A journey through Bangladesh’s ground-breaking agricultural practices
Bangladesh’s agricultural landscape is evolving rapidly, with initiatives focused on modernization, sustainability, and innovation. Projects supported by the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) are working to advance the country’s agriculture through stakeholder collaboration, enhancing productivity, improving mechanization, and embedding sustainable practices.
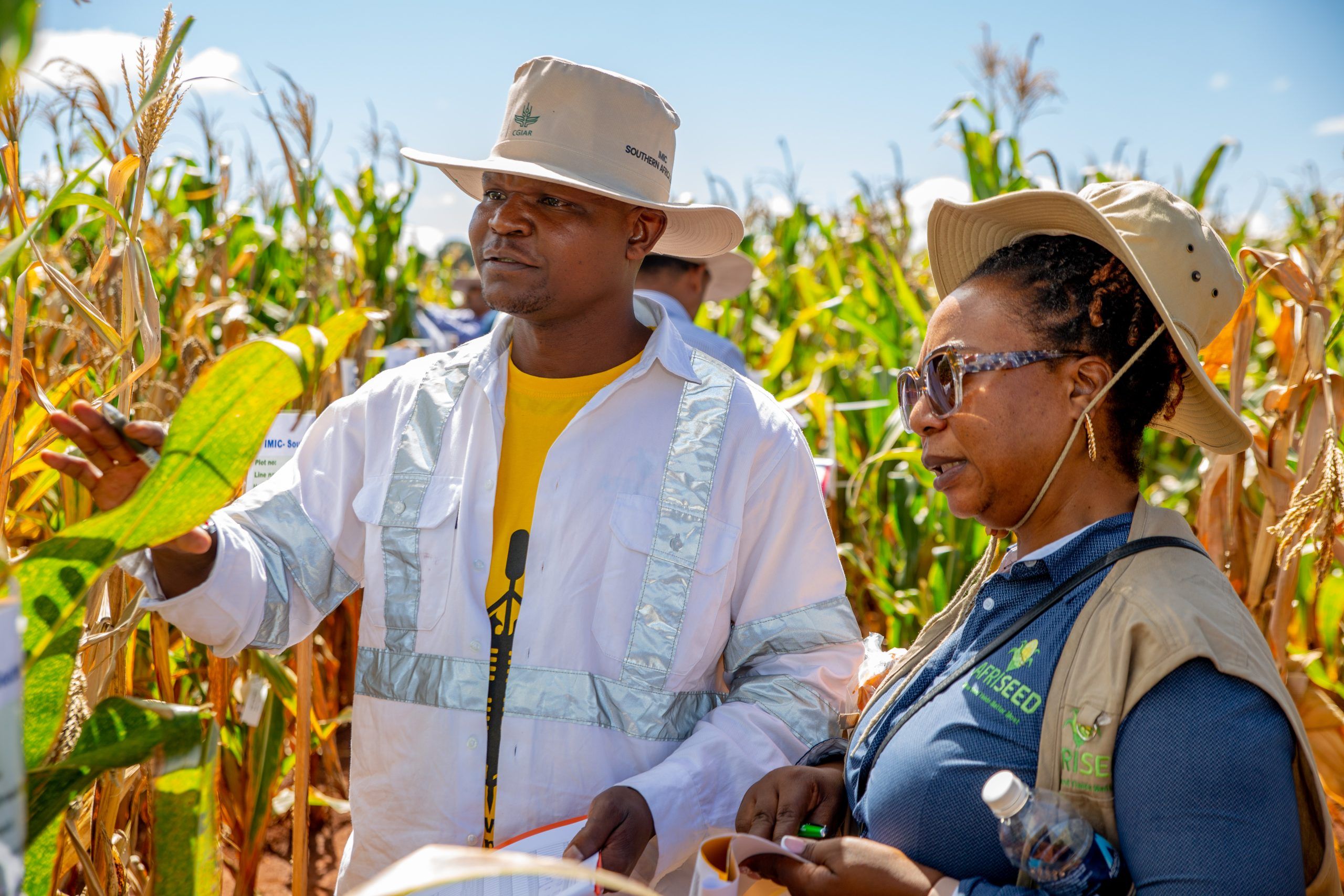
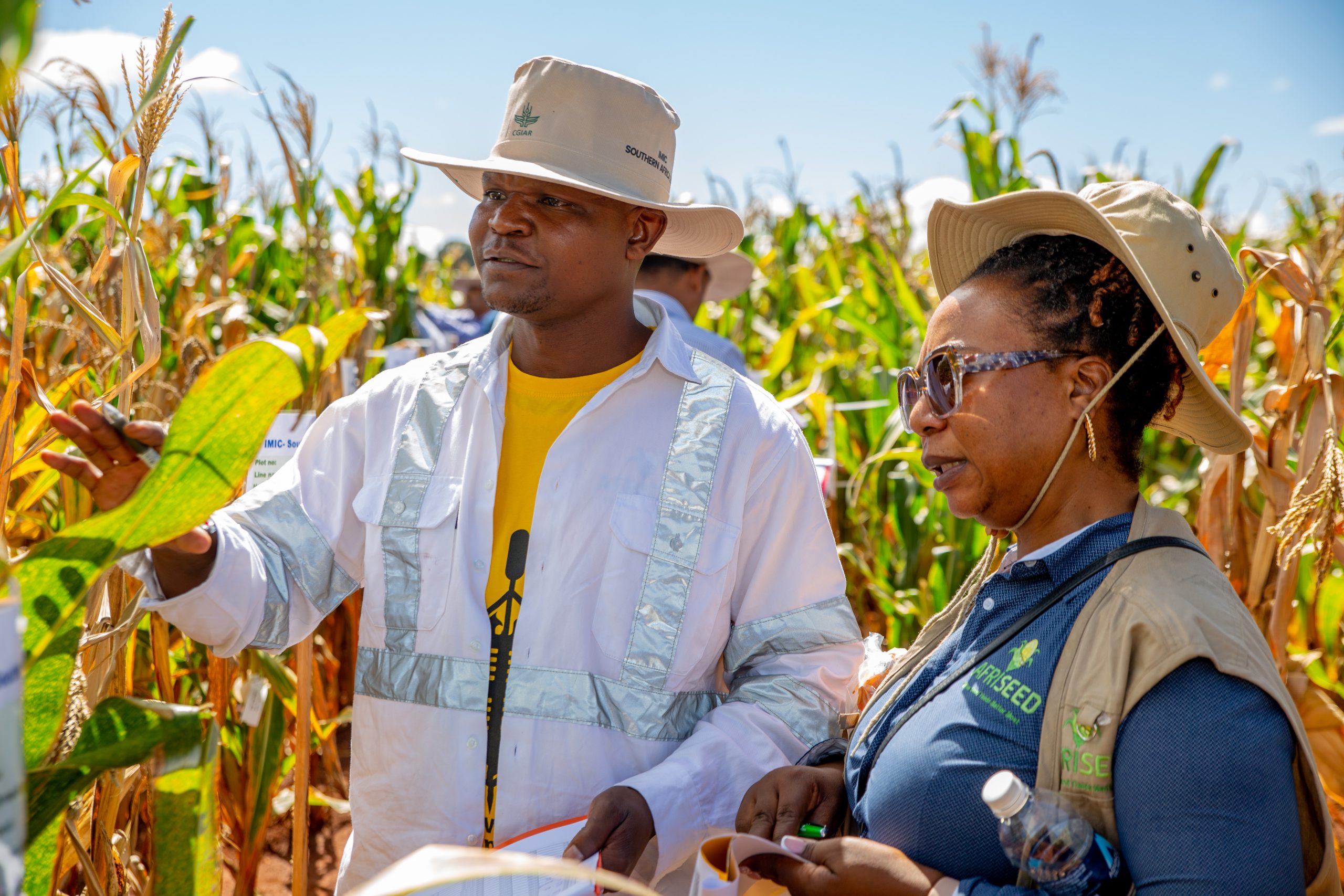
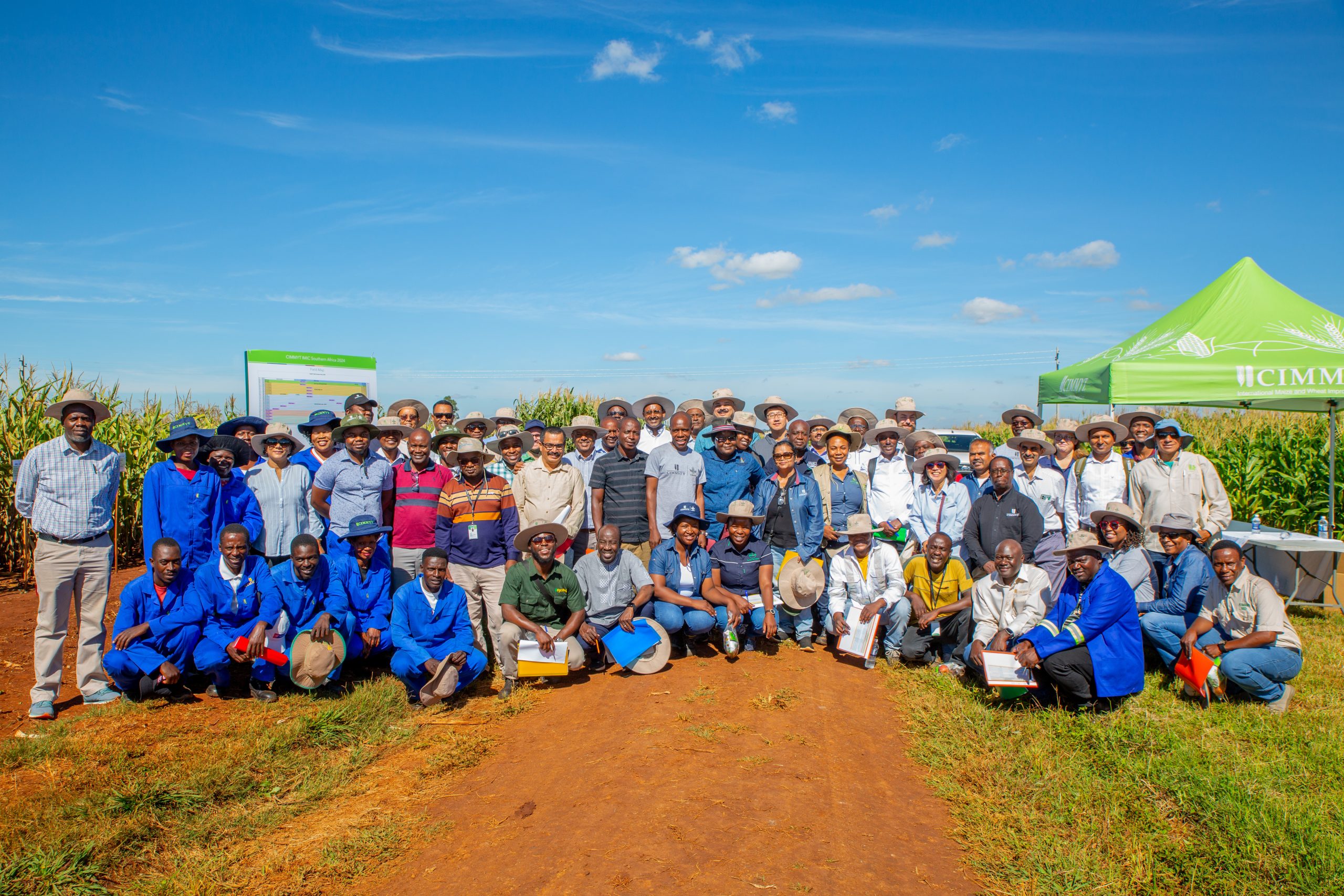
To explore the impact of this work, USAID officials and senior staff from CIMMYT embarked on a comprehensive tour across multiple project sites on 14 – 19 April 2024. The USAID delegation featured Zachary P. Stewart, production systems specialist from the Bureau for Resilience, Environment, and Food Security, and John Laborde and Muhammad Nuruzzaman from the USAID Bangladesh Mission. From CIMMYT, the team included Sieglinde Snapp, program director from the Sustainable Agrifood Systems Program, Timothy J. Krupnik, country representative for Bangladesh, and Owen Calvert, project leader for the Cereal Systems Initiative for South Asia-Mechanization Extension Activity (CSISA-MEA).
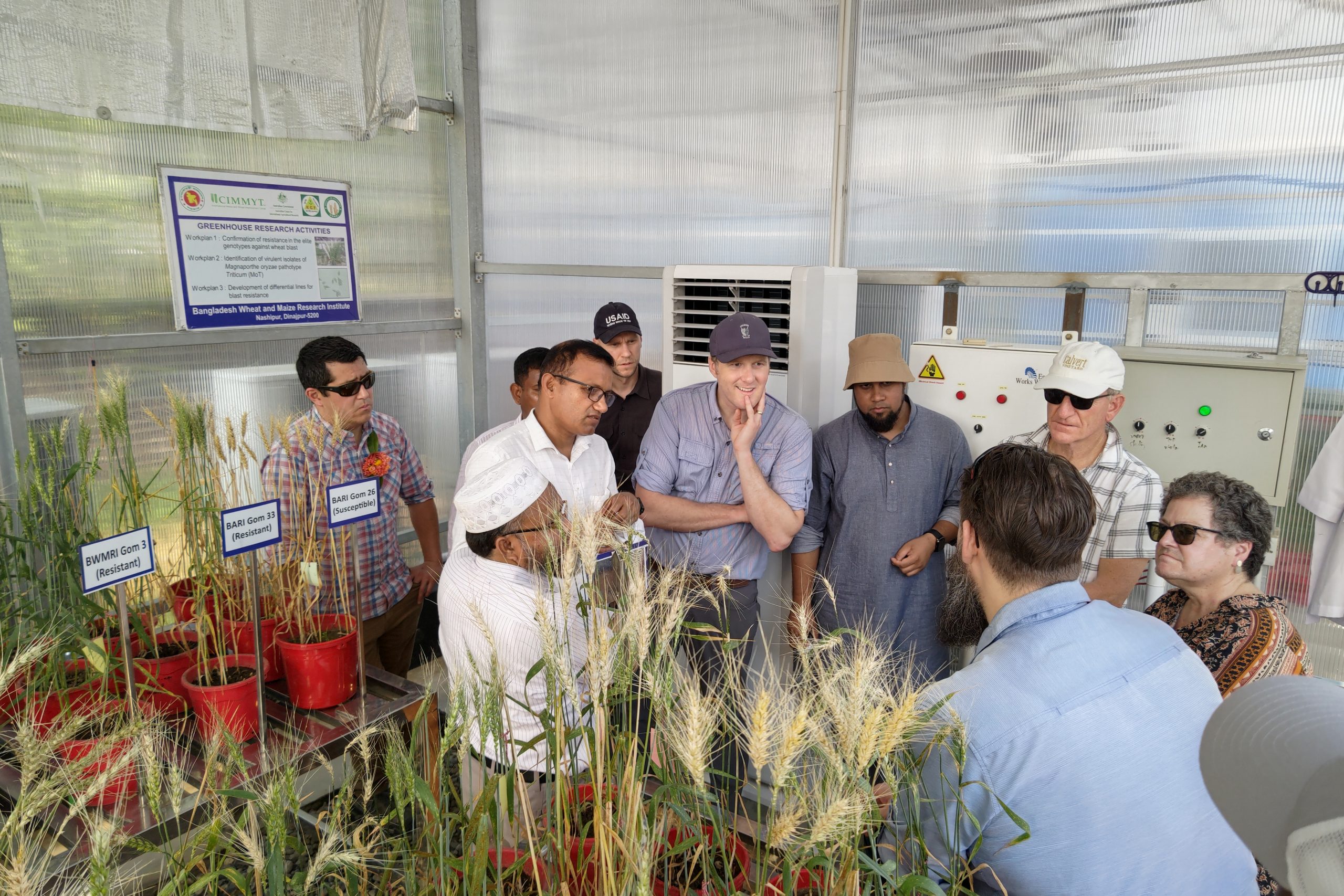

Pioneering agricultural technology
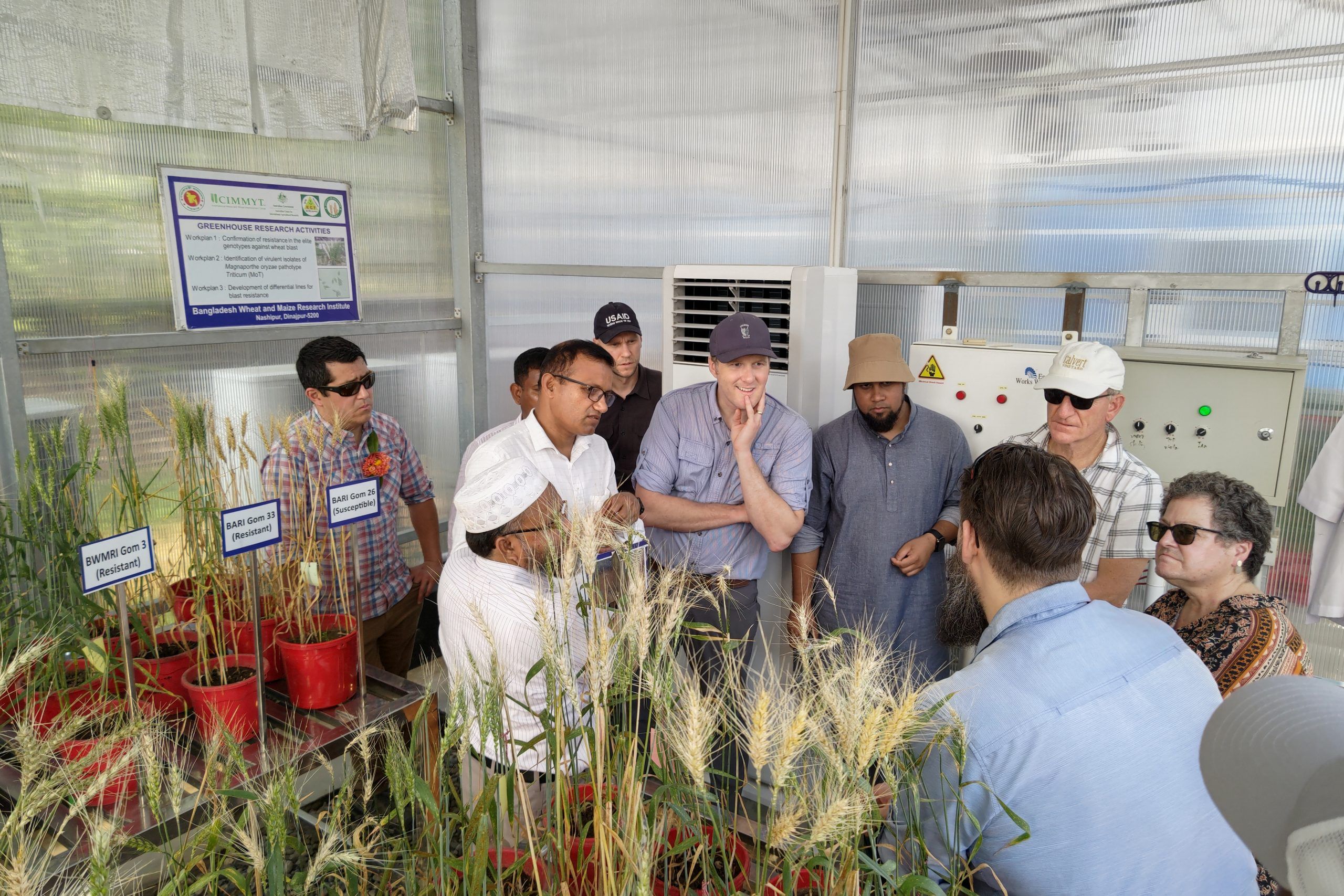
The team visited Dinajpur, Bangladesh to observe the progress of the Transforming Agrifood Systems in South Asia (TAFSSA) CGIAR Initiative, including creative efforts to raise agricultural output, support sustainable practices, and boost the area’s nutrition levels. The integrated strategy of TAFSSA, which combines inclusive community participation with socio-agronomic research, has enabled local farmers to increase revenue, diversify their crop production, and enhance yields. From the premium quality rice (PQR) value chain at the Bengal Auto Rice Mill to the sustainable intensification of mixed farming systems, the visit demonstrated TAFSSA’s dedication to building agricultural resilience and improving lives throughout Bangladesh.
In Faridpur, the team observed CSISA-MEA, a five-year project dedicated to supporting smart mechanization in Bangladesh. This included displays of innovative agricultural machinery, such as onion storage blowers, jute fiber separators, axial flow pumps, and combine harvester spare parts. Stakeholders from various sectors shared insights on how to improve machine service providers’ capacity to manage their businesses effectively.
Sholakundu, a village in Kanaipur Union, Faridpur Sadar, has embraced modern agricultural practices and diversified crop cultivation. This site showcased the impact of mechanized rice transplantation and integrated pest management (IPM) techniques, with the opportunity to observe a live demonstration of mat-type seedling raising for mechanized rice transplantation. Discussions revolved around the benefits of mechanization, IPM activities, and the village’s commitment to enhancing agricultural sustainability and productivity.
Climate-specific farming
The southern coastal region of Bangladesh has long suffered from problems including salinity, drought, waterlogging, and unpredictable weather. Addressing these issues is the USAID-funded Sustainable Intensification Innovation Lab–Asian Mega Delta (SIIL-AMD) project, which encourages climate-resilient farming and better water management.
The initiative engages approximately 400 farmers in trials of improved agronomic techniques through the use of 14 Learning Hubs and the Cluster Farmer Field School (CFFS), aiming to increase output and assist local people in adjusting to the special conditions of the coastal polder zone.
“Bangladesh’s women farmers, especially those in this area and the coastal regions, are incredibly hardworking,” stated Zachary P. Stewart. “Even in the face of adverse weather conditions, their dedication has led to excellent crop yields. If provided with further training and allocated more time, these industrious women could take the lead in driving Bangladesh’s agricultural progress forward.”
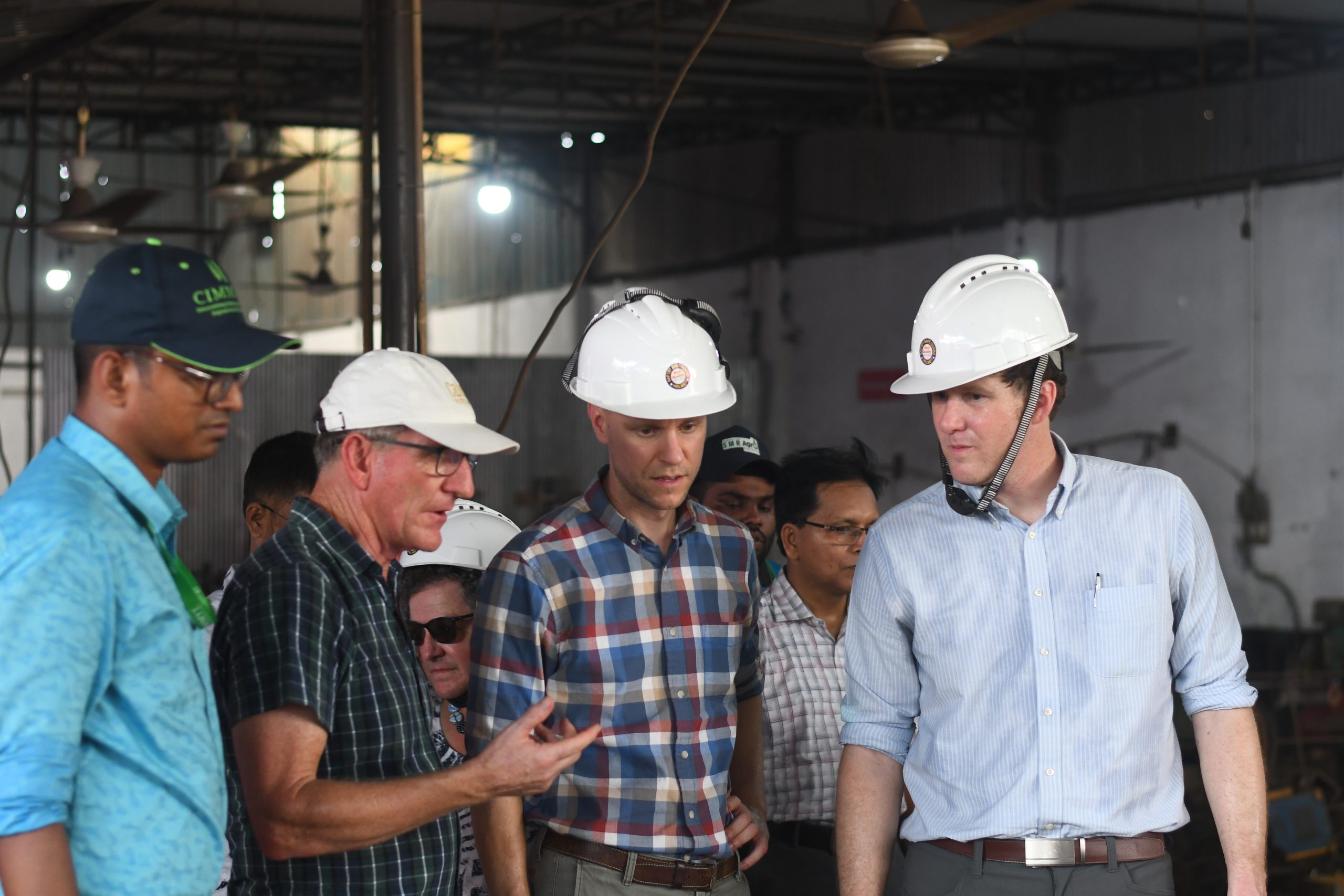

Systemic self-sufficiency
For reasons of development and sustainability, Bangladesh’s agriculture industry is focused on using locally made machinery and spare parts. As USAID personnel visited the SMR Agro Engineering Workshop and Foundry, situated in Jashore Sadar, they witnessed how support by CSISA-MEA has improved the agricultural mechanization market system. SMR Agro Engineering produces high-quality agricultural machinery and spare parts, increasing farmers’ productivity and decreasing labor intensity.
CSISA-MEA’s support has been significant in preparing new industrial layouts, raising labor skill levels, providing technical guidance, and facilitating financing. Moreover, through the development of business partnerships with lead companies, agriculture-based light engineering enterprises (ABLEs), and dealers, CSISA-MEA ensures a strong network that supports the widespread use of mechanized services. This collaborative effort marks a significant step towards enhancing rural livelihoods and achieving sustainable agricultural practices in Bangladesh.
Global research partnerships
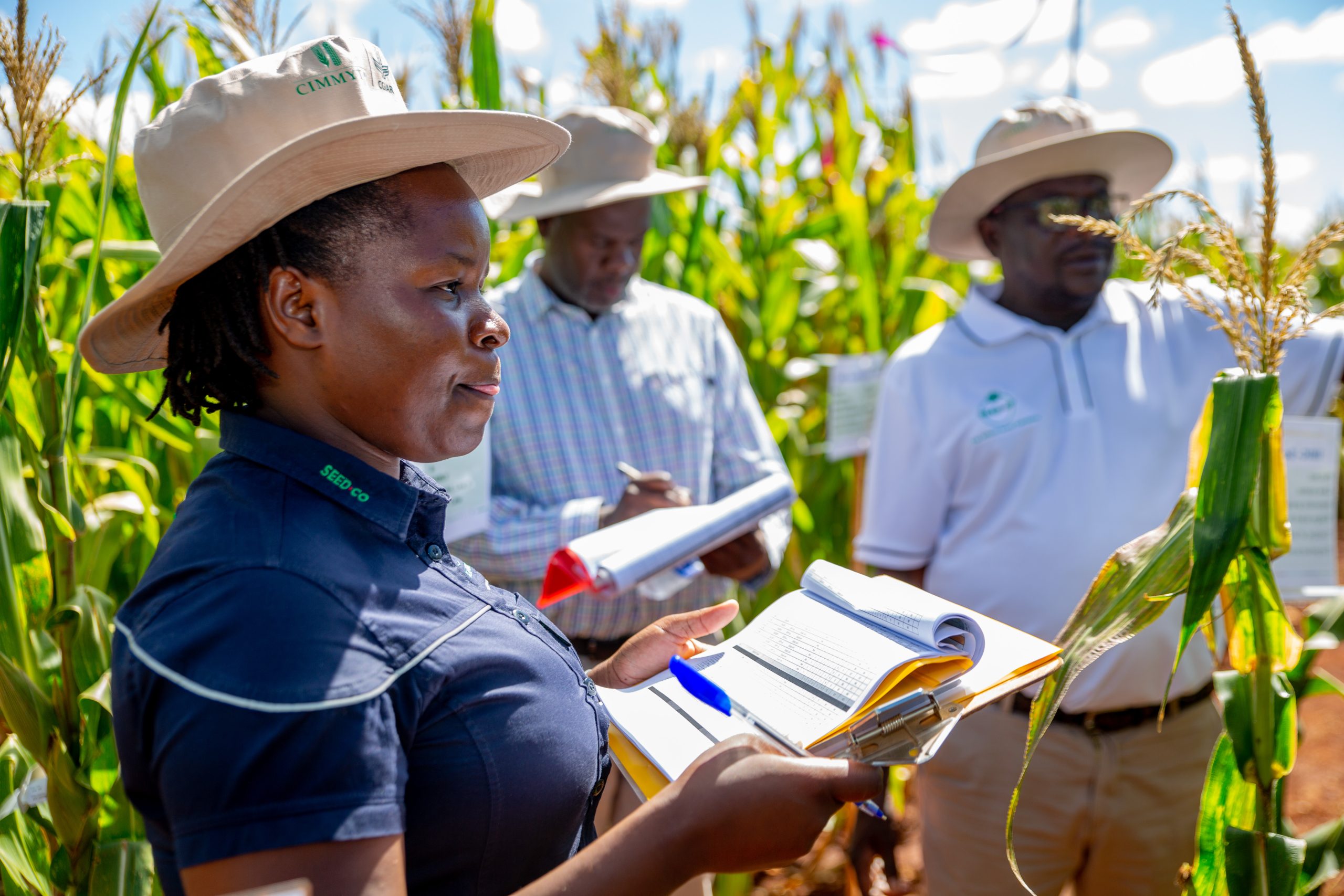
In addition to visiting farmers’ fields, the team also attended the Bangladesh Agricultural Research Institute (BARI), the nation’s largest agricultural research center which focuses on improving crop yields, food security, and employment. The visitors explored the work in mechanization, IPM, and farm machinery, with a tour of BARI’s IPM and toxicology laboratories highlighting the organizations’ sustainable approach to pest management.
The final visit was to Ispahani Agro Limited (IAL), a leading bio-pesticide producer in Gazipur. IAL is at the forefront of bio-rational pest management, creating environmentally friendly, non-toxic inputs. CIMMYT’s assistance has been crucial for the company’s growth, with the tour covering production units, laboratories, and discussions on IAL’s business development.
Overall, the experience offered a comprehensive overview of collaborative activities between USAID, CIMMYT, and Bangladeshi stakeholders. From research and mechanization to bio-rational pest management, the combined efforts boost output and encourage sustainability and responsible environmental behavior.
As Bangladesh continues to embrace modern farming practices, partnerships and projects will play a pivotal role in defining how the country’s agricultural industry evolves into one that is economically viable and sustainable.