Costich retires, but her odyssey continues
Denise E. Costich, the recently retired head of the Maize Collection at the Germplasm Bank of the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), sometimes likes to include a Woody Allen quote in her presentations.
“I have no idea what I’m doing,” declares the text over a photo of a befuddled-looking Allen. “But incompetence never stopped me from plunging in with enthusiasm.”
This is perhaps Costich’s tongue-in-cheek way of acknowledging the unusual trajectory that led her to the Germplasm Bank and her zeal for new and interesting challenges. But it is in no way an accurate reflection of the skill, knowledge and humane managerial style she brought to the job.
“CIMMYT requires individuals with a broad set of experiences,” says Tom Payne, head of the Wheat Collection at CIMMYT’s Germplasm Bank. Though she was not trained as a crop scientist, and despite having never worked in a genebank before, Costich’s rich set of professional and life experiences made her an ideal person for the job.
From Ithaca and back again
Born and raised in Westbury, NY, Costich spent much of her childhood on a tree nursery. Her grandfather was the manager, her father became the sales director and eventually her sister also went into the horticulture business. While her experiences on the nursery contributed to an early interest in plants and ecology, the business aspect of the nursery eluded her. “I just can’t sell things. I’m terrible,” Costich says. “But I really do like to study them.”
This studiousness took her to Cornell University in Ithaca, NY, where she initially declared as a wildlife biology major. Her notion of what it meant to “study things” was influenced by her early heroes, primatologists and field biologists Dian Fossey and Jane Goodall. It involved travel. Fieldwork in faraway places. So, when the opportunity arose at the end of her sophomore year to travel to Kenya with Friends World College, Costich didn’t hesitate.
Costich eventually spent four years in Kenya, studying baboons. When she finally returned to Ithaca, she knew two things. Fieldwork was absolutely her thing, and she wanted to pursue a doctorate.
A chance conversation with her housemates in her last semester led to a post-graduation fieldwork stint in the Brazilian Amazon under the supervision of the legendary tropical and conservation biologist, Thomas Lovejoy. But instead of a dissertation topic, she stumbled across a parasite, a case of leishmaniasis and the realization that the rainforest was not the work environment for her.
Unexpected influences and outcomes continued to mark Costich’s career throughout her graduate studies at the University of Iowa. She found her plant not in the field, but while reading a dusty review paper as an exchange student at the University of Wisconsin. Her study of Ecballium elaterium (a wild species in the Cucurbitaceae, or squash, family) did not take her back to the tropics — where most of her peers were working and where she expected to be headed as a grad student — but rather to Spain where, incidentally, she first learned Spanish.
Several years after defending, Costich landed a tenure-track position in the Biology Department at The College of New Jersey. She continued to publish on Ecballium elaterium. Her career appeared to be settling into a predictable, recognizable academic trajectory — one with no obvious intersection with CIMMYT.
Then Costich saw an ad in the Ecological Society of America bulletin for a managing editor position for all of the Society’s journals. Her husband, a fellow biology Ph.D., had been working as an academic journal editor for several years. When Costich saw the ad she immediately drove over to her husband’s office. “I slapped the thing on his desk and said, ‘Here’s your job!’” she recalls.
Costich was right. Soon after, she was on her way back to Ithaca — where the Society’s offices were located — with a family that now included three children. While it was the right move for her family, it came at the cost of her budding academic career. In Ithaca, she soon found herself stuck in the role of itinerant postdoc.

An amazing turn of events
Costich admits that, especially the beginning, the return to Ithaca was tough, even depressing. Her recollections of these years can sound a bit like a game of musical chairs played with research laboratories. As one post-doc or research project wound down, she’d find herself scanning the campus for her next perch. She became very adept at it. “In ten years, I never missed a paycheck,” Costich says.
The turn of the millennium found Costich scanning the horizon yet again. As the days wound down at her latest post, a maize geneticist moved into the lab next door. What started as hallway jokes about Costich jumping ship and joining the maize lab soon turned into an interview, then a job offer.
The job introduced her to nearly everyone at Cornell working in maize genetics. Costich soon found herself managing the Buckler Lab’s work on maize population genetics. Meanwhile, she dabbled in side projects on Tripsacum, a perennial grass genus that is closely related to maize, and managed a major project on switchgrass. At the end of her postdoc, Buckler set to work trying to create a permanent position for her. Once again, Costich’s trajectory was beginning to take a stable, predictable form.
Then CIMMYT scientist Sarah Hearne showed up. “I’d heard through the grapevine — or maybe through the corn field — that the position of manager of the Maize Collection of CIMMYT’s Germplasm Bank was open… and that they were having a hard time trying to find a person for the position,” Costich recalls. She had met Hearne previously and personally knew and had worked with Suketoshi Taba, the pioneering longtime director of the germplasm bank. Naturally the topic emerged as she and Hearne caught up in Ithaca.
Hearne admitted that the search hadn’t yet been successful. “But I know the perfect person for the job,” she added.
“Yeah, who’s that?” Costich asked, not getting the setup.

A stranger in a strangely familiar land
Costich was not a little surprised by the suggestion. She had never worked at a germplasm bank before. She was finally finding some stability at Cornell.
At the same time, her early dreams of exploring new places through her work, especially the tropics, beckoned. Her youngest son was nearly college-aged. Against the advice of some who had watched her work so hard to establish herself at Cornell, she took the plunge.
By the time she reached the CIMMYT campus in Texcoco, Costich had crisscrossed a good part of the globe, picking up Spanish here, management skills there, a deep knowledge of maize and its biological and cultural evolution yonder. During this life journey, she developed a deep humanism that is all her own.
It all seemed like happenstance, perhaps, until she reached Mexico and — suddenly, counterintuitively — found herself in the field she was perfectly adapted for. “It turned out that being a germplasm bank manager was the perfect job for me, and I didn’t even know it!” Costich says. “I ended up using everything I learned in my entire career.”
That isn’t to say that it was easy, especially at first. Taba, her predecessor, had occupied the post for decades, was a trained crop scientist, and had grown the bank from a regionally-focused collection with 12,000 accessions to the preeminent maize germplasm bank globally with 28,000 accessions, a state-of-the-art storage facility, and a slew of pioneering practices.
Not only had Taba left enormous shoes to fill, during his tenure — as is common in the expansionary phase of many projects — it had been difficult for the bank to keep a full accounting and understanding of all the new material that had been added. According to germplasm bank coordinator Cristian Zavala, by the time Costich joined CIMMYT “we knew very little about the material in our vaults.”
“Taba was primarily a breeder,” Costich says. “I actually think this oscillation between a focus on breeding and a focus on conservation and curation is good for the bank.”





A bank for farmers
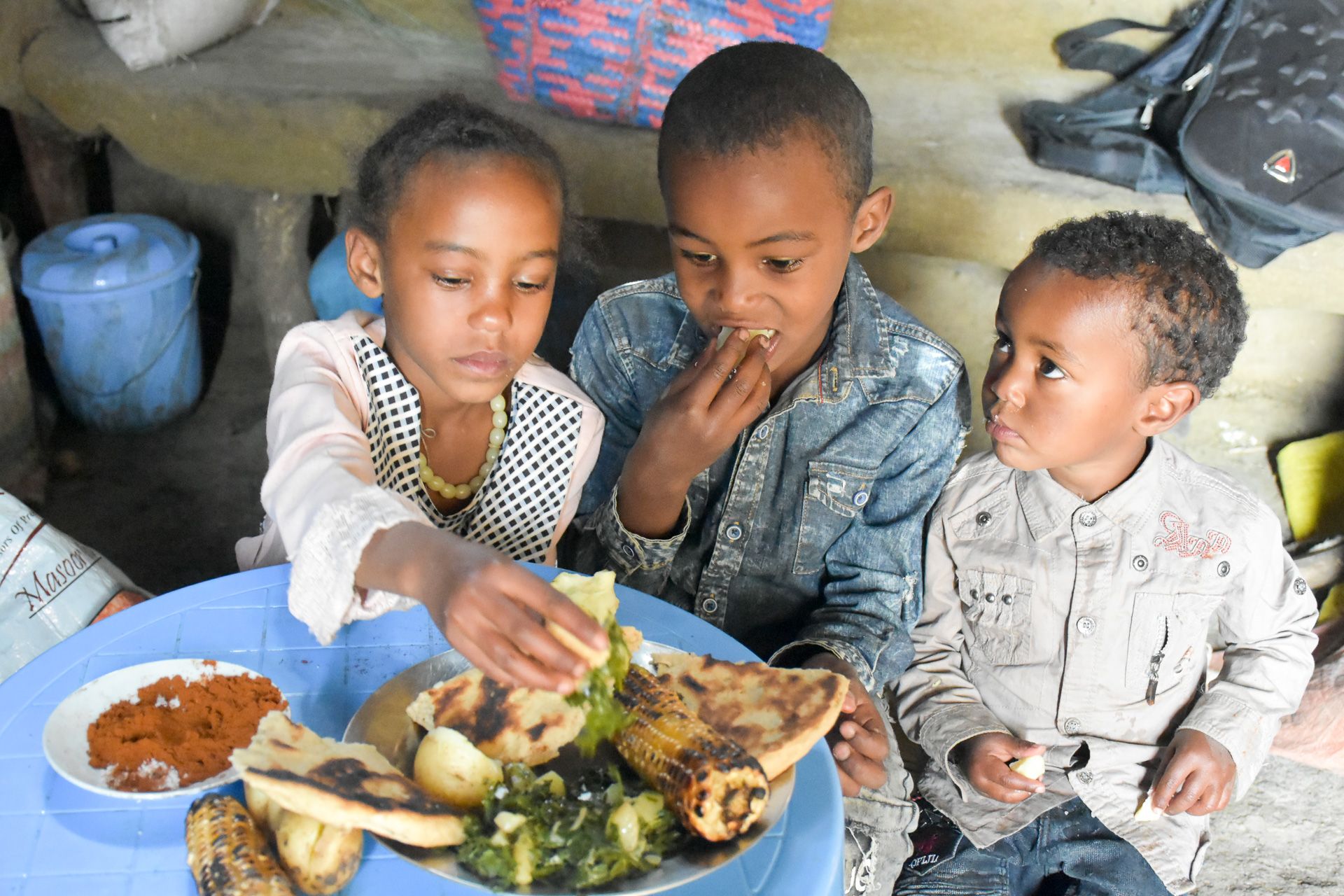
However, according to Zavala, because of the limited knowledge of much material they were working with, many in the bank’s rank-and-file didn’t fully understand the importance of their work. Morale was mixed. Moreover, despite an assumption that her new job would see her working closely with local smallholders, Costich found that the institution was poorly known by everyday farmers in its host country. Where it was known, associate scientist on innovation and social inclusion, Carolina Camacho, notes, there was an assumption that CIMMYT only worked with hybrid varieties of maize and not the native landraces many smallholders in Mexico depend on.
These became the principal axes of Costich’s work at the bank: curation of backlogged material, staff development, and community outreach.
Thus, when Costich realized that records were being kept in a combination of paper and rudimentary digital formats, she sent Zavala, a promising young research assistant at the time, to an internship at the USDA’s Maize Germplasm Bank Collection in Ames, Iowa, to workshops at CGIAR germplasm banks in Colombia (CIAT) and Ethiopia (ILRI), and to meetings on specialized topics in Germany and Portugal.
Zavala had never left the country before, spoke little English, and remembers being “rebellious” at work. “I needed more responsibility,” he says. “Dr. Denise saw that and helped me grow.” Upon returning from an early trip, Zavala helped implement up-to-date traceability and data management processes, including migrating the genebank’s data onto the USDA’s GRIN-Global platform.
But as Payne points out, Costich’s tenure was never about simple bean — or, in this case, grain — counting. “She sees a more human aspect of the importance of the collections,” he says. The main tasks she set for the bank came to be subsumed into the overarching goal of a fuller understanding of the contents of the bank’s vaults, one that encompassed both their biological and sociocultural importance.
When Costich came across a collection of maize landraces from Morelos state assembled by Ángel Kato in the mid 1960s that conserved the name of the farmer who had donated each sample, she worked with Camacho and graduate student Denisse McLean-Rodriguez to design a study involving the donor families and their communities. McLean-Rodriguez, Camacho and Costich set out to compare the effects of ex-situ versus in-situ landrace conservation in both genetic and socioeconomic terms.
Similarly, when a colleague at INIFAP invited Costich to be a judge at a yearly contest for largest ear of Jala landrace maize in Mexico’s Nayarit state, they soon began discussing how they could contribute more than just their participation as judges to the community. Starting in 2016 Costich was a co-lead on a study of the landrace’s genetic diversity as well as an initiative to rematriate Jala seeds conserved at CIMMYT for over 60 years.

A genebank is not an island
Genebanks are bulwarks against genetic erosion. But, as Camacho explains, this mission can be understood in both very narrow and very broad senses. The narrow sense focuses on genetic processes per se: the loss of alleles. The broad sense includes the loss of cultural practices and knowledge built and sustained around the cultivation of a given landrace. Through the initiatives the bank has undertaken during her tenure, Costich has tried to demonstrate, both scientifically and in practice, how germplasm collections such as CIMMYT’s can complement, reinforce, and be enriched by the work of smallholders — de facto germplasm conservators in their own right — while contributing to the difficult task of combating genetic erosion in the broad sense.
One gets the sense that in Costich’s view this isn’t about a one-way process of big institutions “helping” smallholders. Rather it’s about collaboration among all the participants in an interdependent web of conservation. As she argued at her recent exit seminar, Costich views germplasm banks as one link in a chain of food security backups that begins at the farm level.
Indeed, Costich’s most recent initiative demonstrated how innovations intended for one link in the chain can travel upwards and find applications at bigger institutions.
Costich recently led an initiative with community seed banks in the Cuchumatanes mountain range of Guatemala to study the use of DryChain technology in post-harvest storage of maize. This experiment showed the enormous benefits that incorporating such technologies could yield for energy-insecure or low-tech family and community seed reserves.
Ultimately, however, the study led to a second experiment at CIMMYT’s tropical-climate station at Agua Fría in Mexico. With advice from collaborators at UC Davis and an industry partner (Dry Chain America), the seed conditioning team retrofitted an old drying cabinet at the station to dry maize without using heat, but rather by forcing air to circulate through sacks of drying beads. Under the direction of Filippo Guzzon, a postdoc and seed biologist working with Costich, the long-term viability of seeds dried using the accelerated technique versus traditional, slower techniques was tested. The study showed no loss in long-term viability using the accelerated drying technique.

A very busy retirement
At her exit seminar, Costich was presented a plaque in appreciation of her service at CIMMYT by Kevin Pixley, director of the genetic resources program. Terence Molnar, maize breeder with the Genetic Resources Team, has succeeded Costich as the Maize Germplasm Bank Head.
For some of her close colleagues, however, Costich’s departure is not the end of the road. “This is not a forever goodbye,” Guzzon says. “I will continue to be in touch with my cuatita,” says Camacho, who has also left CIMMYT.
For her part, Costich echoes that this is not a forever goodbye at all. Not to her friends and colleagues, and certainly not to her work. At a socially-distanced, maize-based farewell lunch Costich held just days before her departure, she was still busy weaving social connections and furthering collaborations among maize fanatics of all stripes — from chefs and designers to scientists and policy advocates.
She is already considering taking a part time position at her old lab at Cornell and a return to Tripsacum research. At the same time, she will be a visiting scientist at Mexico’s National Center for Genetic Resources (CNRG), where officially she will be heading up part of an international switchgrass study. Costich is hoping to leverage her tenure at CIMMYT by getting involved in a push to help improve the Mexican national system for plant genetic resources. Additionally, she has recently accepted an invitation from Seed Savers Exchange to join their board and she is looking forward to volunteering her time and expertise to various seed-saving initiatives within that organization and their many collaborators.
Asked what she’s looking forward to tackling in her retirement that isn’t work related, Costich betrays her deep allegiance to the plant world. “I don’t know,” she says, “I’m thinking of starting a big vegetable garden.”
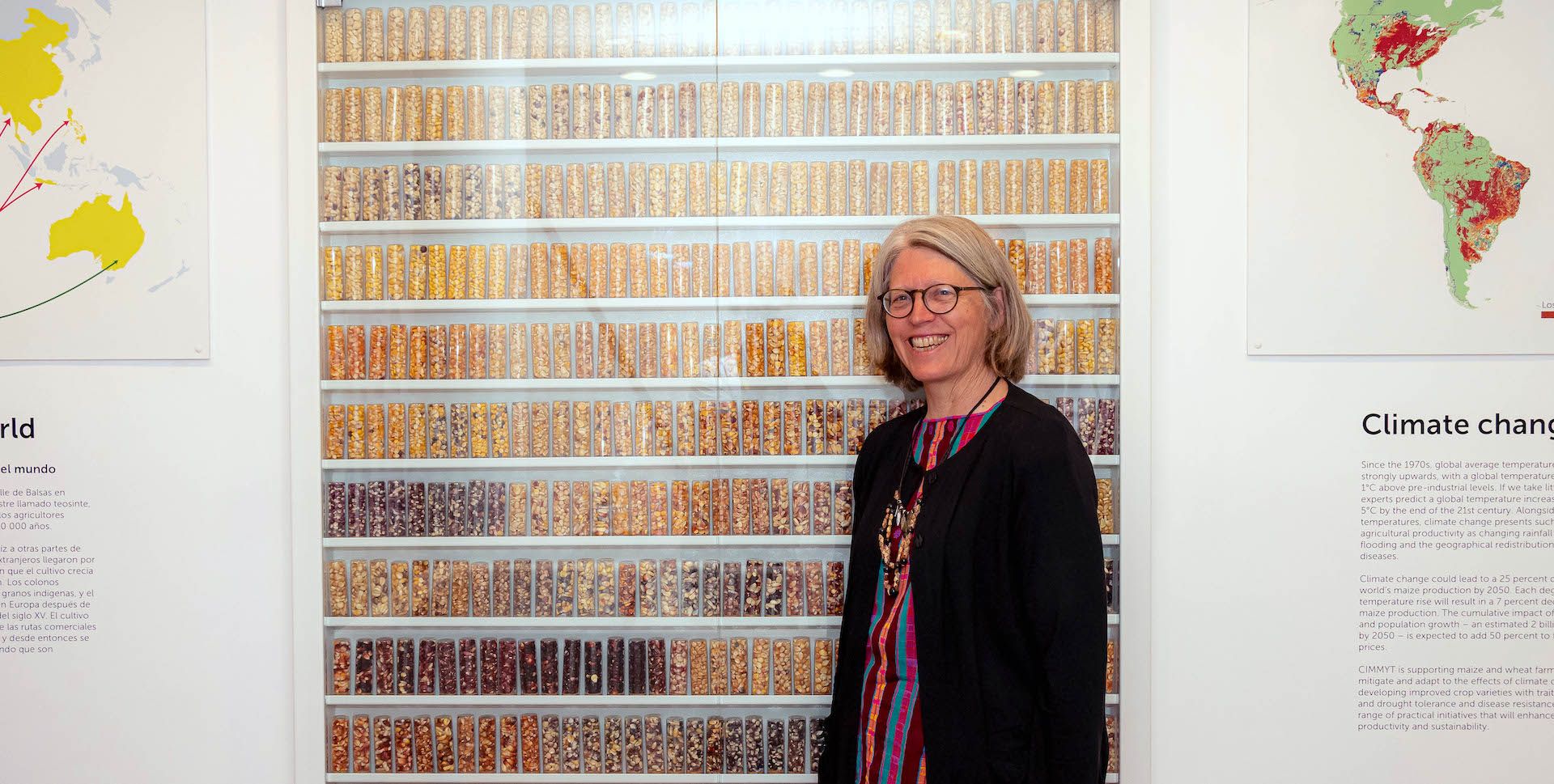
Cover photo: Denise Costich stands for a photo during the inauguration of the CIMMYT Genebank museum in 2019. (Photo: Alfonso Cortés/CIMMYT)