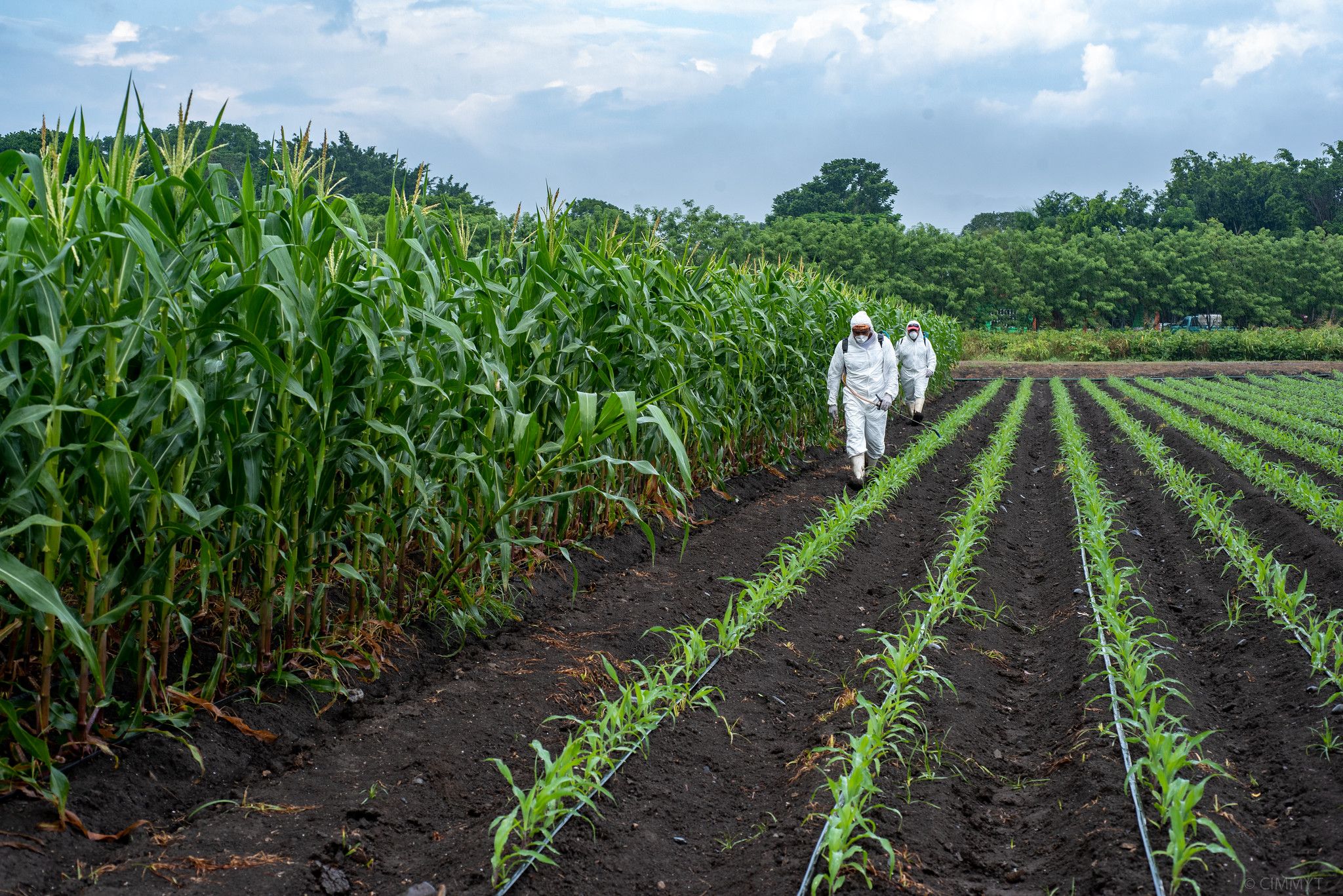
Smallholder farmers, the backbone of food systems around the world, are already facing negative impacts because of climate change. Time to adapt climate mitigation strategies is not a luxury they have. With that in mind, the Agriculture Innovation Mission for Climate (AIM4C) facilitates innovation sprints designed to leverage existing development activities to create a series of innovations in an expedited timeframe.
At the UN COP27 in Egypt, AIM4C announced its newest round of innovation sprints, including one led by the International Center for Maize and Wheat Improvement (CIMMYT) to enable smallholder farmers to achieve efficient and effective nitrogen fertilizer management. From 2022 to 2025, this sprint will steer US $90 million towards empowering small-scale producers in Africa (Kenya, Malawi, Morocco, Tanzania, and Zimbabwe), Asia (China, India, Laos and Pakistan), and Latin America (Guatemala and Mexico).
“When we talk to farmers, they tell us they want validated farming practices tailored to their specific conditions to achieve greater productivity and increase their climate resilience,” said Sieg Snapp, CIMMYT Sustainable Agrifood Systems (SAS) program director who is coordinating the sprint. “This sprint will help deliver those things rapidly by focusing on bolstering organic carbon in soil and lowering nitrous oxide emissions.”
Nitrogen in China
Working with the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS), the sprint will facilitate the development of improved versions of green manure crops, which are grown specifically for building and maintaining soil fertility and structures which are incorporated back into the soil, either directly, or after removal and composting. Green manure can significantly reduce the use of nitrogen-based fertilizers, which prime climate culprits.
“There are already green manure systems in place in China,” said Weidong Cao from CAAS, “but our efforts will integrate all the work being done to establish a framework for developing new green manure crops aid in their deployment across China.”
Triple wins in Kenya
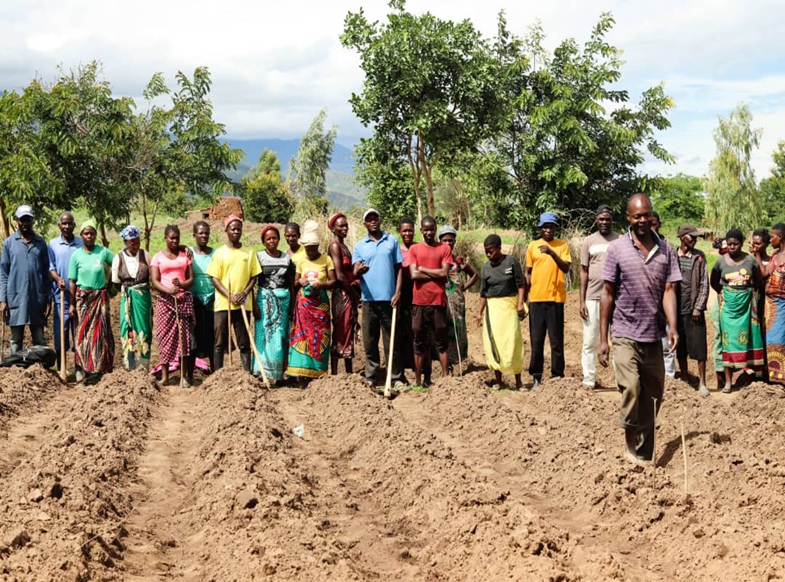
The Kenya Climate Smart Climate Project, active since 2017, is increasing agricultural productivity and building resilience to climate change risks in the targeted smallholder farming and pastoral communities. The innovation sprint will help rapidly achieve three wins in technology development and dissemination, cutting-edge innovations, and developing sets of management practices all designed to increase productive, adaption of climate smart tech and methods, and reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
Agricultural innovations in Pakistan
The Agricultural Innovation Program (AIP), a multi-disciplinary and multi-sectoral project funded by USAID, led by CIMMYT, and active in Pakistan since 2015, fosters the emergence of a dynamic, responsive, and competitive system of science and innovation that is ‘owned’ by Pakistan and catalyzes equitable growth in agricultural production, productivity, and value.
“From its beginning, AIP has been dedicated to building partnerships with local organizations and, smallholder farmers throughout Pakistan, which is very much in line with the objectives and goal as envisioned by Pakistan Vision 2025 and the Vision for Agriculture 2030, as Pakistan is a priority country for CIMMYT. However, a concerted effort is required from various players representing public and private sectors,” said Thakur Prasad Tiwari, senior scientist at CIMMYT. “Using that existing framework to deliver rapid climate smart innovations, the innovation sprint is well-situated to react to the needs of Pakistani farmers. “
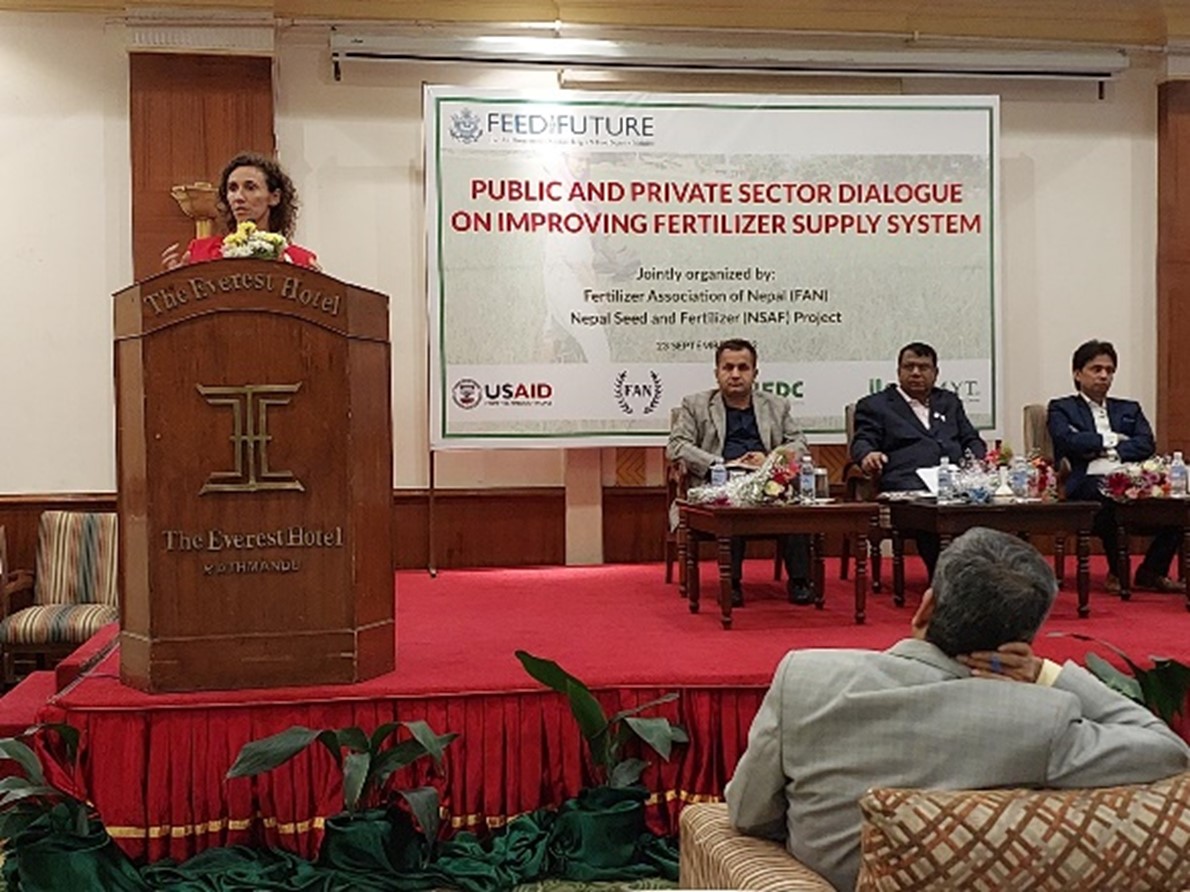
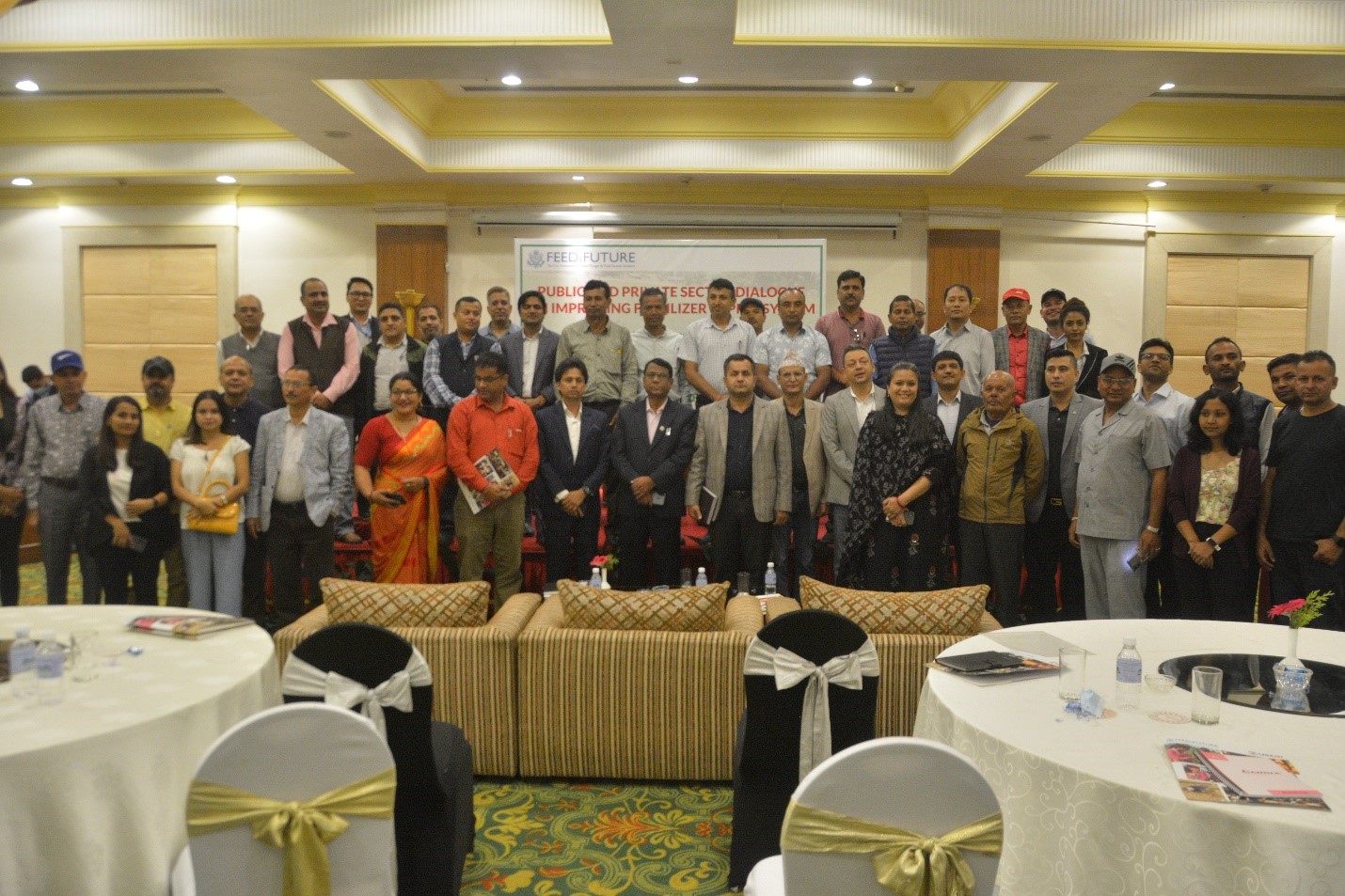
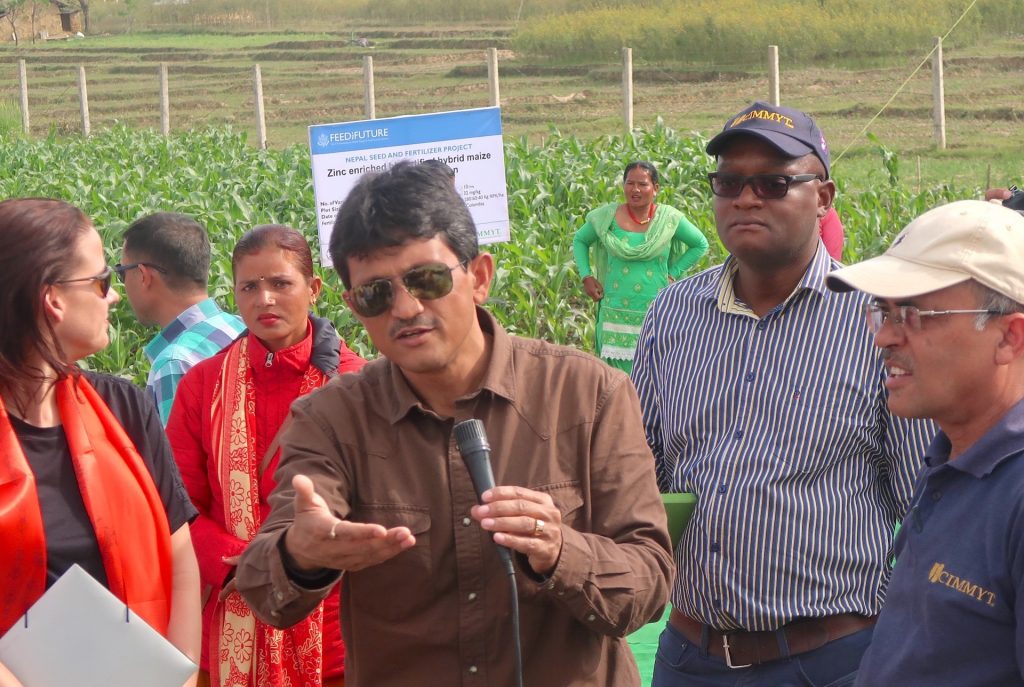
Policies and partnerships for innovations in soil fertility management in Nepal
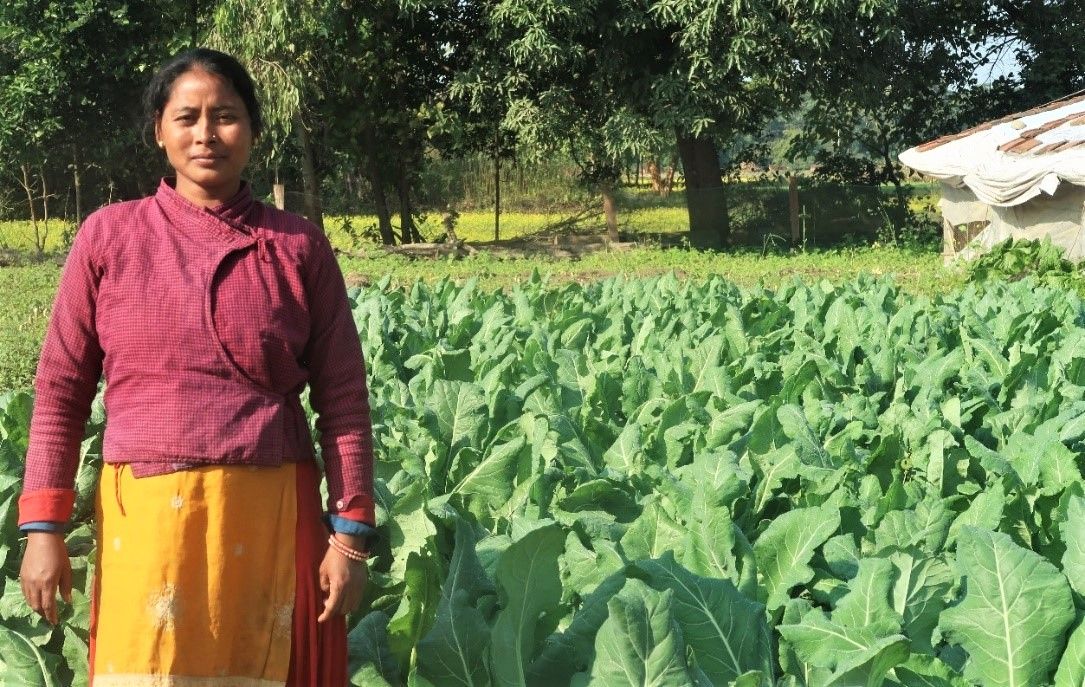
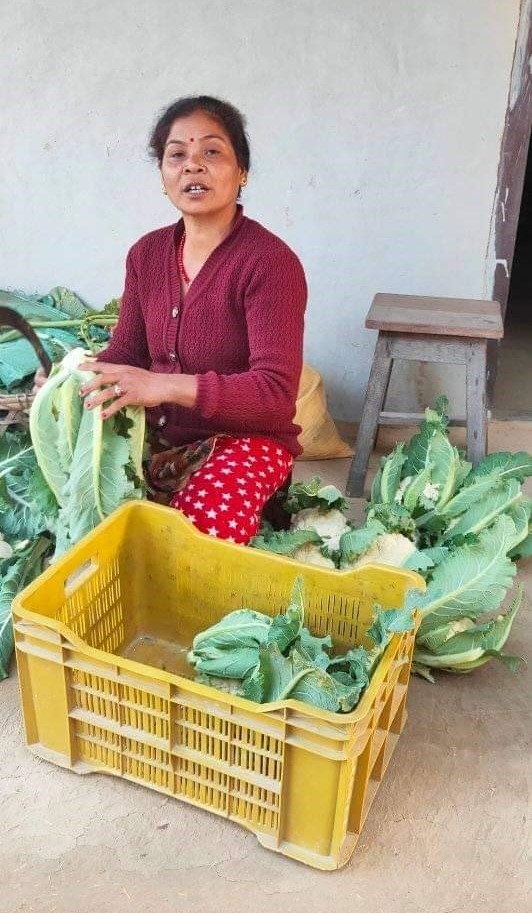
The Nepal Seed and Fertilizer (NSAF) project, funded by USAID and implemented by CIMMYT, facilitates sustainable increases in Nepal’s national crop productivity, farmer income, and household-level food and nutrition security. NSAF promotes the use of improved seeds and integrated soil fertility management technologies along with effective extension, including the use of digital and information and communications technologies. The project facilitated the National Soil Science Research Centre (NSSRC) to develop new domain specific fertilizer recommendations for rice, maize, and wheat to replace the 40 years old blanket recommendations.
Under NSAFs leadership, the Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development (MOALD) launched Asia’s first digital soil map and has coordinated governmental efforts to collect and analyze soil data to update the soil map and provide soil health cards to Nepal’s farmers. The project provides training to over 2000 farmers per year to apply ISFM principles and provides evidence to the MOALD to initiate a balanced soil fertility management program in Nepal and to revise the national fertilizer subsidy policy to promote balanced fertilizers. The project will also build efficient soil fertility management systems that significantly increase crop productivity and the marketing and distribution of climate smart and alternative fertilizer products and application methods.
Public-private partnerships accelerate access to innovations in South Asia
The Cereal Systems Initiative for South Asia (CSISA), established in 2009, has reached more than 8 million farmers by conducting applied research and bridging public and private sector divides in the context of rural ‘innovation hubs’ in Bangladesh, India, and Nepal. CSISA’s work has enabled farmers to adopt resource-conserving and climate-resilient technologies and improve their access to market information and enterprise development.
“Farmers in South Asia have become familiar with the value addition that participating in applied research can bring to innovations in their production systems,” said Timothy Krupnik, CIMMYT systems agronomist and senior scientist. “Moreover, CSISA’s work to address gaps between national and extension policies and practices as they pertain to integrated soil fertility management in the context of intensive cropping systems in South Asia has helped to accelerate farmers’ access to productivity-enhancing innovations.”
CSISA also emphasizes support for women farmers by improving their access and exposure to improved technological innovations, knowledge, and entrepreneurial skills.
Sustainable agriculture in Zambia
The Sustainable Intensification of Smallholder Farming systems in Zambia (SIFAZ) is a research project jointly implemented by the UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), Zambia’s Ministry of Agriculture and CIMMYT designed to facilitate scaling-up of sustainable and climate smart crop production and land management practices within the three agro-ecological zones of Zambia. “The Innovation Sprint can take advantage of existing SIFAZ partnerships, especially with Zambia’s Ministry of Agriculture,” said Christian Thierfelder, CIMMYT scientist. “Already having governmental buy-in will enable quick development and dissemination of new sustainable intensification practices to increase productivity and profitability, enhance human and social benefits while reducing negative impacts on the environment.”
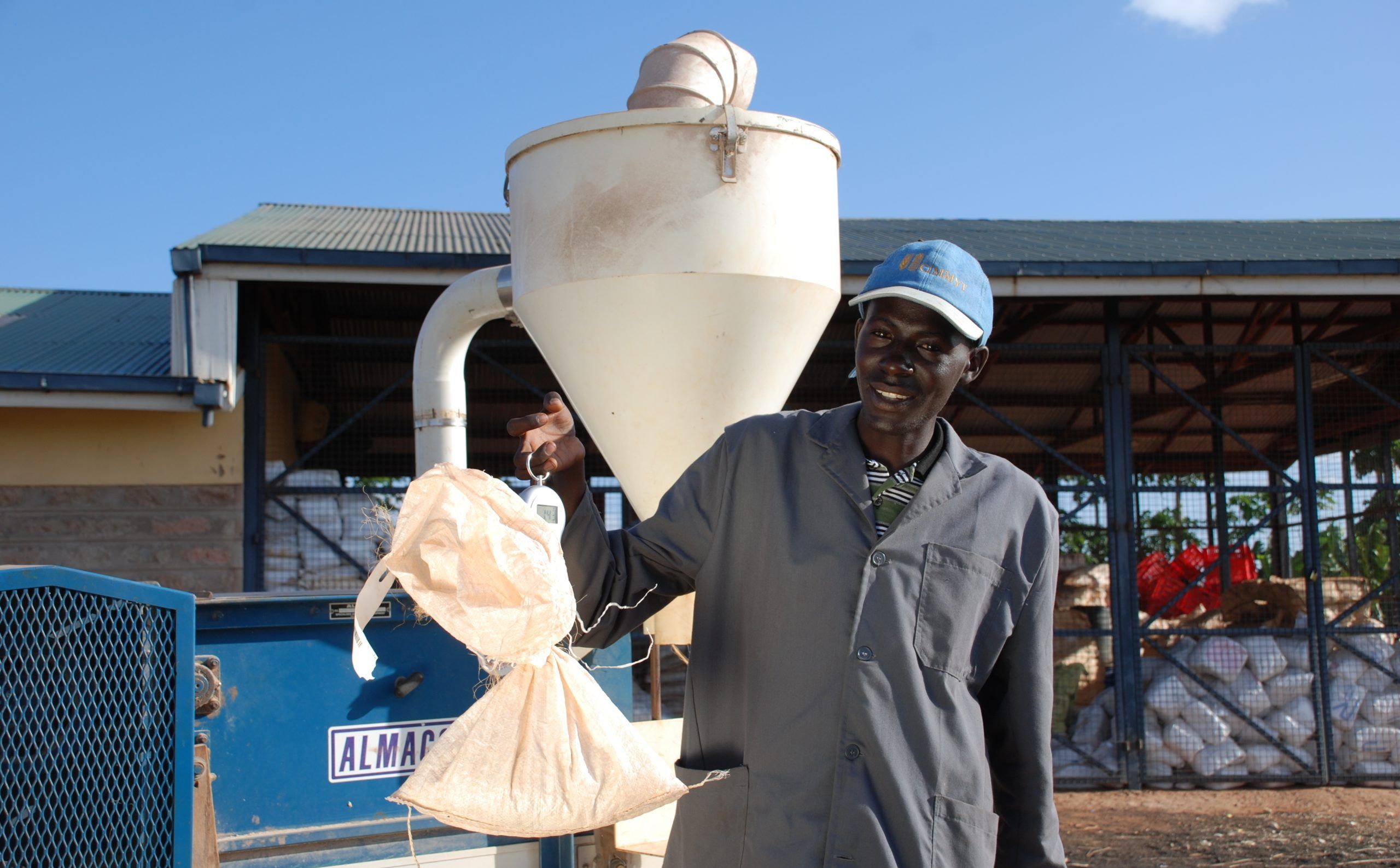
Cover photo: Paul Musembi Katiku, a field worker based in Kiboko, Kenya, weighs maize cobs harvested from a low nitrogen trial. (Florence Sipalla/CIMMYT)