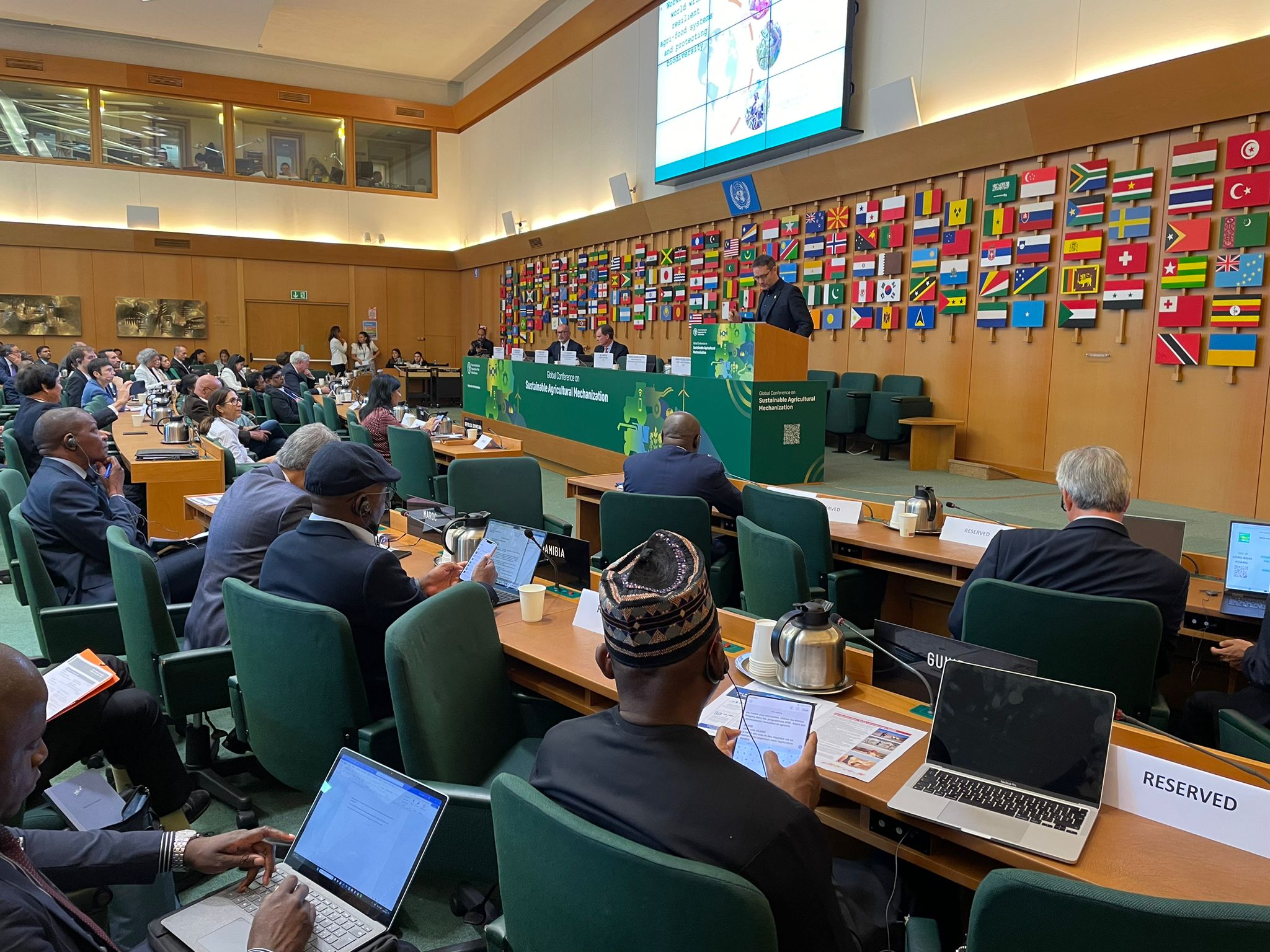
Global Conference on Sustainable Agricultural Mechanization: efficiency, inclusiveness, and resilience
CIMMYT participated in the inaugural Global Conference on Sustainable Agricultural Mechanization, organized by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) from September 27-29, 2023. The gathering provided space for focused dialogues to prioritize actions and strengthen technical networks for sustainable development of agricultural mechanization.
Bram Govaerts, CIMMYT director general, presented a keynote address on September 27 regarding climate change and mechanization. As a global thought leader and change agent for climate resilient, sustainable and inclusive agricultural development, CIMMYT has many specific initiatives centered on mechanization for facilitating machine innovations and scaling-up improved farming practices for sustainability and farmer competitiveness.

Collaboration is a hallmark of CIMMYT’s endeavors in mechanization, including a strong partnership with local governments across Latin America, Africa and Asia, and international cooperation agencies, supporting the Green Innovations Centers installed by GIZ-BMZ and working on accelerated delivery models together with USAID, in Malawi, Zimbabwe and Bangladesh, to name only a few. Further, local value chain actor engagement is crucial and necessary in this work to connect farmers with viable solutions.
CIMMYT has a long history of leading projects aimed at mechanizing the agricultural efforts of smallholder farmers, including the successful MasAgro Productor in Mexico and FACASI (farm mechanization and conservation agriculture for sustainable intensification) in East and South Africa. At present, the Harnessing Appropriate-Scale Farm Mechanization in Zimbabwe (HAFIZ) project is working towards to improve access to mechanization and reduce labor drudgery while stimulating the adoption of climate-smart/sustainable intensification technologies. The project engages deeply with the private sector in Zimbabwe and South Africa to ensure long-term efficacy.
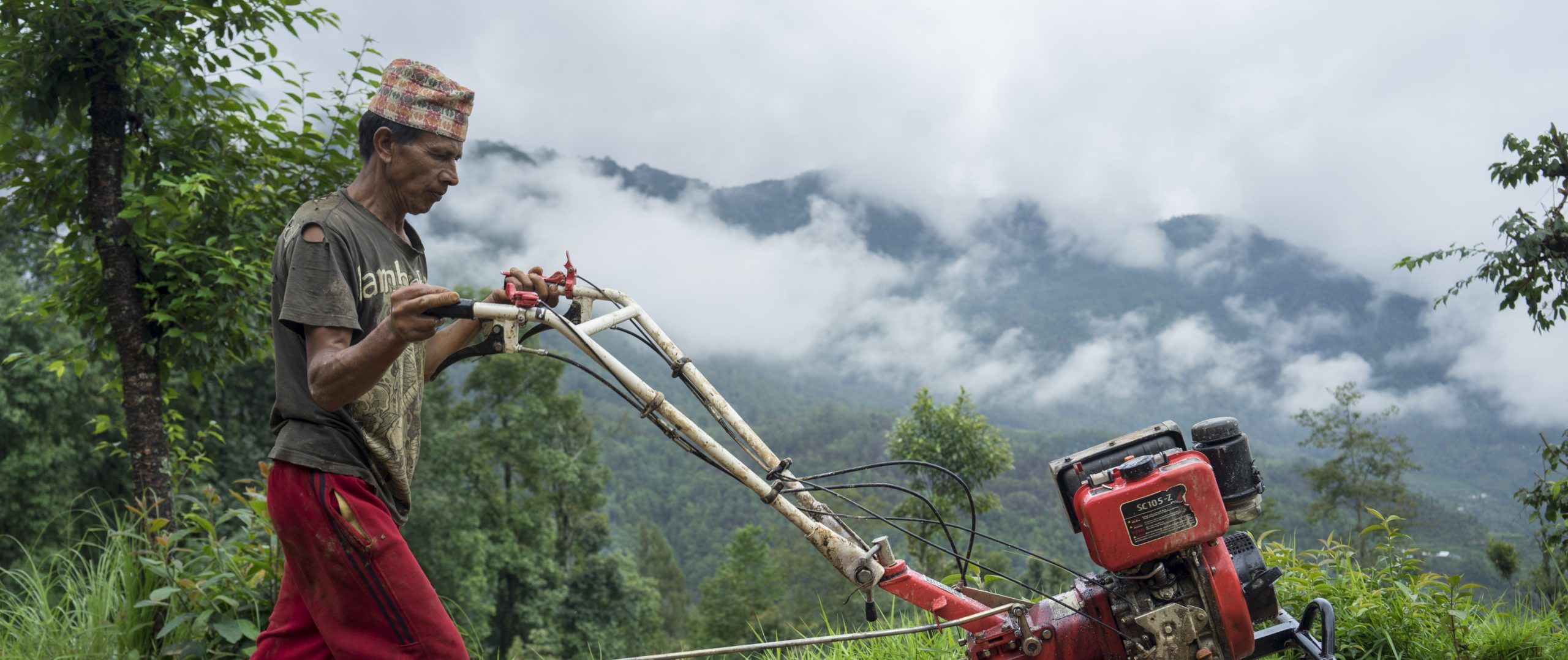
The Scaling Out Small Mechanization in the Ethiopian Highlands project was active from 2017 to 2022 and increased access for smallholder farmers to planting and harvesting machines. Farmers using two-wheel tractors furnished by the project reduced the time needed to establish a wheat crop from 100 hours per hectare to fewer than 10 hours. CIMMYT’s work was in partnership with the Africa-RISING program led by the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) in Ethiopia.
“At CIMMYT, we work knowing that mechanization is a system, not only a technology,” said Govaerts. “Sustainable mechanization efforts require infrastructure like delivery networks, spare parts and capacity development. Working with local partners is the best way to ensure that any mechanization effort reaches the right people with the right support.”
Read these stories about CIMMYT’s efforts to support equal access to agricultural mechanization and scaling up within local contexts.
One-minute science: Mechanization for agriculture
Mechanization is a process of introducing technology or farm equipment to increase field efficiency. CIMMYT’s mechanization work is context specific, to help farmers have access to the appropriate tools that are new, smart and ideal for their unique farming conditions.
New generation of farmers adopts mechanization, making farming more productive and profitable
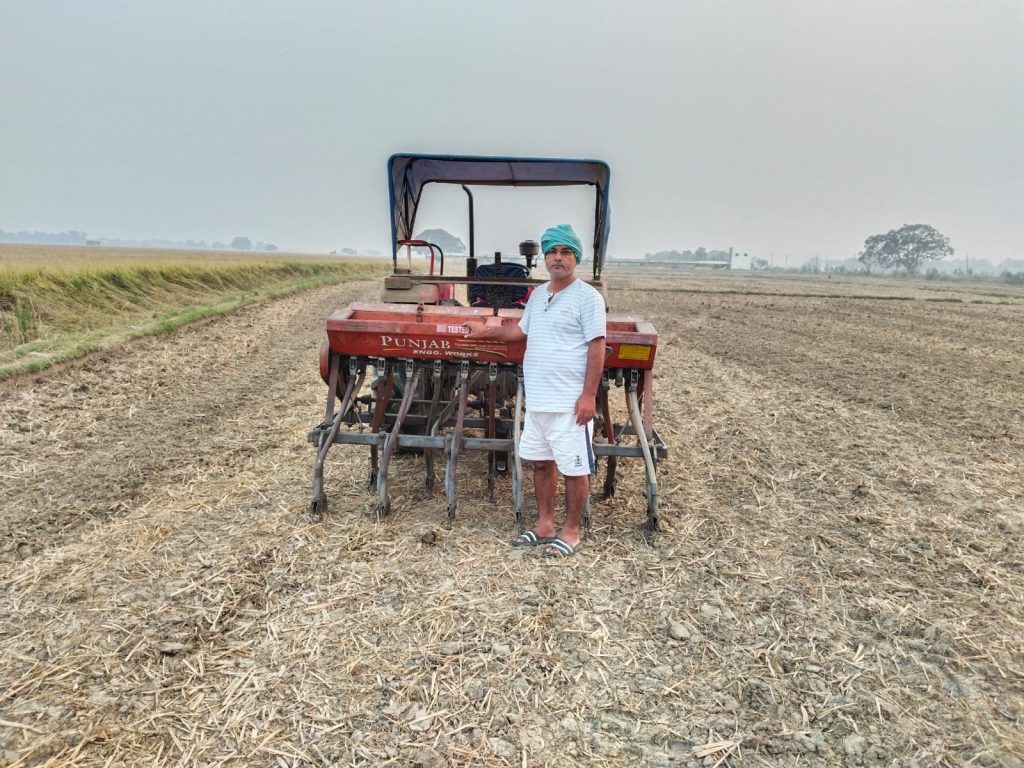
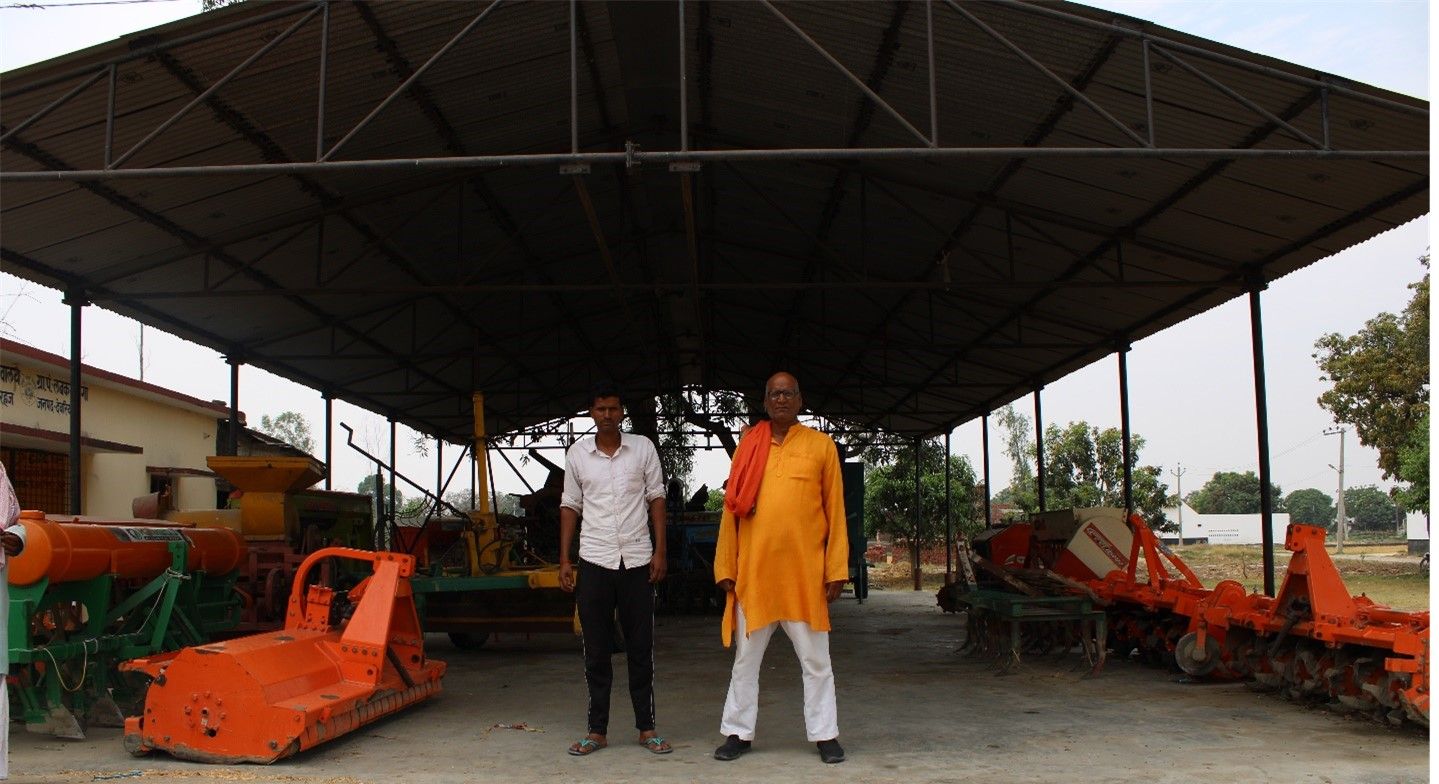
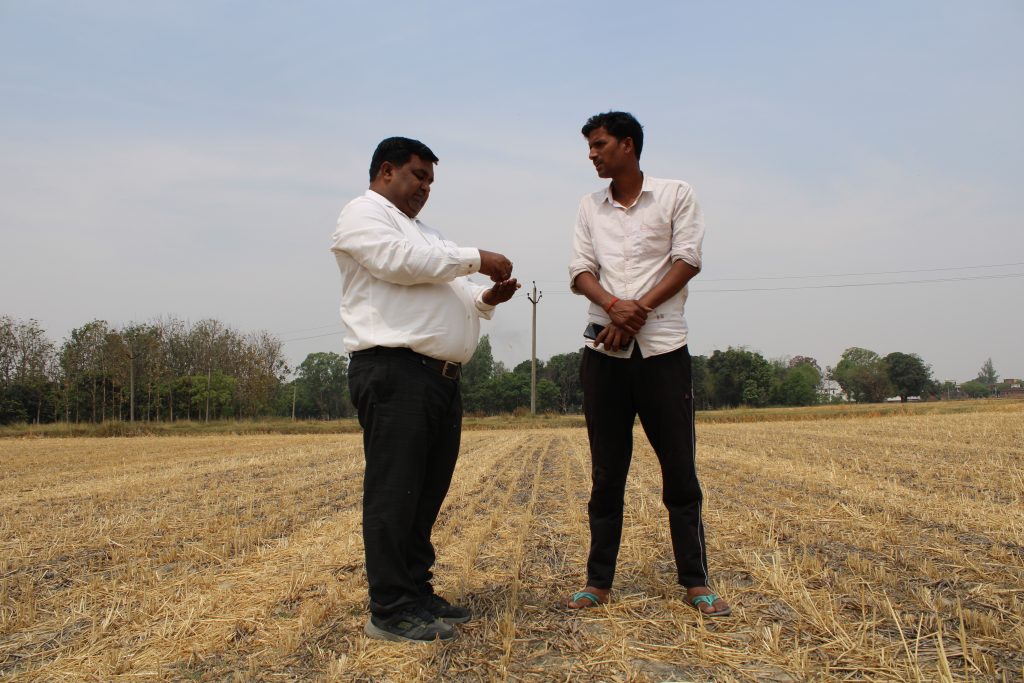
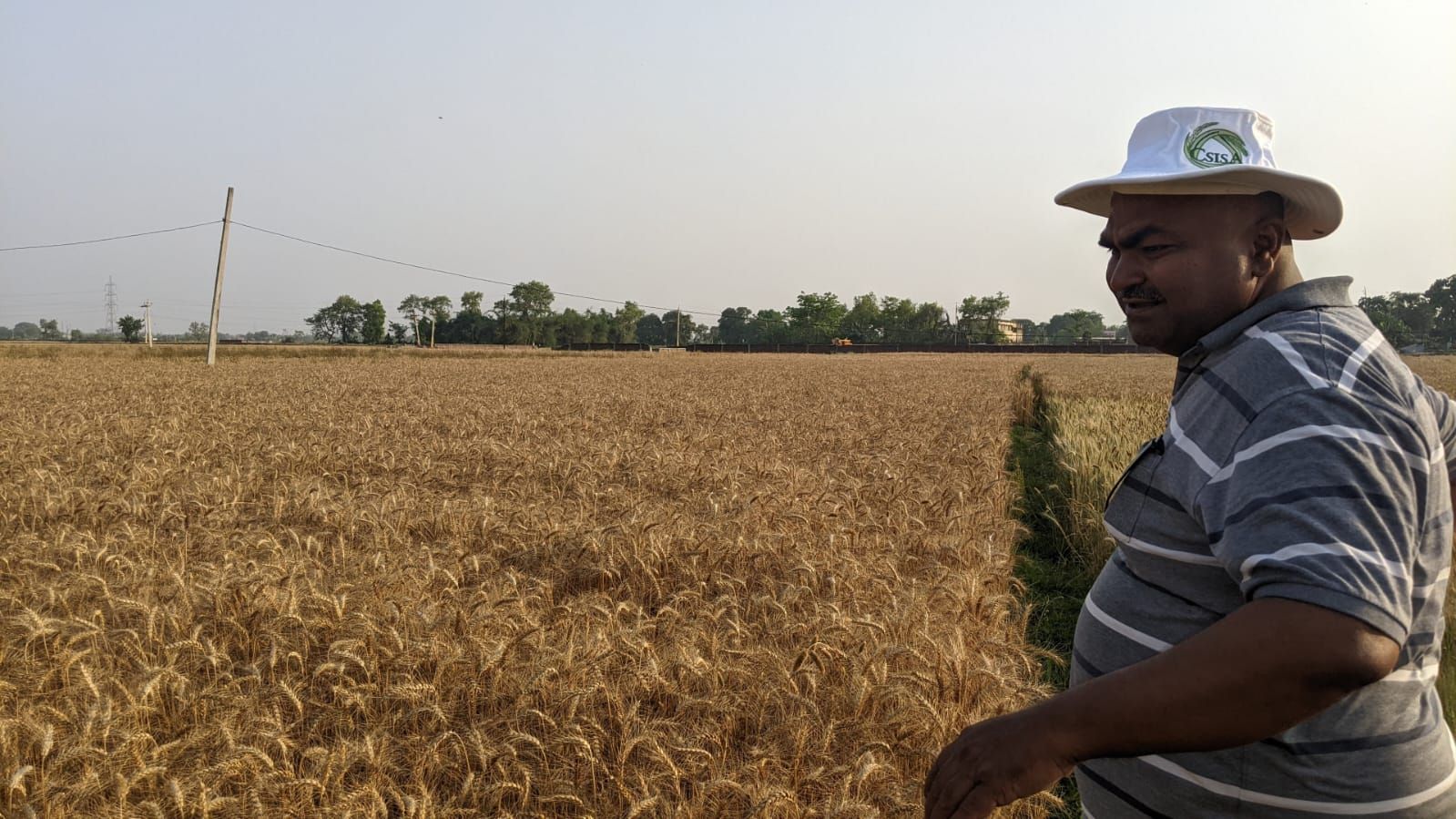
Working with the Cereal Systems Initiative for South Asia (CSISA), CIMMYT is leading mechanization efforts in Northern India. Combined with sustainable agriculture, the next generation of farmers now have access to tractors, seeders and other tools that are increasing yield and reducing back-breaking labor.
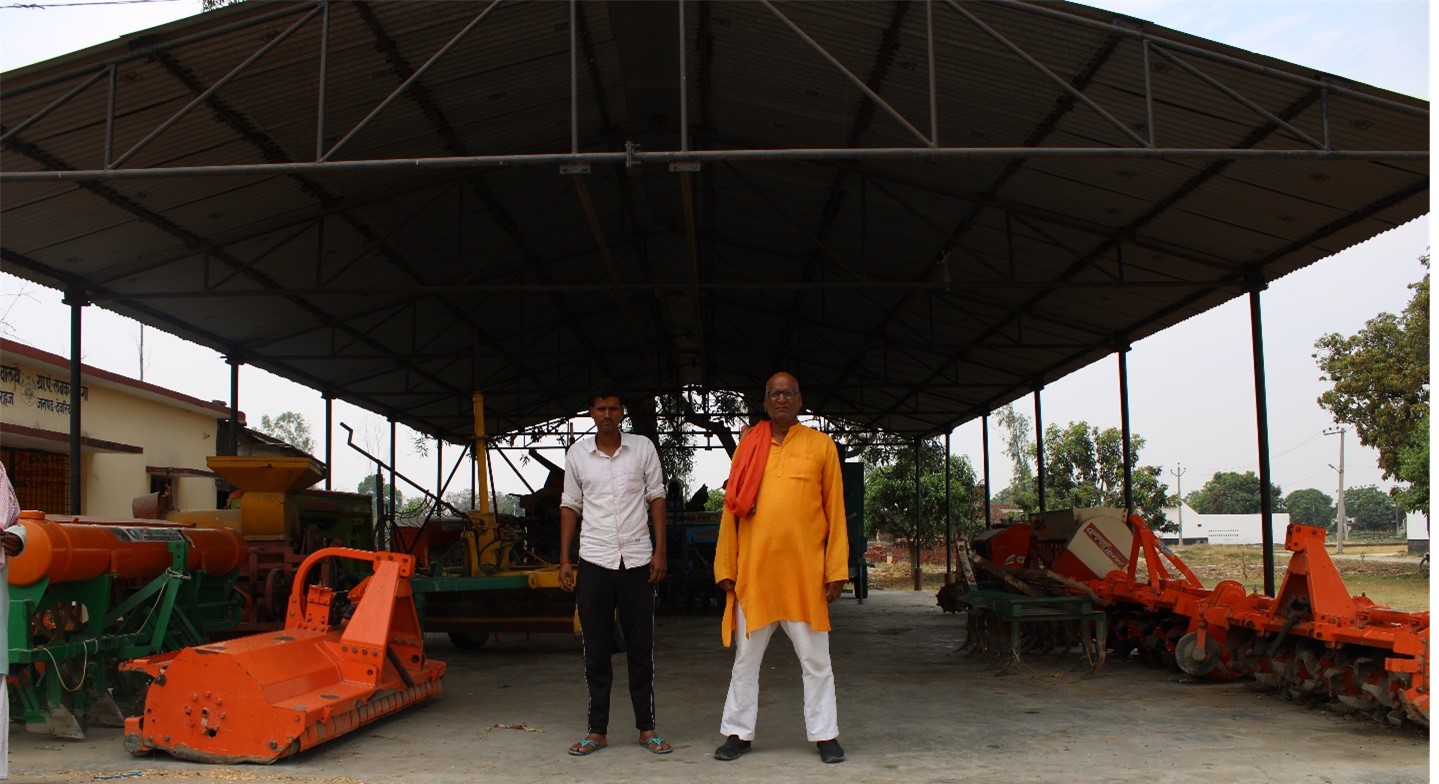

A promising partnership
The delivery of row seeders from India to Benin demonstrates a new path to sustainable South-South business relationships. Developed in India in an iterative design process with farmers, portable row seeders have been a great success. Working with GIC, CIMMYT facilitated a technology and materiel transfer of the portable row seeders to Benin.

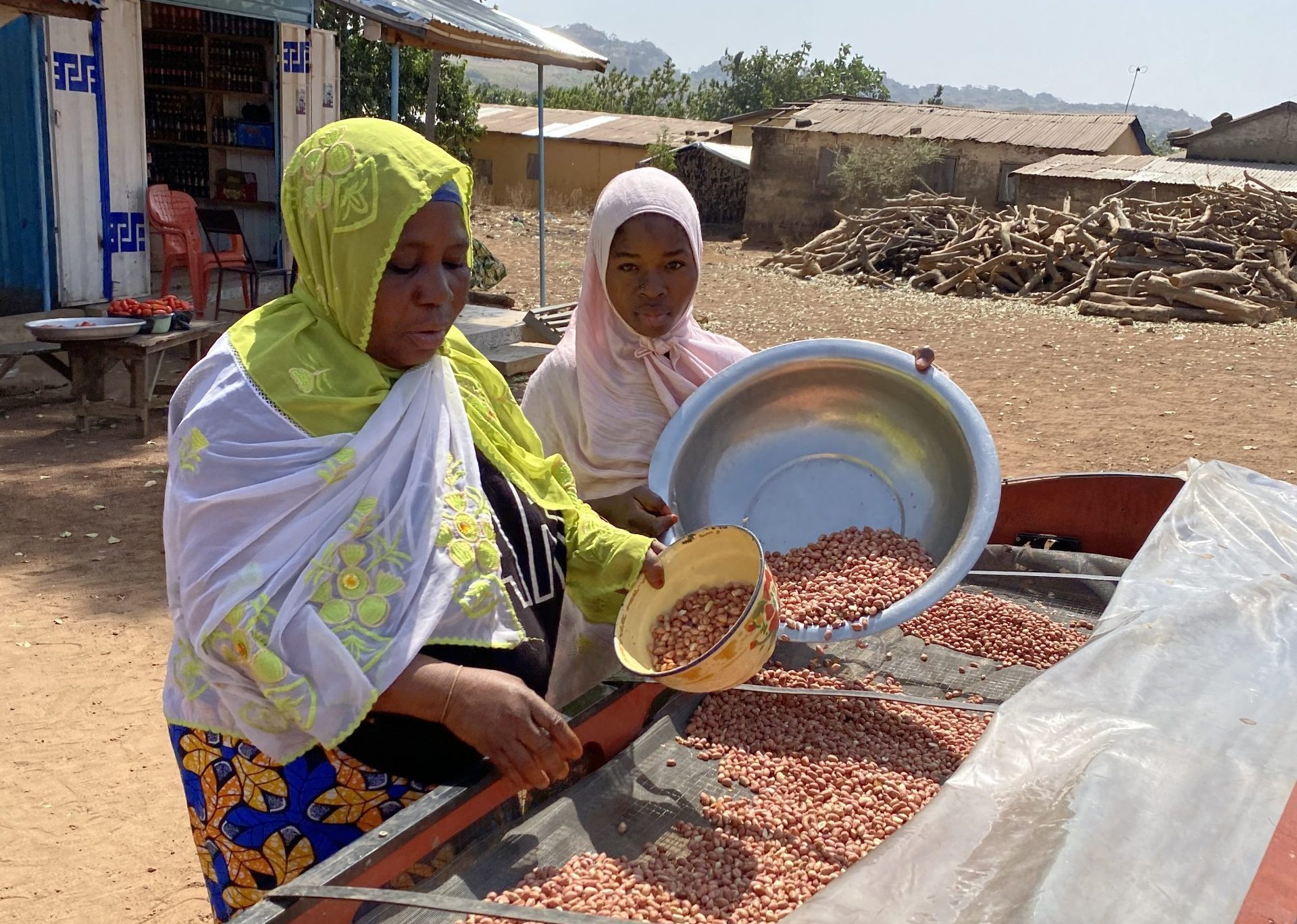
Solar powered dryers boost peanut production in Togo
Peanuts thrive as a crop in Togo and other West Africa countries, but post-harvest is threatened by aflatoxins, so the entire crop needs to dry. Traditionally, farmers, often women, have dried the peanuts in the open air, subject to weather and other pests. However, CIMMYT, working with GIC, has introduced solar-powered dryers, which speeds up the drying process by a factor of four.

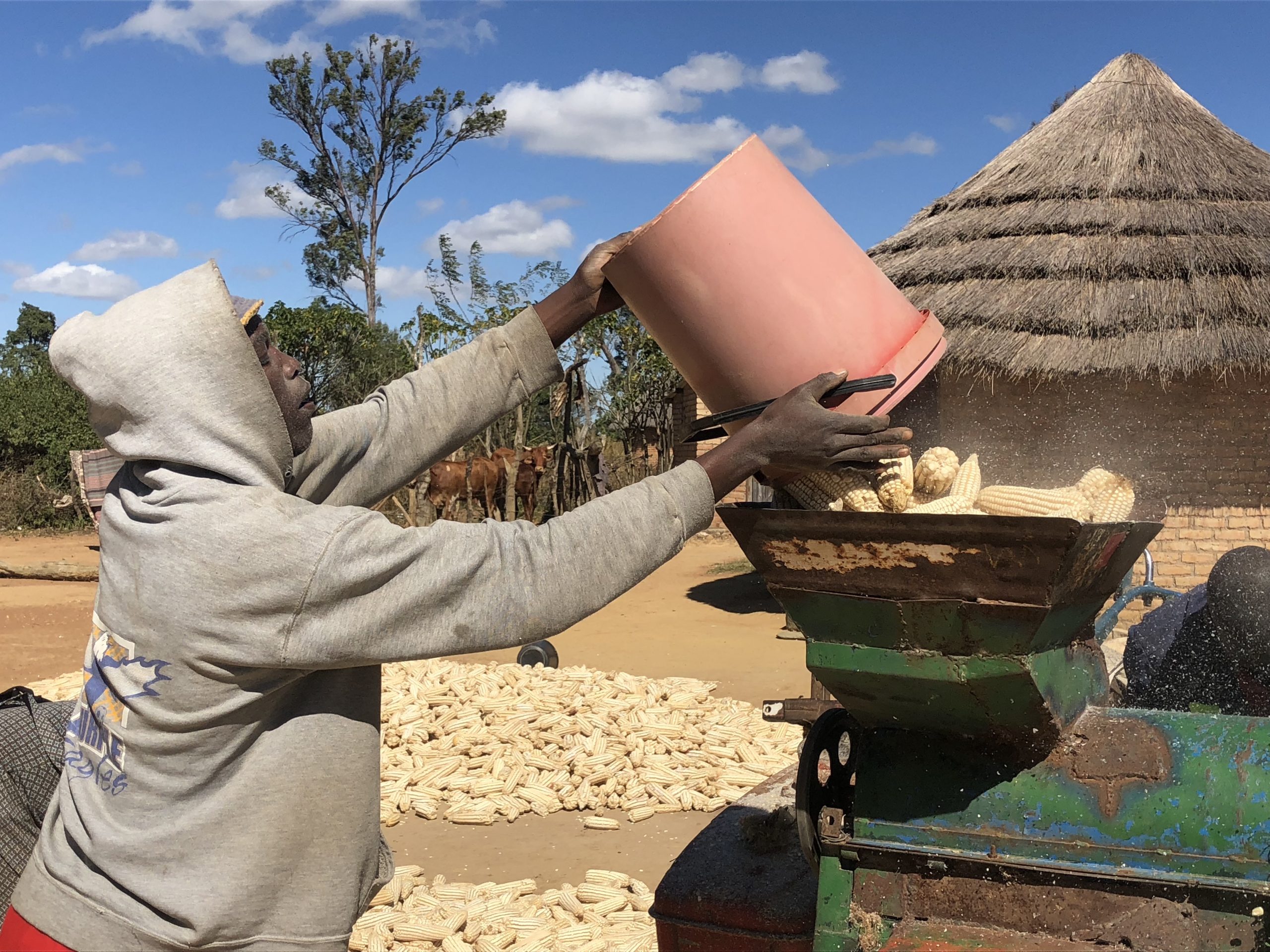
A business model for mechanization is providing hope in Burkina Faso
Working with partners in Burkina Faso, CIMMYT is facilitating smallholder mechanization with a model of cascading effects: one farmer mechanizing can then use their skills and eqBMZuipment to help their neighbors, leading to community-wide benefits.

Visit our mechanization page to read stories about ongoing mechanization initiatives.