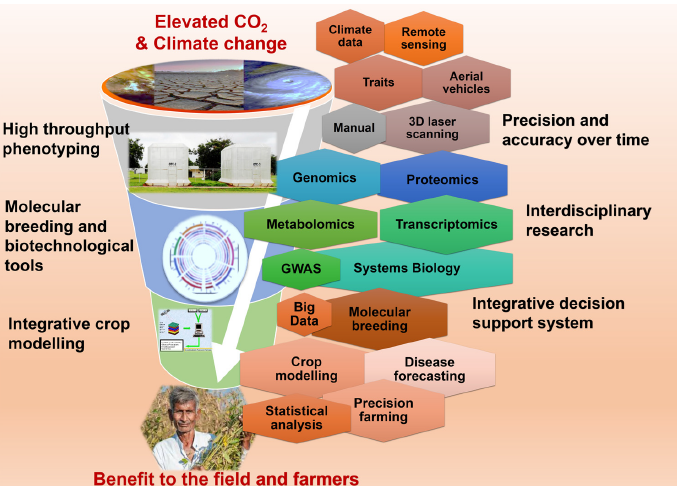
Her role involves implementation of molecular breeding in the maize breeding program in Asia. This includes discovery, validation and application of molecular markers for prioritized traits, genomic selection, and marker-based quality assurance and quality control in maize breeding – through current and past projects like Heat Tolerant Maize for Asia (HTMA), Climate Resilient Maize for Asia (CRMA) and the CGIAR Research Program on Maize (MAIZE). Apart from this, she is currently involved in the Accelerating Genetic Gains in Maize and Wheat (AGG) project for incorporating elite and stress tolerance genetics from Asia in the elite African maize germplasm.
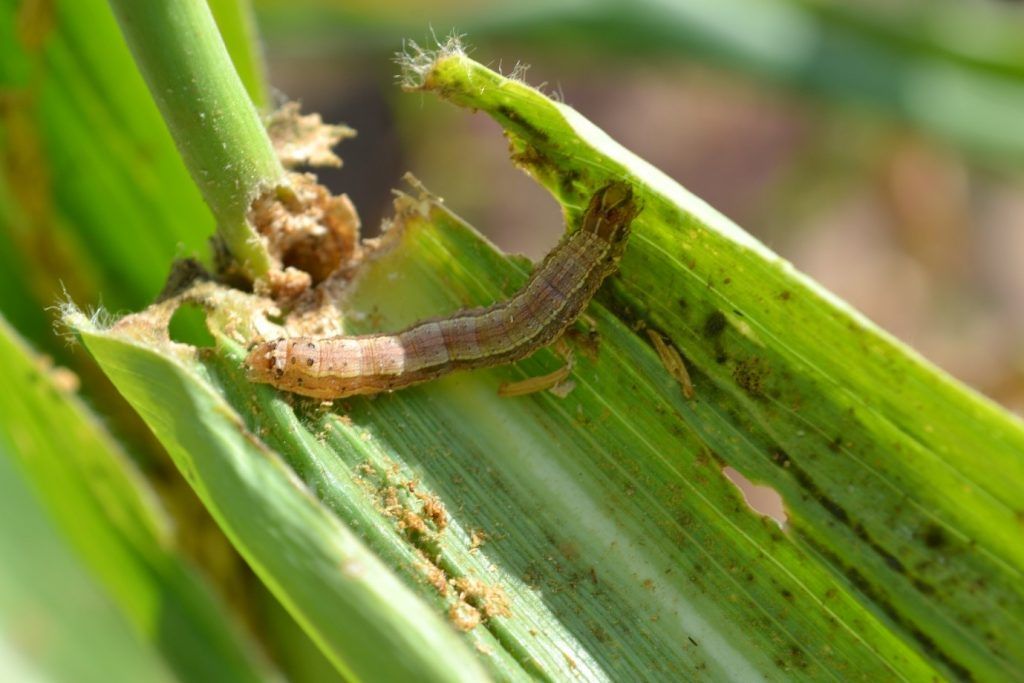
Sudha has been a part of a number of global maize projects including the Stress Tolerant Maize for Africa (STMA) project, which developed improved maize varieties tolerant to stresses such as drought and diseases, and HarvestPlus in maize, developing nutritionally enriched maize cultivars. She has also played a key role in developing CIMMYT’s second-generation tropicalized haploid inducers using marker-assisted breeding.

Bringing genetics and breeding together
Sudha is grateful for the role of CIMMYT in increasing acceptance and use of genomics in breeding programs. “When I started off as a graduate student, any work related to molecular genetics was called biotechnology, and we were considered as a different “breed”, who worked in silos to spend resources on “upstream research”, and whose results never saw any breeding applications. Breeding and molecular genetics were like parallel lines that would never meet,” she explained.
“In course of time, the research communities in applied breeding institutes like CIMMYT have brought about changes in strategies, goals, and more importantly, attitudes, and now all of us work towards one major goal of developing impactful products (varieties) for benefiting resource-constrained farming communities worldwide. All in all, I and my colleagues in the upstream research team in CIMMYT Global Maize Program have an important responsibility of providing core support to the breeding and seed systems teams in developing and delivering impactful products.”
When asked what the most enjoyable part of her work is, Sudha cited the practicality and applicability of her work. “Basically, my job responsibility is to design and implement the best strategies for applying genomics in maize breeding to achieve higher genetic gains,” she explained. “Being in an organization like CIMMYT, what is most satisfying about the role I am in is the translation of upstream research into tools for improving breeding efficiency and in turn into impactful maize varieties that the farming communities around the world cultivate.”