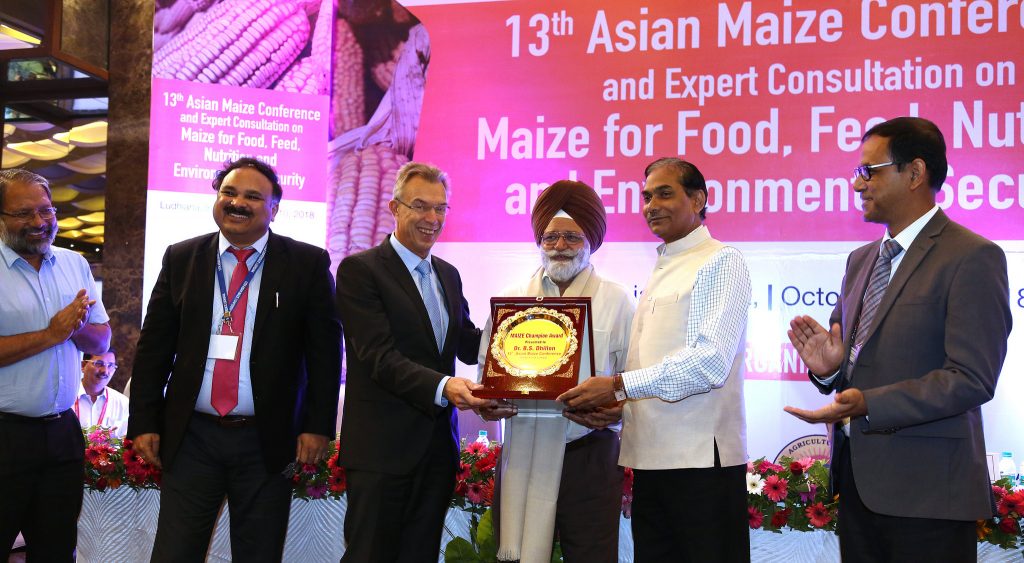
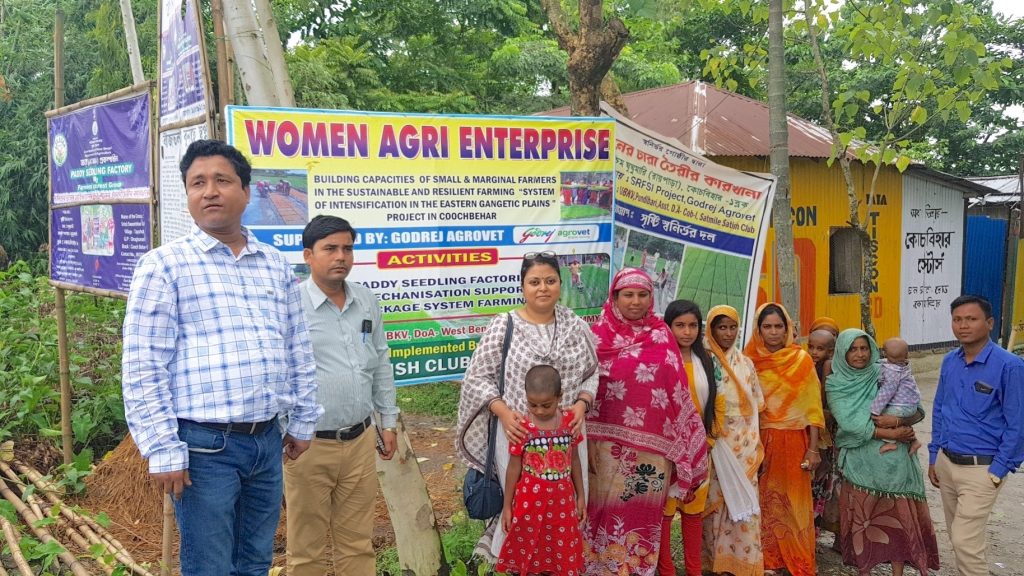
International experts discuss progress and challenges of maize research and development in Asia
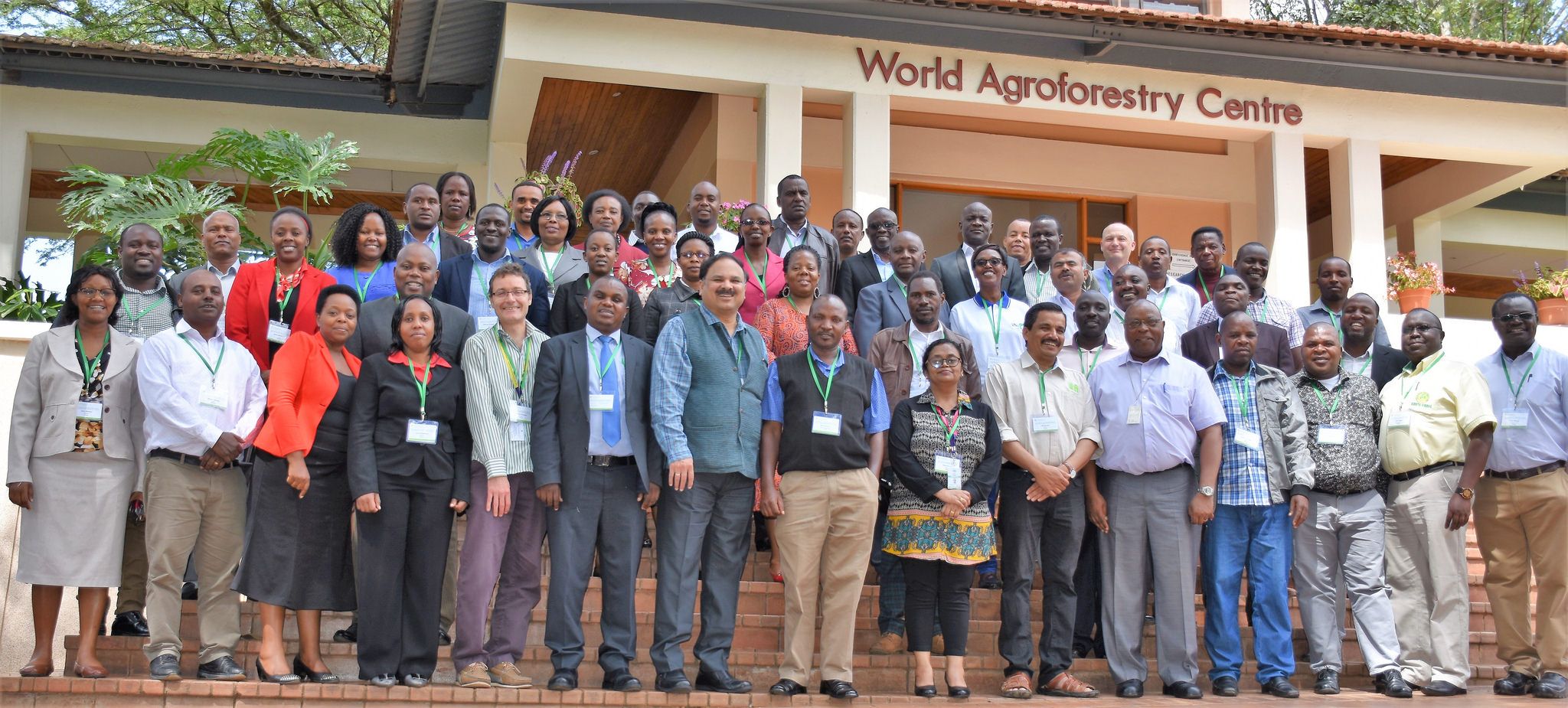
The importance of maize in Asian cropping systems has grown rapidly in recent years, with several countries registering impressive growth rates in maize production and productivity. However, increasing and competing demands — food, feed, and industry — highlight the continued need to invest in maize research for development in the region. Maize experts from around the world gathered to discuss these challenges and how to solve them at the 13th Asian Maize Conference and Expert Consultation on Maize for Food, Feed, Nutrition and Environmental Security, held from October 8 to 10, 2018, in Ludhiana, Punjab, India.
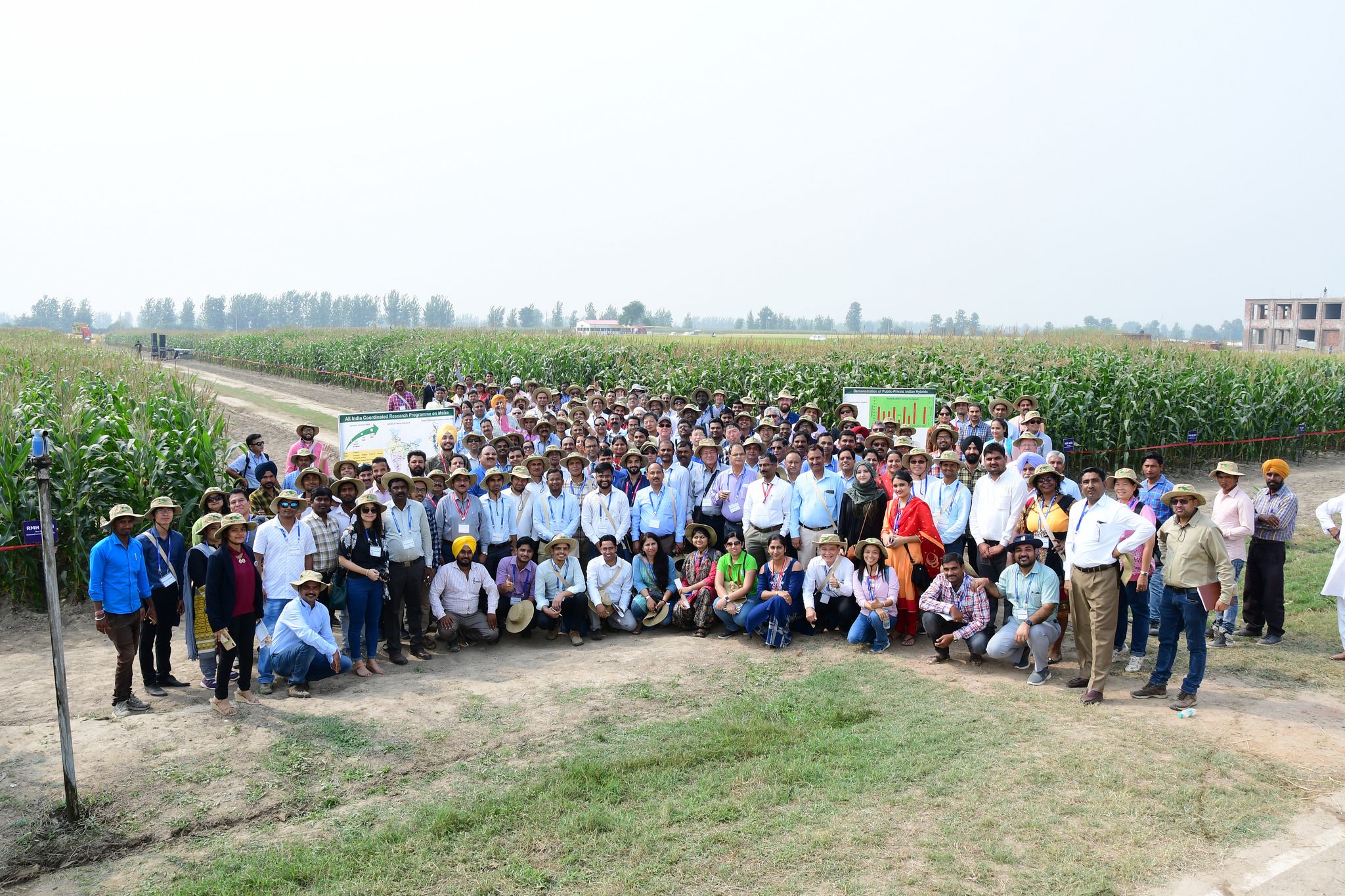
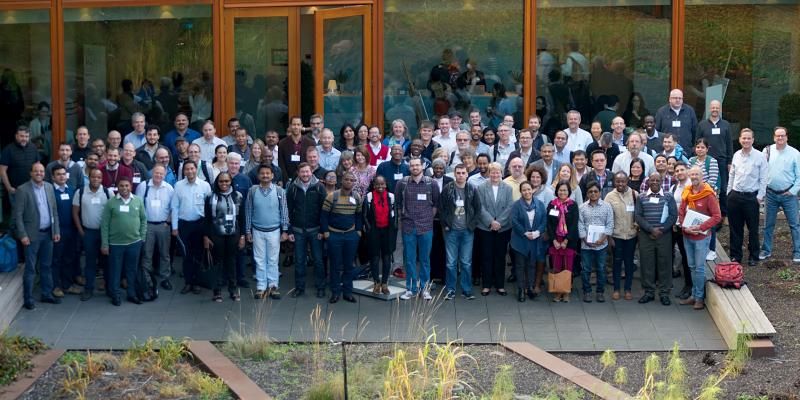
More than 280 delegates from 20 countries attended the conference. Technical sessions and panel discussions covered diverse topics such as novel tools and strategies for increasing genetic gains, stress-resilient maize, sustainable intensification of maize-based cropping systems, specialty maize, processing and value addition, and nutritionally enriched maize for Asia.
The international conference was jointly organized by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), the Indian Institute of Maize Research (ICAR-IIMR), Punjab Agricultural University (PAU), the CGIAR Research Program on Maize (MAIZE), and the Borlaug Institute for South Asia (BISA).
In Asia, maize is rapidly growing in its importance, due to high demand. Maize productivity in the region is growing by 5.2 percent annually compared to a global average of 3.5 percent. However, this is not enough. “Asia produces nearly 80 million tons of maize annually, but demand will be double by the year 2050,” said Martin Kropff, CIMMYT director general, in his opening address at the conference. “We need to produce two times more maize in Asia, using two times less inputs, including water and nutrients. Climatic extremes and variability, especially in South and South East Asia, will make this challenge more difficult. Continued funding for maize research is crucial. We need to work together to ensure that appropriate innovations reach the smallholder farmers.”
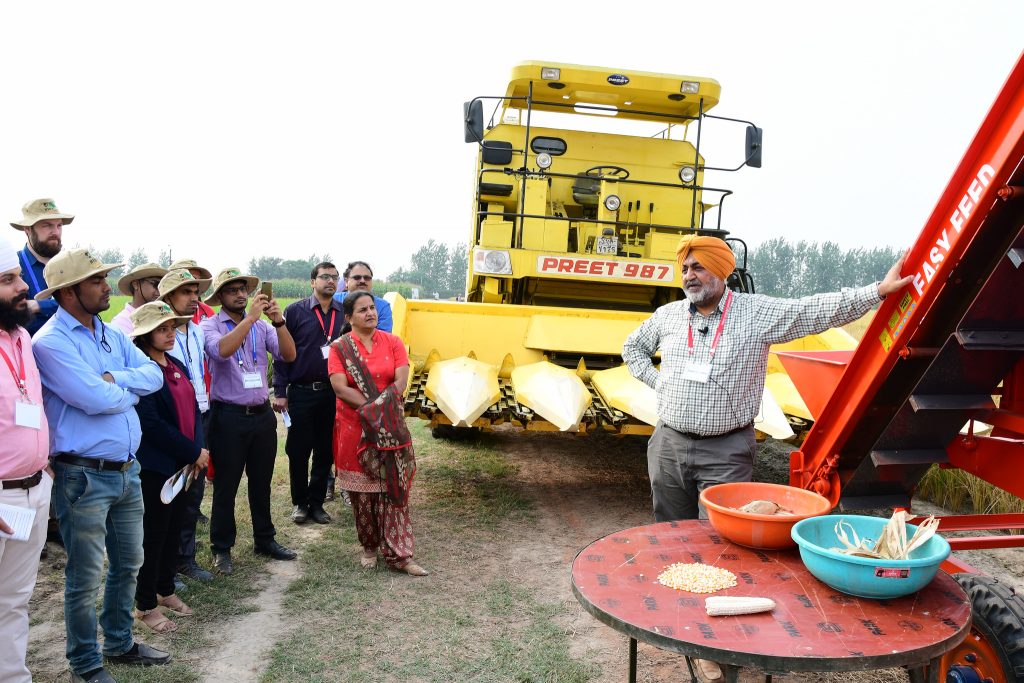

Climate-resilient maize and sustainable intensification
A major theme emphasized at the conference was climate resilience in maize-based systems. South Asia is a hotspot for vulnerability due to climate change and climate variability, which poses great risks to smallholder farmers. “Climate resilience cannot be brought by only a single technology — it has to be through a judicious mix of several approaches,” said B.M. Prasanna, director of CIMMYT’s Global Maize Program and the CGIAR Research Program on Maize.
Great advances have been made in developing climate-resilient maize for Asia since the last Asian Maize Conference, held in 2014. Many new heat- and drought-tolerant maize varieties have been developed through various projects, such as the Heat Stress Tolerant Maize for Asia (HTMA), and Affordable, Accessible, Asian (AAA) maize projects. Through the HTMA project, over 50 CIMMYT-derived elite heat-tolerant maize hybrids have been licensed to public and private sector partners in Asia during the last three years, and nine heat-tolerant maize hybrids have been released so far in Bangladesh, India and Nepal.
Sustainable intensification of maize-based farming systems has also helped farmers to increase yields while reducing environmental impact, through conservation agriculture and scale-appropriate mechanization. Simple technologies are now available to reduce harvest time by up to 80 percent and hired labor costs by up to 60 percent. Researchers across the region are also working to strengthen the maize value chains.

Science and appropriate technologies
CIMMYT has been focusing on developing and deploying new technologies that can enhance the efficiency of maize breeding programs; these include doubled haploid (DH) technology, high-throughput field-based phenotyping, and genomics-assisted breeding. The conference emphasized on the need for Asian institutions to adapt such new tools and technologies in maize breeding programs.
Another topic of interest was the fall armyworm, an invasive insect pest that has spread through 44 countries in Africa and was recently reported in India for the first time. “This pest can migrate very quickly and doesn’t require visas and passports like we do. It will travel, and Asian nations need to be prepared,” Prasanna said. “However, there is no need for alarm. We will be looking at lessons learned from other regions and will work together to control this pest.”
In addition to grain for food and feed, specialty maize varieties can provide beneficial economic alternatives for smallholder maize farmers. Conference participants had the opportunity to hear from Indian farmers Kanwal Singh Chauhan and Yugandar Y, who have effectively adopted specialty maize varieties, such as baby corn, sweet corn and popcorn, into life-changing economic opportunities for farming communities. They hope to inspire other farmers in the region to do the same.
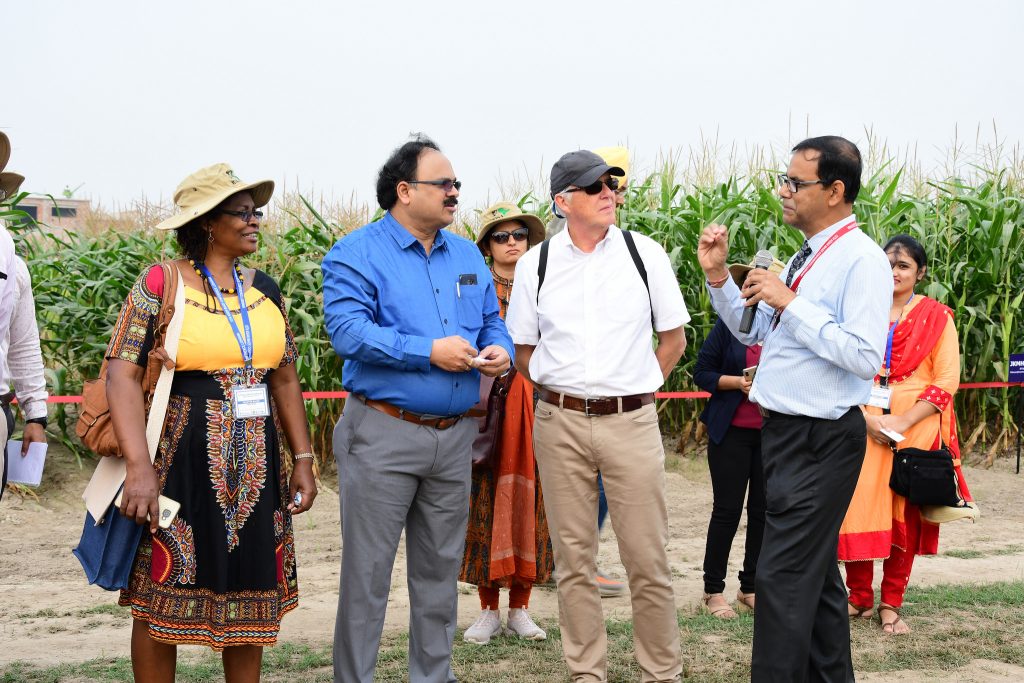
On October 10, conference delegates participated in a maize field day organized at the BISA farm in Ladhowal, Ludhiana. Nearly 100 improved maize varieties developed by CIMMYT, ICAR and public and private sector partners were on display, in addition to scale-appropriate mechanization options, decision support tools, and precision nutrient and water management techniques.
The conference concluded with a ceremony honoring the winners of the 2018 MAIZE-Asia Youth Innovators Award. The awards were launched in collaboration between the CGIAR Research Program on Maize and YPARD (Young Professionals for Agricultural Development) to recognize the contributions of innovative young women and men who can inspire fellow youth to get involved in improving maize-based agri-food systems in Asia. Winners of the first edition of the awards include Dinesh Panday of Nepal, Jie Xu of China, Samjhana Khanal of Nepal, and Vignesh Muthusamy of India.







































 EL BATAN, Mexico (CIMMYT) — Through pure coincidence, Susanne Dreisigacker fell into the world of agricultural science and landed in Mexico. Her interest in genetics and biology solidified when she arrived at the
EL BATAN, Mexico (CIMMYT) — Through pure coincidence, Susanne Dreisigacker fell into the world of agricultural science and landed in Mexico. Her interest in genetics and biology solidified when she arrived at the 

