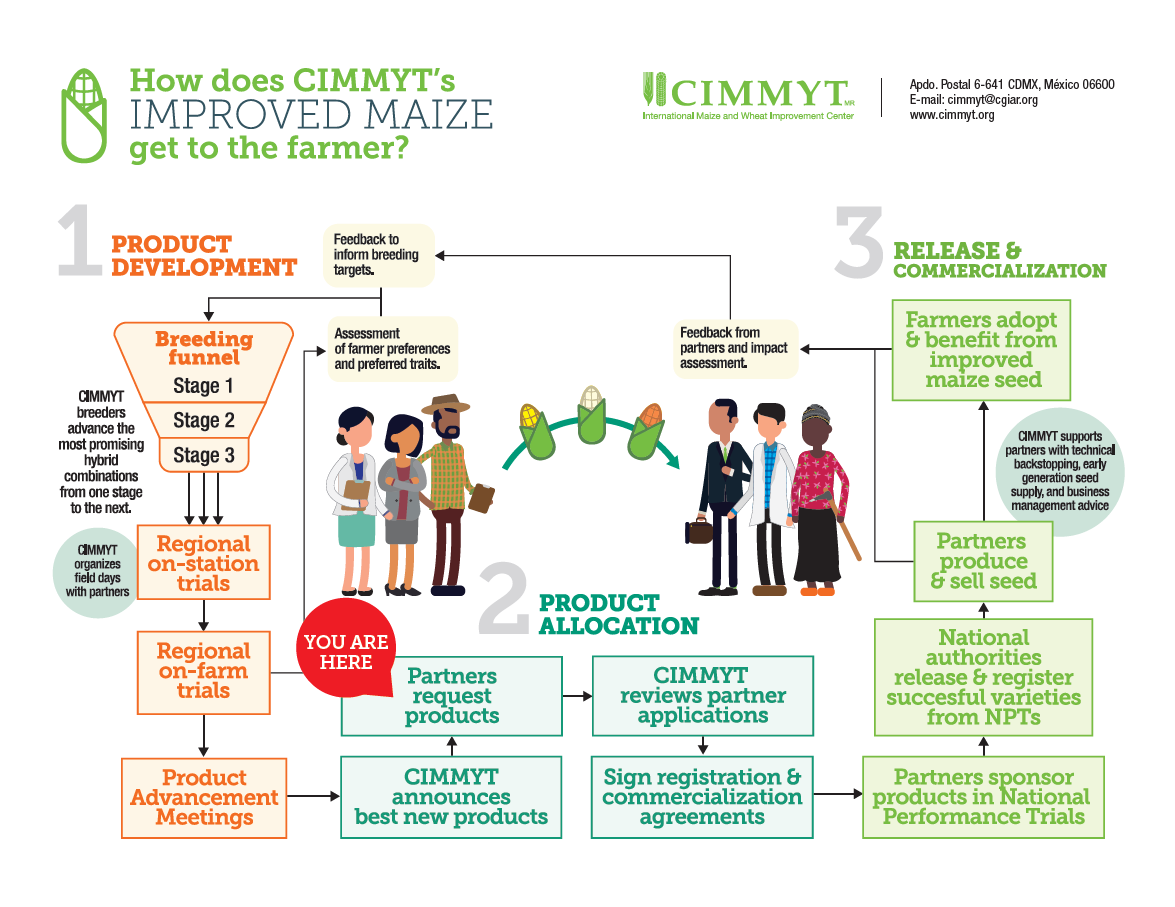
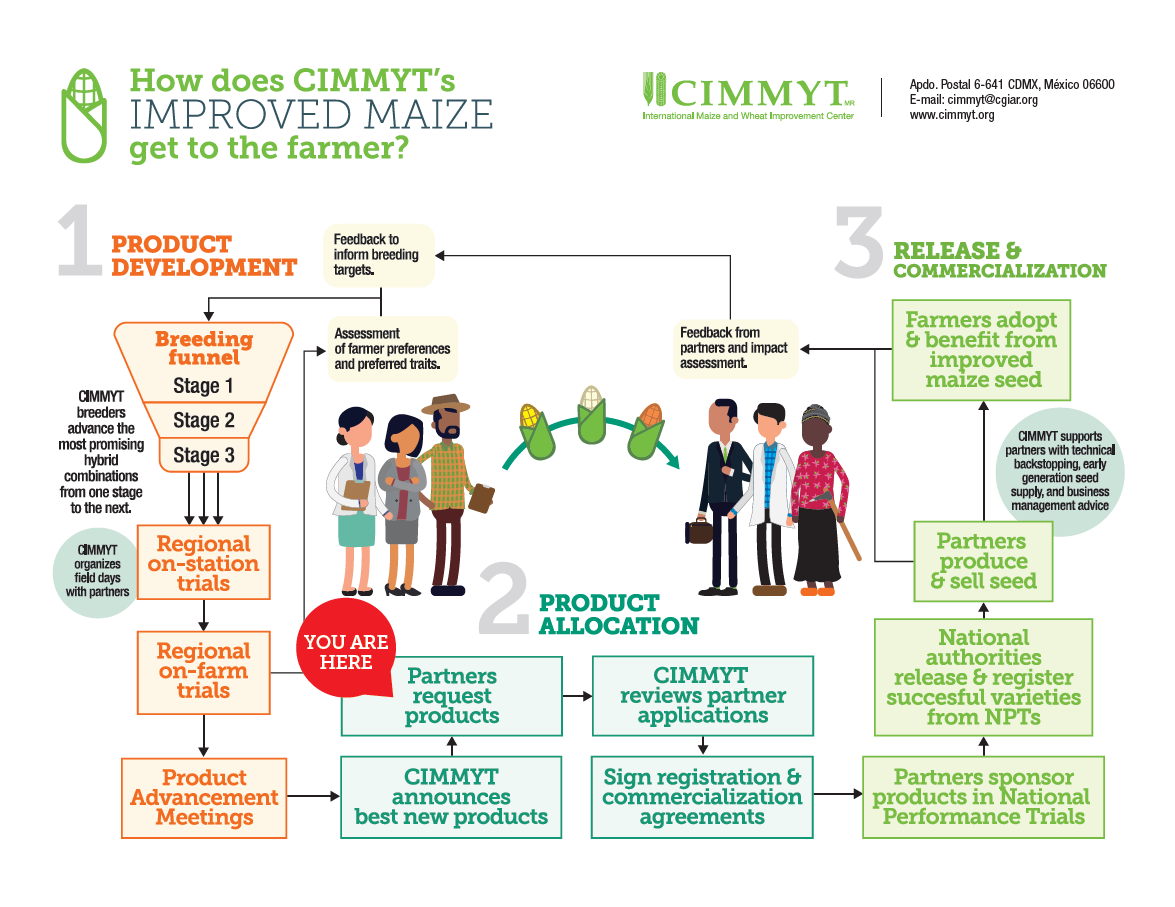
In maize research, farmers’ priorities are our priorities
Figuring out what kinds of crops and crop varieties farmers want – high yielding, disease resistant, drought tolerant, early maturing, consumer-preferred, nutritious etc. – is a crucial step in developing locally adapted, farmer-friendly and market preferred varieties as part of more sustainable seed grain sectors.
While scientists aim to develop the best crop varieties with multiple traits, there are always trade-offs to be made due to the limits of genetics or competing preferences. For example, a variety may be more tolerant to drought but perform less well in consumer taste preferences such as sweet grains, or it may be higher yielding but more vulnerable to pests and diseases. Some of these trade-offs, such as vulnerability to pests or adverse climate, are not acceptable and must be overcome by crop scientists. The bundle of traits a crop variety offers is often a major consideration for farmers and can be the difference between a bumper harvest and a harvest lost to pests and diseases or extreme weather conditions.
Economists from the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) have been working with smallholder farmers across sub-Saharan Africa to document their preferences when it comes to maize. Results from Ethiopia were recently published in the journal PLOS ONE.
In a survey with almost 1,500 participants in more than 800 households, researchers found that both male and female farmers valued drought tolerance over other traits. For many farmers in areas where high-yielding, medium-maturing hybrids were available, early maturity was not considered a priority, and sometimes even disliked, as farmers felt it made their harvests more vulnerable to theft or increased their social obligations to share the early crop with relatives and neighbors if they were the only ones harvesting an early maize crop. Farmers therefore preferred varieties which matured more in sync with other farmers.
The team also found some gender differences, with female farmers often preferring taste over other traits, while male farmers were more likely to prioritize plant architecture traits like closed tip and shorter plants that do not easily break in the wind or bend over to the ground. These differences, if confirmed by ongoing and further research, suggest that gender differences in maize variety choices may occur due to differentiated roles of men and women in the maize value chains. Any differences observed should be traced to such roles where these are distinctly and socially differentiated. In aspects where men and women’s roles are similar — for example, when women express preferences in their role as farmers as opposed to being custodians of household nutrition — they will prioritize similar aspects of maize varieties.
The results of the study show that overall, the most important traits for farmers in Ethiopia, in addition to those that improve yields, are varieties that are drought and disease tolerant, while in taste-sensitive markets with strong commercial opportunities in green maize selling, farmers may prioritize varieties that satisfy these specific consumer tastes. The findings of the study also highlight the impact of the local social environment on variety choices.
By taking farmers’ preferences on board, maize scientists can help develop more sustainable maize cropping systems which are adapted to the local environment and respond to global climatic and economic changes driven by farmers’ and consumers’ priorities.

Drought and striga tolerance come out top for Kenyan farmers
In related research from western Kenya, published in June 2022 in Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, results showed that farmers highly valued tolerance to drought, as well as tolerance to striga weed, low nitrogen soils and fall armyworm, in that order. CIMMYT researchers surveyed 1,400 smallholder farmers across three districts in western Kenya.
The scientists called for a more nuanced approach to seed markets, where seed prices might reflect the attributes of varieties. Doing so, they argue, would allow farmers to decide whether to pay price premiums for specific seed products thereby achieving greater market segmentation based on relative values of new traits.
“Both studies show that farmers, scientists and development experts in the maize sector are grappling with a wide array of demands,” said Paswel Marenya, CIMMYT senior scientist and first author of both studies.
“Fortunately, the maize breeding systems in CIMMYT, CGIAR and National Agricultural Research Systems (NARS) have produced a wide range of locally adapted, stress tolerant and consumer preferred varieties.”
The results of both these studies provide a framework for the kinds of traits scientists should prioritize in maize improvement programs at least in similar regions as those studied here in central Ethiopia or western Kenya. However, as Marenya noted, there is still work to do in supporting farmers to make informed choices: “The challenge is to implement rigorous market targeting strategies that sort and organize this complex landscape for farmers, thereby reducing the information load, search costs and learning times about new varieties. This will accelerate the speed of adoption and genetic gains on farmers’ fields as envisaged in this project.”
Read the studies:
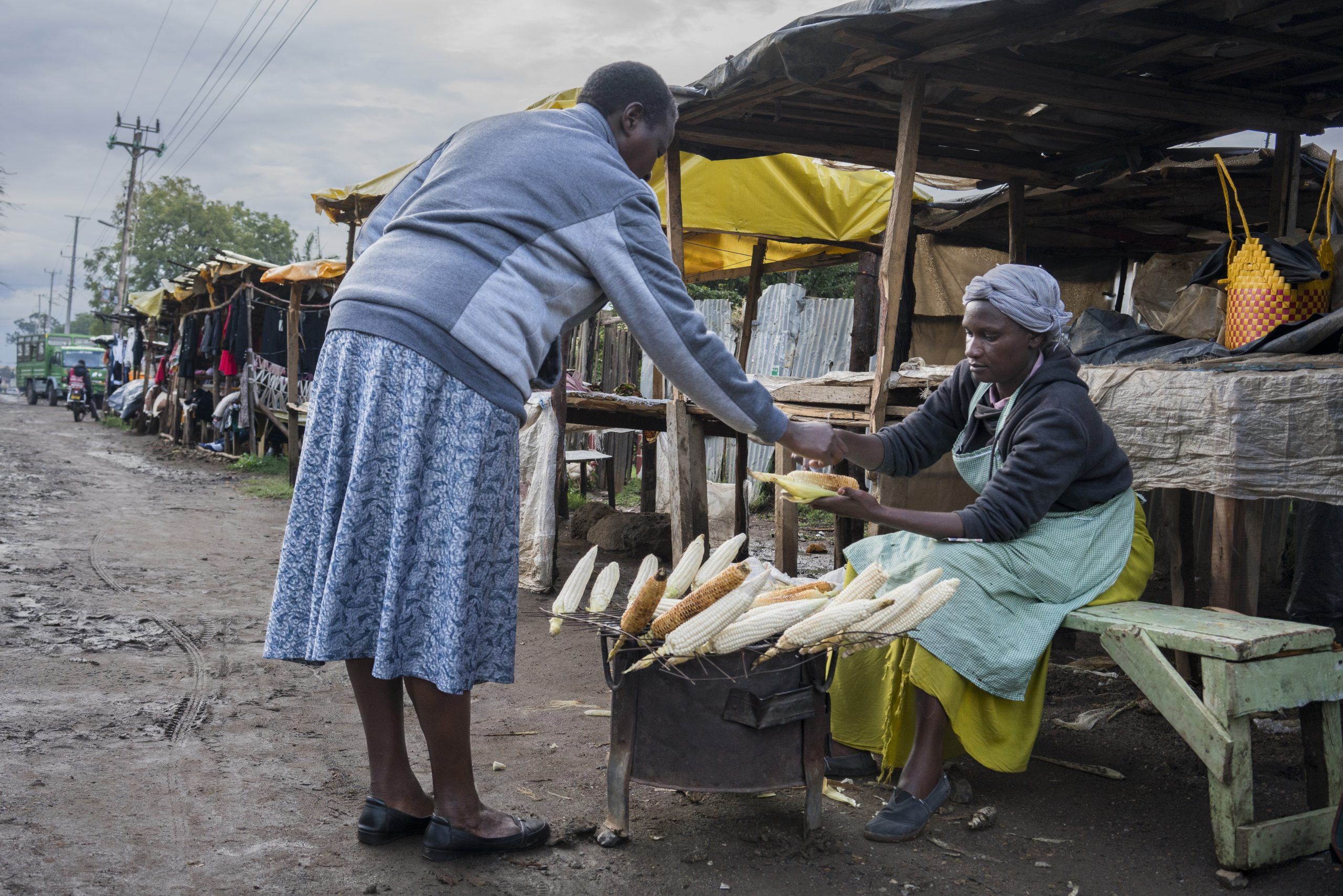
Cover photo: Roadside vendor sells roasted maize cobs to a customer in Timau, Kenya. (Photo: Peter Lowe/CIMMYT)