For certified seed to reach a farmer’s field for cultivation, it passes through many hands – international and national breeding programs, government regulatory agencies, private seed companies, and retailers or agrodealers. These organizations each play an important role in the design, testing, production and distribution of improved maize and wheat varieties.
Together, these processes, actors, and the relationships between them form a seed system, which incorporates the production, conservation, exchange, and use of propagation materials for crops. As defined by the CGIAR Community of Excellence for Seed Systems Development (COE), seed systems are complex, involving arrangements between public and private sectors, layers of regulation, and years of research and development, and are specific to each crop, country, agroecological environment and market context.
The International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) has extensively researched and worked with the facets and actors of cereal seed systems in Latin America, Asia and Africa, specifically in relation to cereal crops, and with maize and wheat in particular.
The role of CIMMYT scientists in supply and demand
Breeding teams use traditional and advanced techniques to identify improved maize and wheat breeding lines according to the desired traits determined by farmers and consumer markets. In addition to higher grain yields, other preferred traits include more and larger grains or fruit, resistance to pests and diseases, tolerance to environment pressures (such as drought or poor soils), better nutritional quality, or flavor and ease of processing.
These lines are used for further breeding, testing, seed multiplication by public and private sector partners. Others engage in varietal testing on farmers’ fields and support seed companies in production.

To foster smallholder farmers’ access to these improved varieties, CIMMYT implements a seed systems strategy divided into supply side development, concerning breeding and seed production, and demand side development, covering issues related to variety distribution and uptake. On the supply side, CIMMYT scientists’ work is carried out in three phases:
- Product development phase: Breeders advance through CIMMYT’s breeding funnel (pipeline) the most promising materials from one improvement stage to the next. The best candidates are first tested in field trials at research stations and then in farmers’ fields. Afterwards, CIMMYT organizes field days to showcase the best performing materials to public and private sector partners.
- Product allocation phase: Local partners request new CIMMYT products and sign licensing agreements that protect the new seed from private ownership claims and help accelerate marketing and distribution in target regions at affordable prices.
- Release and commercialization phase: Farmers can obtain and benefit from seed of improved maize and wheat once national authorities register and release varieties that excel in national performance trials and public and private sector partners begin seed production and marketing or distribution.
On the demand side, CIMMYT scientists work to support seed systems development though its work on:
- Farmer preferences and demand for varieties: Scientists look to understand current and future preferences and needs for varieties. This involves the use of innovative tools, such as product concept testing, on-farm testing and ranking, and participatory varietal evaluation.
- Seed industry development: Small and medium sized seed businesses, as well as agrodealers, play a critical role in the distribution of seed. Our work looks to understand entry points for support to the seed industry for advancing faster uptake of new varieties by farmers.
- Consumer demand for grain: The preferences of consumers and agroindustry for grain and grain-based foods provide an important source of demand for new varieties. CIMMYT scientists engage with consumers and agroindustry for innovation in food product design and testing consumer acceptance. Insights gains are reported back to breeding and seed production teams for design of future cereal varieties.
Gender-sensitive seed systems
A team of social scientists at CIMMYT with expertise in economics, gender and marketing works to understand the needs and preferences of farmers, consumers, and the agroindustry for new varieties. They develop retail strategies, such as targeted marketing, in-store seed assessment support and price incentives, promote the adoption of better policies in support of seed companies and seed markets.
CIMMYT explores mechanisms to help seed companies adapt their products to women’s preferences. Research shows that beyond yield potential, women seek different characteristics in seeds than men. For example, women are more inclined to favor a variety with a longer grain shelf life. Similarly, when women engage in participatory variety selections, they tend to make more objective evaluations of varieties than men.
Our experts advance strategies to promote inclusive and effective delivery systems, helping both female and male farmers obtain the seed that works best for their specific needs. This ongoing model gives CIMMYT feedback from farmers and public and private sector partners, which informs subsequent breeding research.
Why are cereal seed systems important?
CIMMYT contributes to new improved seeds getting to farmers, consumers and agroindustry, which ultimately leads to lasting positive impacts in terms of food security and economic development.
Cereals such as maize and wheat play a critical role in global food security. Increasing their productivity in the Global South remains a key developmental priority. Smallholders face increasing pressure to sustain and increase their yields in the face of three main issues: climate change, which increases the frequency of severe drought, floods, and pest and disease outbreaks; rapidly rising costs of inputs, such as land, labor, fertilizer; and unfavorable marketing conditions for their grain.
As a critical entry point for improved agricultural technology, seed systems are in urgent need of improvement and modernization. Since the onset of the Green Revolution in the 1960s, the discovery, development, and delivery of improved seed for smallholder farmers has remained an essential part of global and local initiatives to increase smallholder productivity.
What does a sustainable, inclusive, and productive seed system look like?
For the future, there are serious challenges for expanding and deepening the impact from investments in breeding. Market intelligence systems are urgently needed to support breeding teams in future product design and evidence-based prioritization. Innovation is needed in terms of how actors within the systems inform and support farmers to experiment with new seeds.
CIMMYT is working with CGIAR partners to implement a new, 10-year strategy. Effective seed systems achieve the widespread adoption of varieties that capture the gains from crop improvement and connect actors along the value chain so that all can benefit from a productive crop, from seedbank to soil. In close collaboration with national agricultural research systems (NARS), CGIAR has had historic success introducing improved cultivars to smallholder producers of staple crops, with high return on investment. However, there is still some standing criticism that large, public breeding programs take a technologically-biased and supply-pushed approach to agricultural innovation.
Cereal crop breeding programs can become more demand-oriented by employing more market segmentation strategies – breaking down target client markets into smaller, more geographically and demographically specific groups – and developing a more accessible description and profile of its products. Using similar approaches, CGIAR is likely to expand demand-oriented programs in genetic innovation and seed systems development in the new phase of operations.
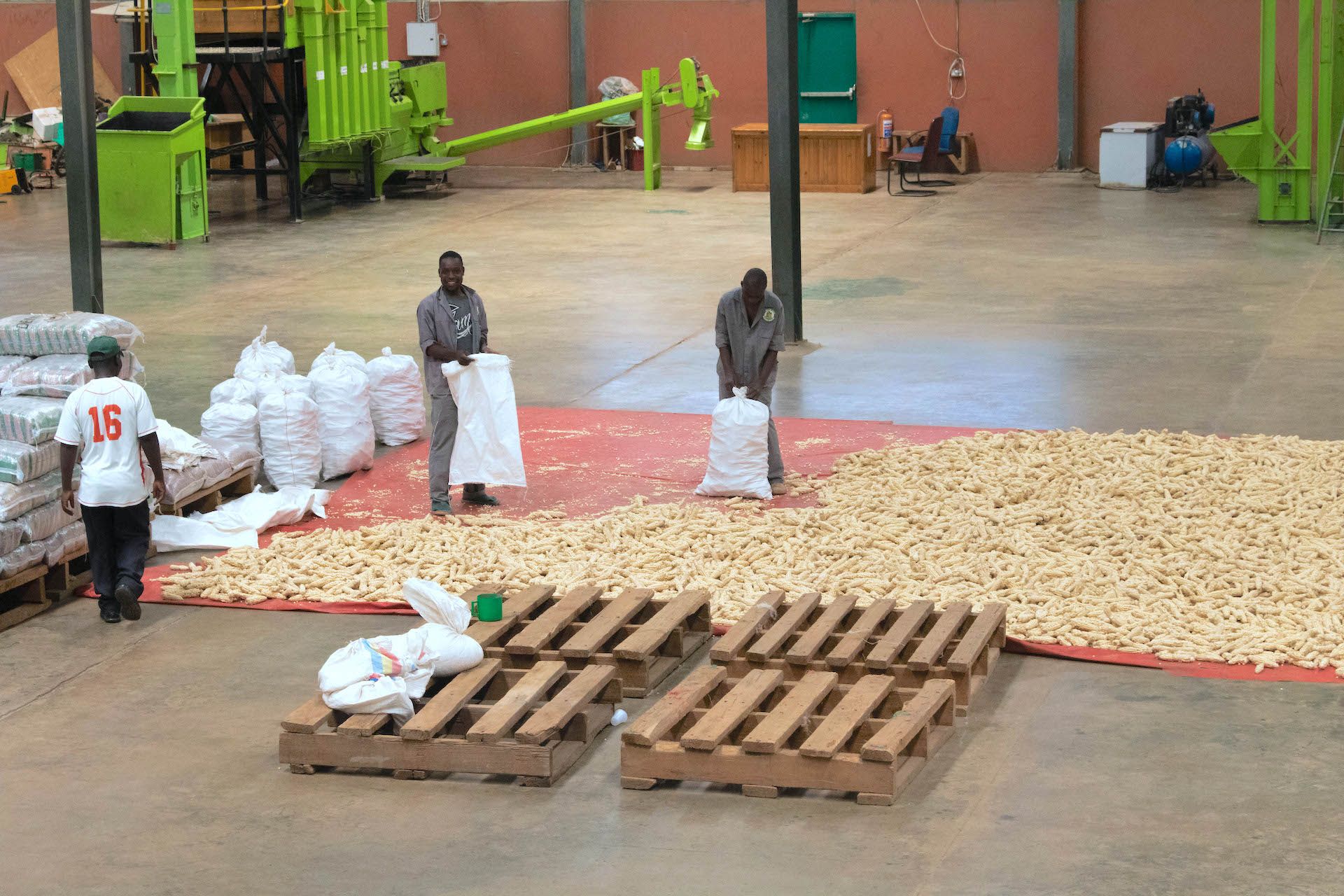
Cover photo: Staff members bag maize at the Demeter Seeds warehouse. (Photo: Emma Orchardson/CIMMYT)