CIMMYT releases 22 new maize inbred lines for the tropics and subtropics
CIMMYT is pleased to announce the release of 22 new CIMMYT maize lines (CMLs). The CMLs were developed at various breeding locations of CIMMYT Global Maize Program by multi-disciplinary teams of scientists. These lines are adapted to the tropical/subtropical maize production environments targeted by CIMMYT and the partner institutions. CMLs are freely available to both public and private sector breeders worldwide under CIMMYT’s standard material transfer agreement (SMTA).
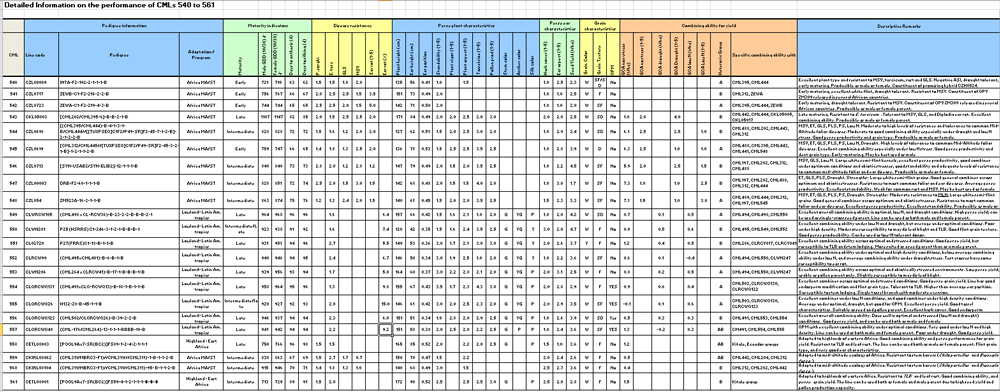
Prior to their release, the CMLs are intensively evaluated for per se performance (especially under abiotic and biotic stresses) and performance in hybrid combinations (combining ability). Release of a CML does not guarantee high combining ability or per se performance in all environments; rather, it indicates that the line is promising or useful as a hybrid component or as a parent for pedigree breeding for one or more target mega-environments. The descriptions of the lines include heterotic group classification, along with information on their specific combining ability with widely-used CIMMYT lines. Instances where CMLs within a given heterotic group have good combining ability with other lines from the same heterotic group are also cited; the resulting hybrids may be useful either as single-cross products or as female parents of three-way or double-cross hybrids. Some of the new releases and previously-released CMLs have already been used as parents of successful hybrids or improved open pollinated varieties (OPVs) by public and private sector institutions. A brief description of each of the 22 new CMLs is presented below (the information in parentheses for each CML is the line code).
Further details about the lines are provided in CML540-561 Details. A limited quantity of seed of the CMLs can be obtained by sending a request to the CIMMYT Germplasm Bank.
Download table in XSLX format
CML540 (CZL00009)
An early-maturing, drought tolerant late-maturing resistance to maize streak virus (MSV), turcicum leaf blight (TLB), common rust (PS), and gray leaf spot (GLS). This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group A line and combines well with CML395 and CML444. The line is producible as a male or female parent.
CML541 (CZL0717)
An early-maturing, white-grained, flint inbred late-maturing resistance to MSV and good drought tolerance. This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group B line and combines well with CML312 and lines derived from the Zimbabwe Early White A (ZEWA) synthetic. The line is a component of the commercial OPV ZM309, which has been released for commercial cultivation in several African countries.
CML542 (CZL0723)
An early-maturing, drought tolerant late-maturing resistance to MSV. This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group A line and combines well with CML395, CML444, and lines derived from Zimbabwe Early White B (ZEWB) synthetic. The line is a component of the commercial OPV ZM309, which has been released in several African countries. The line is usable either as a male or female parent.
CML543 (CKL05003)
A late-maturing inbred line with white, semi-dent grain. This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group B line and combines well with CML442, CKL5005 and CKL5017. The line also combines well with group B tester CML444. The line was developed from sources combining MSV resistance and drought tolerance. It has excellent combining ability for grain yield, and is resistant to TLB, and tolerant to MSV, GLS and Diplodia ear rot. CML543 has moderate resistance to maize lethal necrosis (MLN). The line can be used as either a male or female for seed production.
 CML544 (CZL0610)
CML544 (CZL0610)
An intermediate-maturity, white-grained, semi-dent inbred line that has moderate-to-high levels of resistance to common midaltitude foliar diseases – MSV, TLB, GLS, Phaeosphaeria leaf spot (PLS) and PS. This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group B line and combines well with CML488, CML443, and CML312. The line also combines well with group B tester CML202. It has moderate-to-excellent combining ability, especially under drought and low soil N. The line can be used as male or female for seed production, and has been used in several commercial hybrids in eastern and southern Africa.
CML545 (CZL0619) An early-maturing, white-grained, dent-type inbred line that has high levels of resistance to common mid-altitude foliar diseases (MSV, TLB, GLS, PLS, PS) and tolerance to low soil N and flowering stage drought. This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group A line and combines well with CML488, CML395, CML443, and CML441. The line also combines with the group A line CML548. The line exhibits excellent combining ability, especially under low soil N stress. The line is best used as a male in three-way hybrid formation, although it can also be used as a component of early-maturing single-cross females. It has been used in one commercial hybrid in southern Africa.
CML546 (CZL0713)
An intermediate-maturity, white-grained, large semi-flint type inbred line with adequate levels of resistance to common mid-altitude foliar and ear diseases, especially MSV and GLS, and tolerance to low soil N stress. This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group B line and combines well with CML197, CML312, and CML488. The line also combines well with group B tester CML202. The line exhibits excellent per se productivity, has good standability, and is a good combiner under both optimum and abiotic stress conditions. It can be used as a male or female parent, and is a component of one commercial hybrid in southern Africa.
CML547 (CZL00003)
An intermediate-to-late-maturing, large white-grained, semi-flint inbred line with adequate levels of resistance to TLB, GLS, and PLS. This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group B line and combines well with CML197, CML312, and CML488. The line also combines well with group B testers CML202 and CML444. The line is drought tolerant and a good general combiner across optimum and abiotic stress conditions. It exhibits average per se productivity but has excellent plant type and standability. The line is best used as a component of intermediate-to-late-maturing single-cross females and has been used in several commercial hybrids in eastern and southern Africa.

CML548 (CZL054)
A white-grained, semi-flint, intermediate-maturity inbred line with good levels of resistance to MSV, TLB, GLS, PLS and PS, and moderate resistance to MLN. This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group A line and combines well with CML489 and CML444. The line also combines well with group A testers CML197, CML312, and CML545. The line is drought tolerant, has good per se productivity, and is an excellent combiner under optimum conditions and drought stress. It is best used as a male parent in three-way hybrid formation, although it can also be used as a parent of single-cross females. The line has been used as a parent in one commercial hybrid in southern Africa.
CML549 (CLWRCW105)
A late-maturing, white semi-dent tropical late-maturing excellent overall combining ability in optimal, low N, and drought conditions. This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group A line and combines well with CML494 and CML550. The line also combines with group A tester CML498. The line has good resistance to foliar diseases and ear rots, and can be used as a seed parent for single-cross hybrids due to its high per se yield.
CML550 (CLWN201)
An intermediate-maturity, white flint tropical line with excellent combining ability under low N and drought conditions, but average performance under optimal conditions. This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group B line, and combines well with CML495, CML549, and CML552. The line can be used as a donor for low N stress tolerance. The line has good per se yield and could be used as female parent. It has moderate susceptibility to maydis leaf blight and TLB.
CML551 (CL02720)
A late-maturing, yellow flint tropical line with excellent combining ability across optimal and drought stress conditions. This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group B line, and combines well with CML286, CLRCY017, and CLRCY041. The line has good per se yield and resistance to ear rots, but is susceptible to TLB and stem lodging. It is more suited for use as a female seed parent than as a male parent.
CML552 (CLRCW99)
A late-maturing, white semi-flint tropical line with excellent combining ability under both optimal and high density conditions. This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group A line, and combines well with CML494, CML550, and CLWN247. The line can be used either as a male or female parent in seed production.
 CML553 (CLWN206)
CML553 (CLWN206)
A late-maturing, white flint, tropical line with excellent combining ability across optimal and stressed environments. This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group A line, and combines well with CML494, CML550, and CLWN247. The line has excellent resistance to ear rots, but is slightly susceptible to maydis leaf blight. Due to its lower-than-average per se yield, it is best used as a male parent for hybrid seed production.
CML554 (CLQRCWQ131)
A late-maturing, white flint, QPM tropical line with excellent combining ability under optimal conditions and abiotic stress. This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group A line, and combines well with CML503, CLRCWQ130, and CLRCWQ122. The line has good per se grain yield, good endosperm modification, and resistance to TLB. The line is best suited for use as a female seed parent.
CML555 (CLQRCWQ26) An intermediate-maturity, white-grained, semi-flint, QPM tropical line with excellent combining ability under low N conditions. This line is classified a CIMMYT heterotic group A line, and combines well with CML503, CLRCWQ130, and CLRCWQ123. The line has excellent per se yield, good endosperm modification, and is usable either as a seed or pollen parent.
CML556 (CLQRCWQ123)
A late-maturing, white grained, semi-dent, QPM line with excellent combining ability under optimal, low N, and drought conditions. This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group B line, and combines well with CML491, CML553, and CML554. The line has good per se yield and can be used either as a male or female parent.
CML557 (CLQRCWQ48)
A late-maturing, white-grained, semi-flint, QPM line with excellent combining ability under optimal conditions and very good performance under low N and high density stress. This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group AB line and combines well with CML491, CML554, and CML555. The line has good root strength, excellent per se yield, and good endosperm modification. It can be used as either as a male or female parent.
CML558 (CETL08003) A late-maturing, white-grained, flint-type highland line with resistance to the most important highland diseases, especially TLB and PS. This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group AB line. The line combines with materials from both the Kitale and Ecuador highland groups. The line has excellent combining ability and good per se yield, and can be used either as a female or male parent for hybrid seed production. It has been used as a parent in one three-way cross released in Ethiopia.
CML559 (CKIRL08062)
An intermediate-maturity, white grained line adapted to the mid-altitude ecologies of eastern and southern Africa. This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group AB line as it combines well with CML442, CML204, and CML312. The line is resistant to spotted stem borer (Chilo partellus) and African stem borer (Busseola fusca), the major field insect pests of eastern and southern Africa, and also has appreciable levels of resistance to MSV and other common foliar diseases, including TLB and GLS.
CML560 (CKIRL08104)
An intermediate-maturity, white-grained inbred line adapted to the midaltitude ecologies of eastern and southern Africa. This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group B line as it combines well with CML312, CML202, and CML442. The line is resistant to spotted stem borer (Chilo partellus) and African stem borer (Busseola fusca). The line also has appreciable levels of resistance to MSV and other common foliar diseases, including TLB and GLS.
CML561 (CETL08001)
An intermediate-maturity, white-grained, flint-type highland line well-adapted to the midaltitude ecologies of eastern Africa. This line is classified as a CIMMYT heterotic group B line with resistance to TLB and PS. The line has excellent combining ability, per se productivity, and can be used both as a female or male parent. The line is being used as a parent in one three-way cross hybrid released in Ethiopia.
 Mobile phones promise new opportunities for reaching farmers with agricultural information, but are their potential fully utilized? CIMMYT’s agricultural economist Surabhi Mittal and
Mobile phones promise new opportunities for reaching farmers with agricultural information, but are their potential fully utilized? CIMMYT’s agricultural economist Surabhi Mittal and  What can be done? Agro-advisory providers need to develop specific, appropriate, and timely content and update it as often as necessary. This cannot be achieved without a thorough assessment of farmers’ needs and their continuous evaluation. To ensure timeliness and accuracy of the provided information, two-way communication is necessary; Mittal and Mehar suggest the creation of helplines to provide customized solutions and enable feedback from farmers. The information delivery must be led by demand, not driven by supply. However, even when all that is done, it must be remembered that merely receiving messages over the phone does not motivate farmers to start using this information. The services have to be supplemented with demonstration of new technologies on farmers’ fields and through field trials.
What can be done? Agro-advisory providers need to develop specific, appropriate, and timely content and update it as often as necessary. This cannot be achieved without a thorough assessment of farmers’ needs and their continuous evaluation. To ensure timeliness and accuracy of the provided information, two-way communication is necessary; Mittal and Mehar suggest the creation of helplines to provide customized solutions and enable feedback from farmers. The information delivery must be led by demand, not driven by supply. However, even when all that is done, it must be remembered that merely receiving messages over the phone does not motivate farmers to start using this information. The services have to be supplemented with demonstration of new technologies on farmers’ fields and through field trials. Farmers need to be more involved in developing and refining technology. This was one of the key conclusions of a technology working group comprised of leading Asian scientists, representatives of farmer groups and entrepreneurs who met during “The 50 Pact,” an international conference jointly organized by the Borlaug Institute for South Asia (BISA) and the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) to celebrate 50 years of Dr. Norman Borlaug’s first visit to India. Held in New Delhi during 16-17 August, the event brought together more than 200 participants from agriculture institutions, the government, think tanks, industry, and civil society of various countries including Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Belgium, Germany, India, Malaysia, Mexico, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and the United States.
Farmers need to be more involved in developing and refining technology. This was one of the key conclusions of a technology working group comprised of leading Asian scientists, representatives of farmer groups and entrepreneurs who met during “The 50 Pact,” an international conference jointly organized by the Borlaug Institute for South Asia (BISA) and the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) to celebrate 50 years of Dr. Norman Borlaug’s first visit to India. Held in New Delhi during 16-17 August, the event brought together more than 200 participants from agriculture institutions, the government, think tanks, industry, and civil society of various countries including Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Belgium, Germany, India, Malaysia, Mexico, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and the United States. Technology and innovations will play a key role
Technology and innovations will play a key role  Farming systems all over the world face complex problems in terms of production, such as natural resource depletion, climate change, increasing food demand, and volatile prices. Farmers have to adapt to continuously changing conditions to produce food. ‘Farming systems design’ is an approach that aims at modifying designs of farming systems to sustainably increase the overall productivity and profitability of the systems—and, hopefully, the welfare of individual farming families—while considering interactions in the system. Interactions are important features of farm system structure and operation. They may occur between the various components, including crop-crop, crop-livestock, and farm-household as well as on-farm-off-farm activities as they compete for the same resources.
Farming systems all over the world face complex problems in terms of production, such as natural resource depletion, climate change, increasing food demand, and volatile prices. Farmers have to adapt to continuously changing conditions to produce food. ‘Farming systems design’ is an approach that aims at modifying designs of farming systems to sustainably increase the overall productivity and profitability of the systems—and, hopefully, the welfare of individual farming families—while considering interactions in the system. Interactions are important features of farm system structure and operation. They may occur between the various components, including crop-crop, crop-livestock, and farm-household as well as on-farm-off-farm activities as they compete for the same resources. For Peter Carberry, chair of the Program Committee and deputy director at the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (
For Peter Carberry, chair of the Program Committee and deputy director at the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (





 To achieve food security, smallholder farmers in Southern Africa require access to improved seed and inputs for higher yields. “Seed is one of the key movers in agricultural development,” says John MacRobert, New Seed Initiative for Maize in Southern Africa (NSIMA) leader, indicating the importance of going beyond developing improved seed varieties to encompass their dissemination, promotion, and adoption in developing strategies around seed development. These issues, together with NSIMA’s to date progress (the project is in its third phase) and strategies for the next phase, were discussed at a meeting in Lusaka, Zambia, during 7-9 August 2013. About 50 participants from institutions collaborating on the project led by CIMMYT and funded by the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (
To achieve food security, smallholder farmers in Southern Africa require access to improved seed and inputs for higher yields. “Seed is one of the key movers in agricultural development,” says John MacRobert, New Seed Initiative for Maize in Southern Africa (NSIMA) leader, indicating the importance of going beyond developing improved seed varieties to encompass their dissemination, promotion, and adoption in developing strategies around seed development. These issues, together with NSIMA’s to date progress (the project is in its third phase) and strategies for the next phase, were discussed at a meeting in Lusaka, Zambia, during 7-9 August 2013. About 50 participants from institutions collaborating on the project led by CIMMYT and funded by the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation ( But do smallholder farmers have access to the new seeds, technologies, and information? The answer is often no. “Integrating stress tolerant maize and legumes, such as pigeon peas, beans, and cowpeas, leads to sustainable production systems. We need effective seed road maps to enhance access and availability of improved maize and legume seeds,” CIMMYT regional director for Southern Africa Mulugetta Mekuria said, giving an example of one such gap in the system.
But do smallholder farmers have access to the new seeds, technologies, and information? The answer is often no. “Integrating stress tolerant maize and legumes, such as pigeon peas, beans, and cowpeas, leads to sustainable production systems. We need effective seed road maps to enhance access and availability of improved maize and legume seeds,” CIMMYT regional director for Southern Africa Mulugetta Mekuria said, giving an example of one such gap in the system. “Private sector players steer away from smallholders viewing them as high risk because of their poor infrastructure, lack of credit, and land tenure, while governments may not view them as a viable investment,” Jenrich summarized the lack of interest in smallholders’ problems. Zaka Superseeds proves them wrong; cooperating with smallholders can, in fact, be beneficial for seed companies, as they can work more closely with the community consuming their seed. Zaka, for example, is removing a product from its selection after consultations with the community during which they found out the discussed maize variety has a long maturity period and is thus undesirable.
“Private sector players steer away from smallholders viewing them as high risk because of their poor infrastructure, lack of credit, and land tenure, while governments may not view them as a viable investment,” Jenrich summarized the lack of interest in smallholders’ problems. Zaka Superseeds proves them wrong; cooperating with smallholders can, in fact, be beneficial for seed companies, as they can work more closely with the community consuming their seed. Zaka, for example, is removing a product from its selection after consultations with the community during which they found out the discussed maize variety has a long maturity period and is thus undesirable. “Maize production is likely to suffer the most due to climate change compared to other crops in Southern Africa,” said CIMMYT physiologist Jill Cairns, who presented on CIMMYT work under the
“Maize production is likely to suffer the most due to climate change compared to other crops in Southern Africa,” said CIMMYT physiologist Jill Cairns, who presented on CIMMYT work under the  “The trip was an eye opener for me. We have no mass rearing facility in Ethiopia; neither do we practice artificial infestation of stem borers. We only undertake natural infestation for our trials, which does not give uniform infestation, leading us to wrong conclusions,” said Midekssa Ardessa from Bako Agricultural Research Center at the Ethiopian Institute of Agricultural Research (EIAR), who visited CIMMYT-Kenya during 21-27 July 2013 with a team of scientists from Ethiopia, Uganda, Tanzania, and Mozambique, to gain hands-on experience in breeding insect-resistant maize. “We are now very knowledgeable on mass rearing of stem borers and on running an insectary after our visit and practical sessions at the CIMMYT Katumani Insectary,” added Abiy Dibaba from EIAR’s Melkasa Agricultural Research Center. “At the CIMMYT Kiboko Postharvest Lab, we learned a lot about maize weevils and the larger grain borer, and how to screen maize for resistance against these postharvest pests.”
“The trip was an eye opener for me. We have no mass rearing facility in Ethiopia; neither do we practice artificial infestation of stem borers. We only undertake natural infestation for our trials, which does not give uniform infestation, leading us to wrong conclusions,” said Midekssa Ardessa from Bako Agricultural Research Center at the Ethiopian Institute of Agricultural Research (EIAR), who visited CIMMYT-Kenya during 21-27 July 2013 with a team of scientists from Ethiopia, Uganda, Tanzania, and Mozambique, to gain hands-on experience in breeding insect-resistant maize. “We are now very knowledgeable on mass rearing of stem borers and on running an insectary after our visit and practical sessions at the CIMMYT Katumani Insectary,” added Abiy Dibaba from EIAR’s Melkasa Agricultural Research Center. “At the CIMMYT Kiboko Postharvest Lab, we learned a lot about maize weevils and the larger grain borer, and how to screen maize for resistance against these postharvest pests.” The annual IRMA project’s program has trained more than 50 scientists since its inception in 2009. “Most of us talk very easily and confidently about insect rearing. However, it is quite a challenge when we engage in the practical aspects,” said Tefera. “What we have exposed you to is just a tip of the iceberg in the business of mass rearing of insects. There is still a lot to learn, much of it by yourself as you engage in the practical aspects of it.” The participants appreciated the effort taken by the organizers. One of them, Egas Nhamucho of IIAM, said: “Infestation of maize with stem borers was a real learning point for me, a real delicate task of picking out very tiny 10 insect larvae, ensuring that you do not pierce and kill them with the camel brush, and carefully and strategically placing them on each maize plant. The practical sessions really made me appreciate some of the tasks we have always taken for granted.”
The annual IRMA project’s program has trained more than 50 scientists since its inception in 2009. “Most of us talk very easily and confidently about insect rearing. However, it is quite a challenge when we engage in the practical aspects,” said Tefera. “What we have exposed you to is just a tip of the iceberg in the business of mass rearing of insects. There is still a lot to learn, much of it by yourself as you engage in the practical aspects of it.” The participants appreciated the effort taken by the organizers. One of them, Egas Nhamucho of IIAM, said: “Infestation of maize with stem borers was a real learning point for me, a real delicate task of picking out very tiny 10 insect larvae, ensuring that you do not pierce and kill them with the camel brush, and carefully and strategically placing them on each maize plant. The practical sessions really made me appreciate some of the tasks we have always taken for granted.”
 Scientists from the Heat Stress Tolerant Maize for Asia (HTMA) project and representatives from collaborating public and private sector institutions from the region,
Scientists from the Heat Stress Tolerant Maize for Asia (HTMA) project and representatives from collaborating public and private sector institutions from the region,