Positive Solutions for Nature in Colombia: A Review
In a world where environmental and agrifood challenges demand urgent responses, the CGIAR-led Positive Solutions for Nature (Nature+) initiative is transforming agriculture into a catalyst for ecological regeneration and sustainable development.
In Colombia, CIMMYT has played a key role in implementing several activities under this initiative. These efforts have not only improved agricultural productivity but also promoted biodiversity conservation, sustainable resource management, and the strengthening of rural communities—with a special focus on youth, women, and native maize.
One of the first steps in Colombia was conducting a diagnosis and mapping key actors within agrifood systems across different regions. This assessment identified major challenges such as limited access to native seeds, soil degradation, and lack of access to fair market opportunities for smallholder farmers.
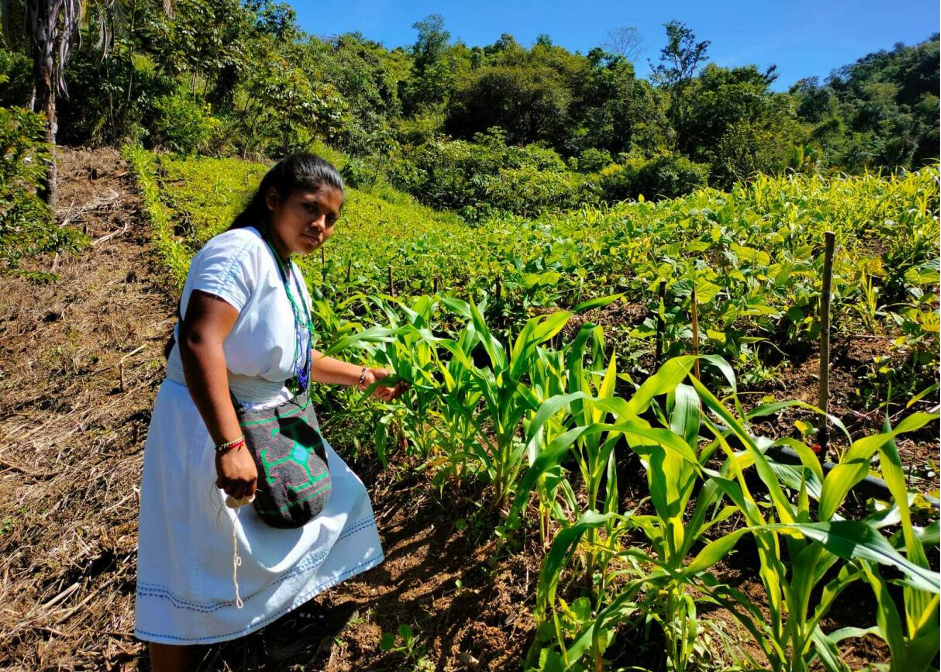
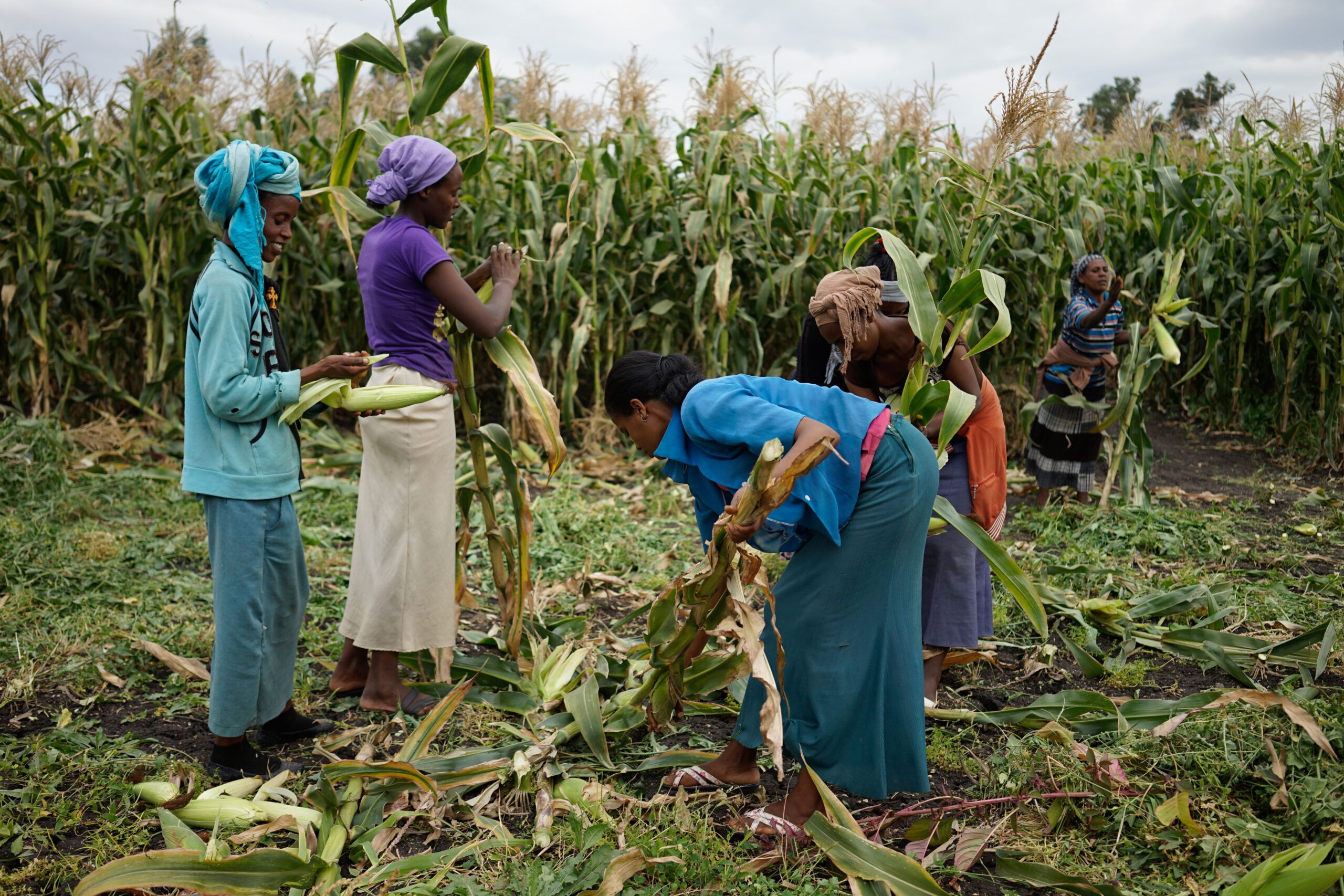
To ensure that promoted practices aligned with local realities and needs, CIMMYT worked closely with farmers to co-create solutions. A significant example was the support given to women producers to conserve native maize varieties. Workshops held in Cesar, Nariño, Putumayo, and Valle del Cauca included childcare spaces, enabling full participation by women.
Another important milestone was facilitating dialogue between producers and niche markets, helping connect farmers growing native maize with potential buyers. This has been key to revitalizing the value chain for these crops. In parallel, twelve community seed banks were strengthened in various regions, ensuring the availability of native varieties and encouraging intergenerational knowledge exchange.
CIMMYT also conducted extensive training activities, benefiting hundreds of farmers in the post-harvest management of native grains and seeds. In workshops held during 2023 and 2024, over 780 producers—many of them women—received training in practices such as harvesting, drying, shelling, and hermetic storage, which reduced post-harvest losses and improved seed quality.
Infrastructure improvements further supported these efforts. One standout example is the YEL-PUE Cumbe seed bank in Cumbal, Nariño—established with support from CIMMYT and the Bioversity-CIAT Alliance. This seed bank not only conserves agricultural biodiversity but also serves as an intergenerational learning hub, where farmers, students, and technicians share experiences and knowledge.
A key component of the initiative has been youth participation. Through collaboration with the José María Falla Educational Institution and youth networks like Herederos del Planeta, students have engaged in agroecological maize production. This involvement fosters stronger rural ties and ensures the continuity of traditional knowledge for future generations.
While challenges remain, the implementation of Positive Solutions for Nature in Colombia has demonstrated that agricultural production can go hand in hand with environmental conservation and community well-being. Thanks to collaborations with research centers such as CIMMYT, many Colombian farmers are now adopting regenerative practices, enhancing agrobiodiversity and boosting resilience to both climate and economic shocks.
Looking ahead, these efforts will continue within the CGIAR Multifunctional Landscapes Science Program. CIMMYT, in collaboration with other CGIAR centers, will focus on participatory varietal selection, business models to enhance the value of agrobiodiversity, connections to niche markets, and the empowerment of women as agents of biodiversity conservation.