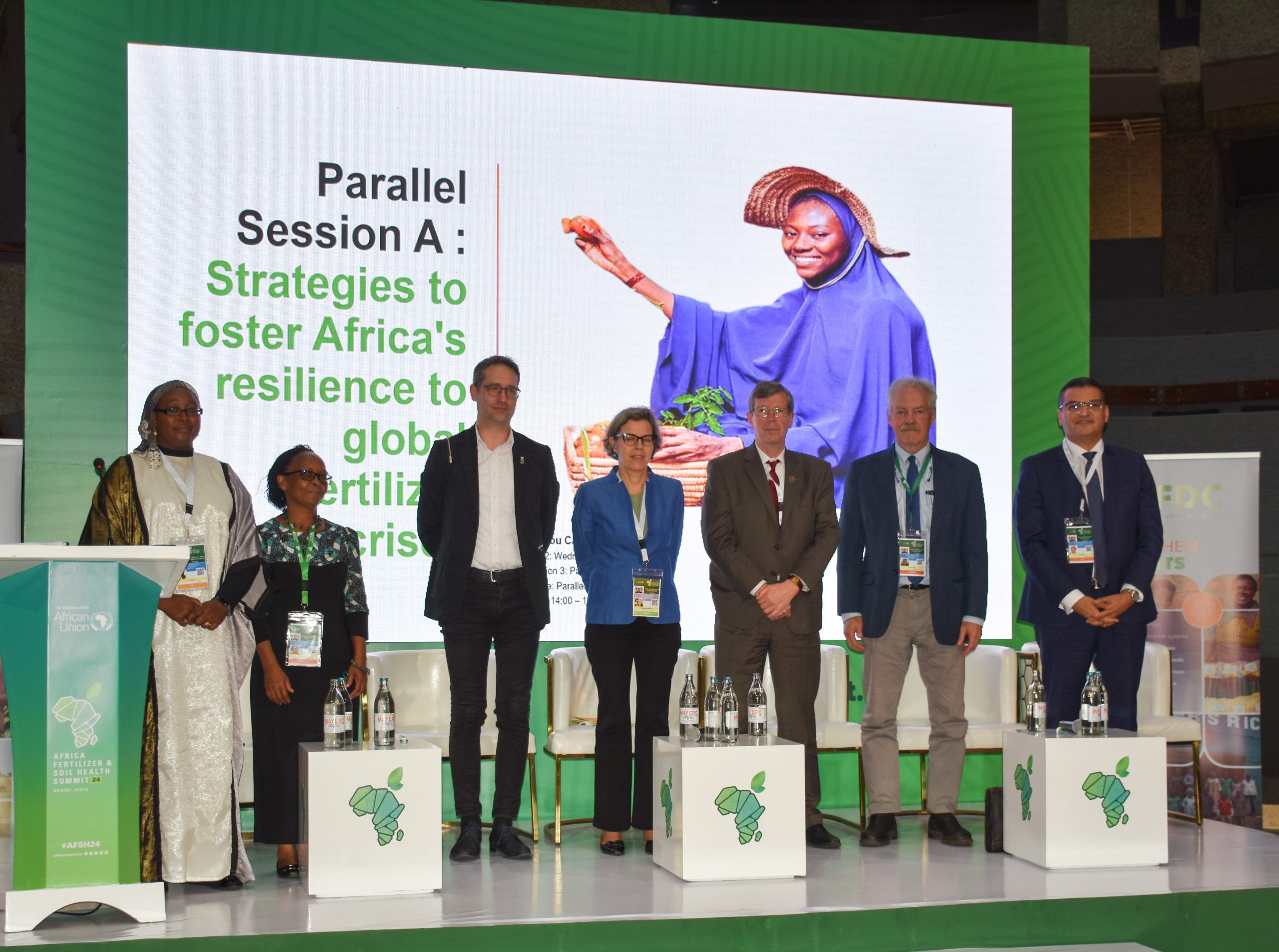
Experts discuss strategies to address soil health challenges and the fertilizer crisis in Africa

Improving soil health is critical to sustainable agriculture, and for addressing climate change, tackling environmental challenges, and enhancing food security. Through projects by CIMMYT and partners, potential scalable solutions are under development, but additional work is still required.
“To effectively scale up soil health initiatives, we need to prioritize investments and establish a framework that maximizes returns,” said Bram Govaerts, CIMMYT director general, during the 2024 Africa Fertilizer and Soil Health (AFSH) Summit in Nairobi, Kenya. “It is crucial to use simple, quantifiable indicators for systematic assessments and decision-making, and to broaden these indicators to foster investment from public, private, and civil actors.”
As a keynote speaker in the “Strategies to Foster Africa’s Resilience to the Global Fertilizer Crisis” parallel session, Govaerts highlighted the intertwined challenges of soil health and fertilizer accessibility. “95% of our food comes from the soil, yet in 14 countries the cost of fertilizer has more than doubled. Fertilizers contribute to 2% of global greenhouse gas emissions and are often mismanaged—overused in some regions and underutilized in others.”
The transition to a more sustainable and climate-resilient approach to soil health and fertilizer use requires a comprehensive structure that considers broader aspects of agricultural sustainability. “To enhance soil health effectively, a clear framework is necessary that includes investment prioritization, integrated soil management, extension and advisory services, and the utilization of data and technology,” Govaerts added.
This recommended framework included identifying and prioritizing investment opportunities, balancing organic and inorganic inputs, strengthening extension systems, and leveraging technology to provide farmers real-time advice.
One practical example of effective soil health management in practice is CIMMYT’s Southern Africa Accelerated Innovation Delivery Initiative (AID-I) Rapid Delivery Hub. The project helps farmers cope with high fuel and fertilizer prices by providing them with innovative tools and information to manage cost and supply disruptions. This addresses systemic weaknesses in agriculture by accelerating market-based delivery of improved seed, fertilizer, and critical information to farmers.
“Under AID-I, rapid soil testing has been prioritized. Collaborating with the International Fertilizer Development Center (IFDC) and mobile soil labs like those in Zambia exemplify innovative data point collection strategies,” said Govaerts.
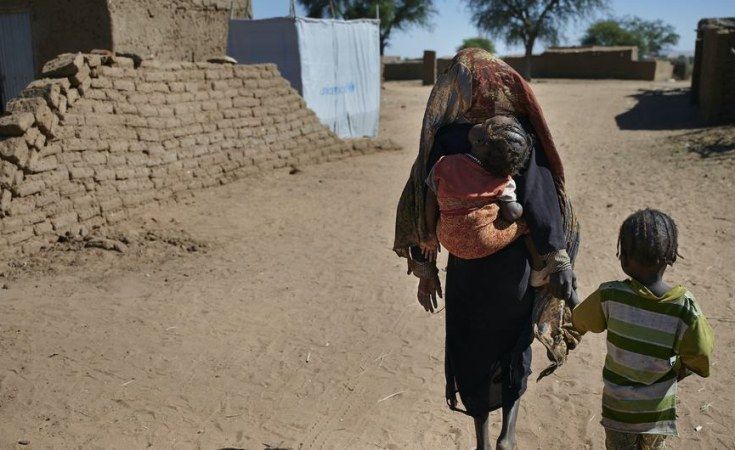
During the panel discussion, Anne Muriuki, principal research officer at the Kenya Agricultural and Livestock Research Organization (KALRO) highlighted the key challenges that African countries face in accessing fertilizers during global crises and the impact on agricultural productivity. “Farmers face scarcity and high costs, leading to reduced yields and increased reliance on unsustainable fertilizers. These issues not only reduce agricultural productivity, but they also aggravate food insecurity and economic instability.”
David Nielsen, a former World Bank official, stressed the importance of having site-specific soil information and investing in human capital and educational institutions to increase soil science expertise and improve the availability of site-specific information. “These two issues should be high priorities. They are crucial, especially when fertilizer access is limited, but they remain vital even with adequate fertilizer supply.”
Douglas Kerr, vice president of business development at the IFDC discussed how governments, international non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and the private sector can collaborate to ensure continuous access to fertilizer during a global crisis. The Sustain African Program was an example of IFDC’s role in gathering market information and developing a concept that has since been integrated into ongoing operations. “In a nutshell, multi-stakeholder collaboration needs to be open, transparent, supportive, and unified.”
Charlotte Hebebrand, director of communications and public affairs at the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI), emphasized the need to increase fertilizer production within Africa, improve access to markets, and address response constraints to reduce shocks. “A major focus is on repurposing subsidies. It is sensitive but critical to determine the most efficient way to support farmers and promote soil health.”
Mehti Filali, senior vice president of OCP in West Africa, highlighted successful case studies from Ethiopia and Nigeria, where domestic initiatives and regional cooperation have resulted in significant agricultural growth. “Ethiopia has doubled crop production and created tailored fertilizer formulas, while Nigeria’s initiative has consolidated fertilizer procurement, created jobs, and saved US $250 million in foreign exchange. OCP’s contribution, though modest, has been critical, marked by significant milestones such as soil testing and the development of blending units.”
As Africa continues to face these challenges, the response must be dynamic, drawing on both local knowledge and scientific data. Robust data governance is essential for integrating soil health into market-driven decision-making, promoting crop diversification, and integrating organic and inorganic inputs for sustainable agriculture. “Let us remember the importance of integrating soil fertility management in a step-by-step manner, prioritizing action tailored to specific locations and conditions. Sophisticated extension systems, backed up by robust data, are crucial,” Govaerts concluded.