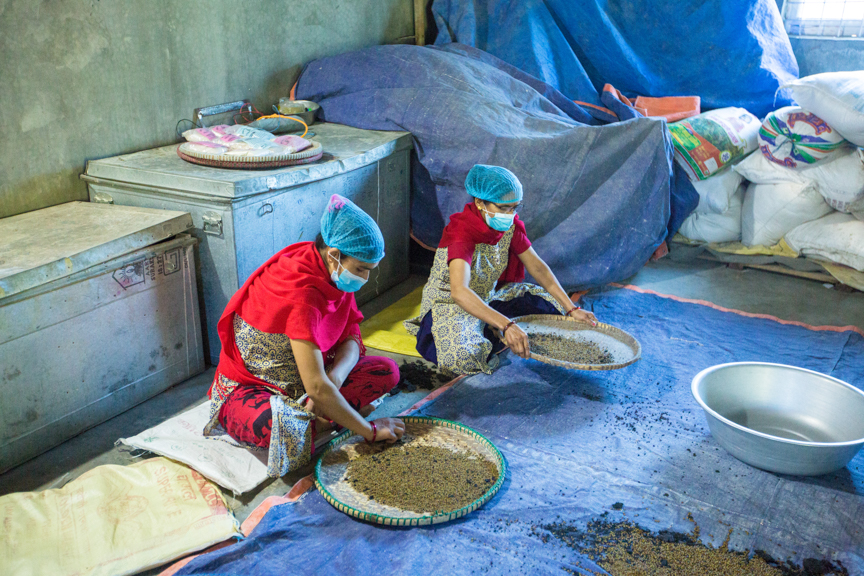
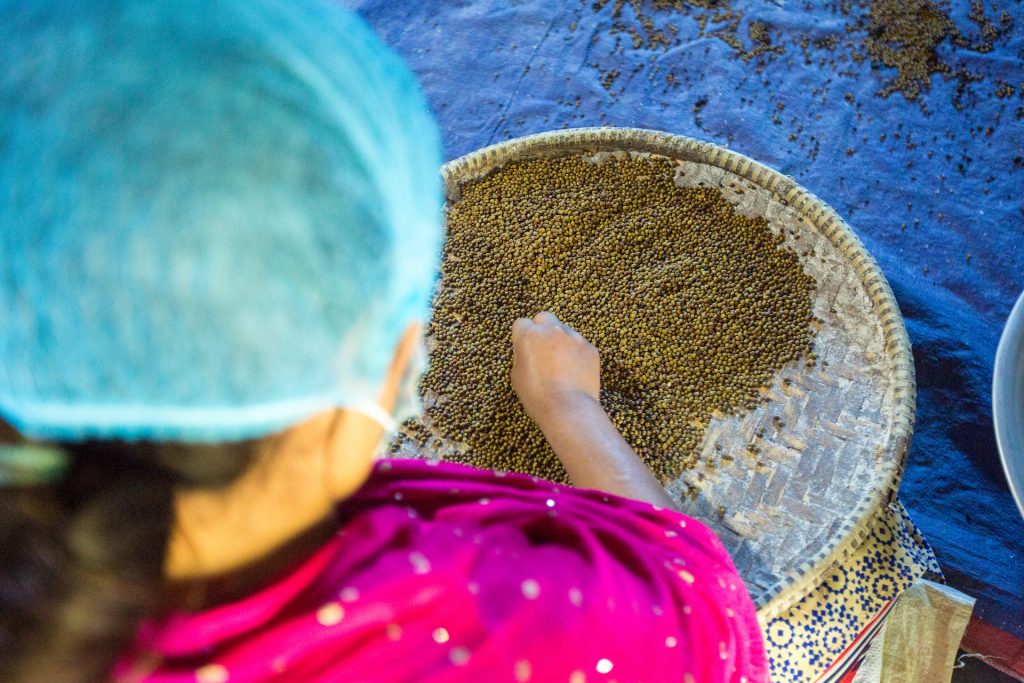
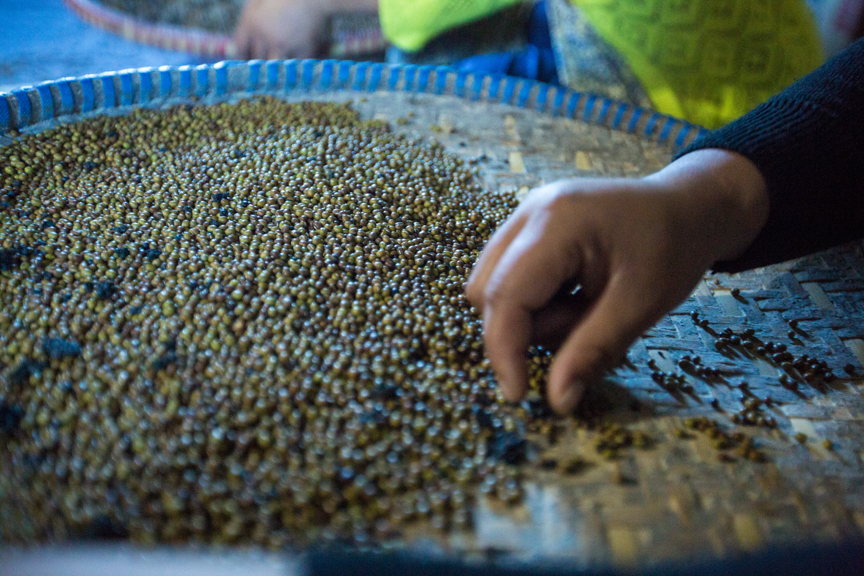
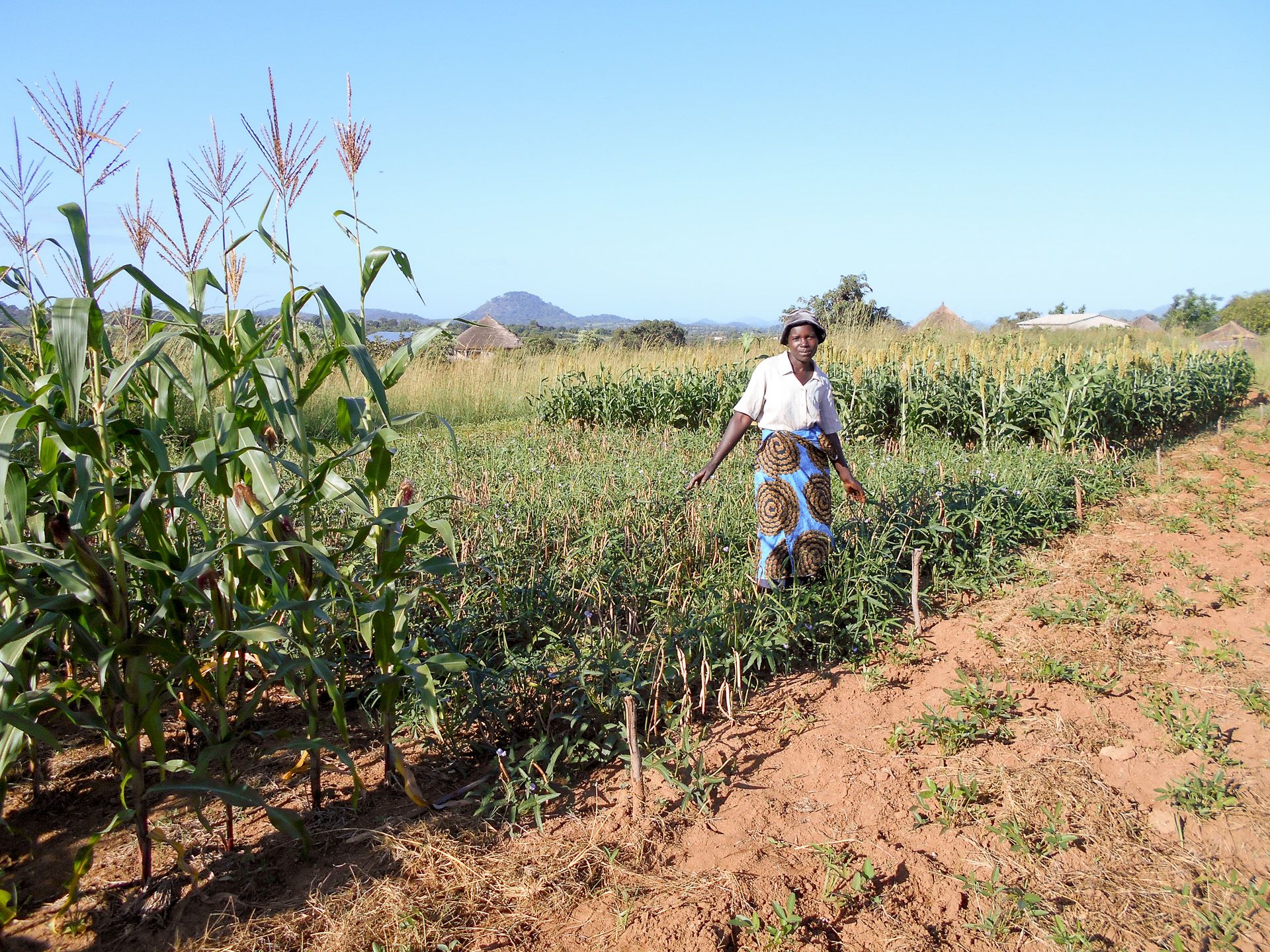
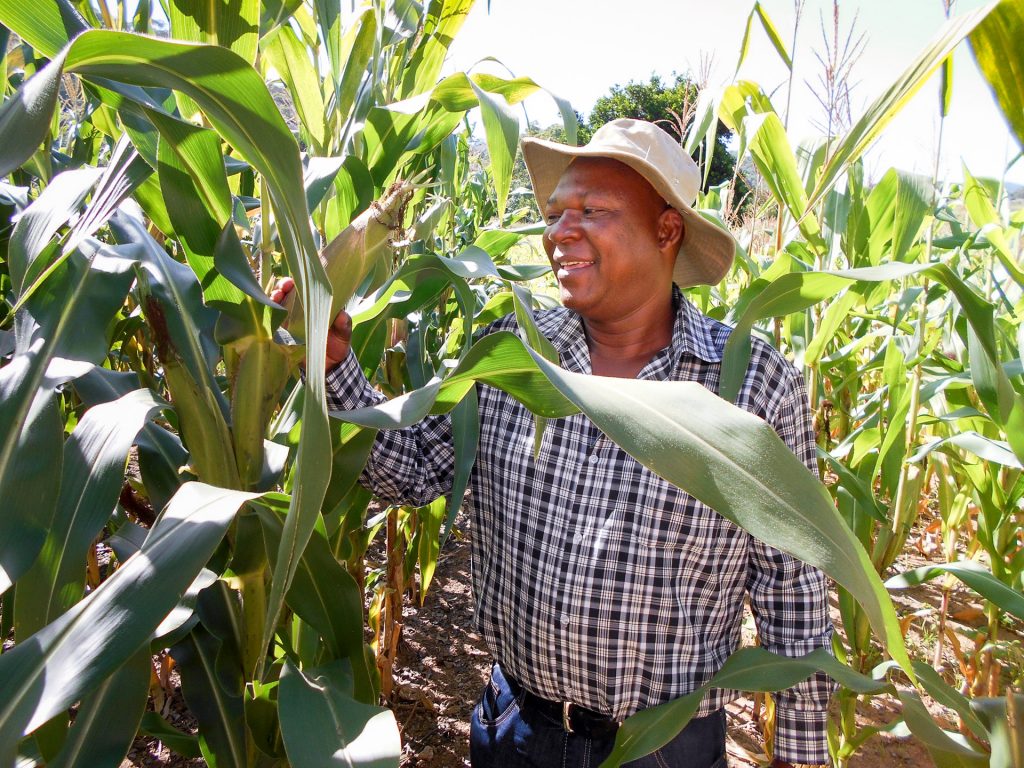
Reaching farmers in the last mile with seeds they can trust
Seed companies play a crucial role in delivering improved seed varieties to smallholder farmers. Masindi Seed Company Limited, located in Uganda’s mid-western region, is one such enterprise.
It traces its beginnings back to the Masindi District Farmers Association (MADFA) more than a decade ago. At the time, the association, which was comprised of about 9,000 farmers, was organized into a seed out-grower scheme of the then government-led Uganda Seed Project.
While its members were well trained, operated professionally and did their out-grower work diligently, the association faced one major challenge that almost broke it up: the ‘certified’ seed they bought from some seed firms could not germinate.
“At the time that we were operating solely as a farmers’ association, we did our best to grow maize seed for various seed companies who would then go on to produce and supply certified seed,” said Eugene Lusige, Masindi Seed general manager. “But we soon realized that a lot of the certified seed that we bought was of very poor quality due to their inability to germinate or because of low germination rates. This caused our farmers huge losses. We instead took this situation as a blessing in disguise, venturing into the certified seed production business based on our experience.”
Such turn of events meant the association had to not only produce the right seed, at the right price, at the right time and with the attributes their farmers desired, but also had to provide an opportunity to generate income for its members. By establishing Masindi Seed Company in 2009, the association members fulfilled their dream and ended up killing several birds with one stone by addressing multiple seed production challenges.
Over the past few decades, the liberalization of the Ugandan seed industry has seen it morph from government control, largely with the support of public sector research institutions, to increased private sector participation. This saw a resurgence in local and foreign-based seed firms involved in seed production, processing and marketing, which significantly contributed to increased delivery of certified seed to farming communities.

Reliable and beneficial partnerships
As one of the enterprises operating in the formal seed market, Masindi Seed has grown from strength to strength over the years, working closely with the National Crops Resources Research Institute (NaCRRI) of the National Agricultural Research Organization (NARO) in Uganda. The Longe 5D, an open pollinated variety (OPV) — an improved version of the Longe 5 — was the first certified seed that ushered them into the seed production and marketing landscape in 2009. The company accessed hybrids and parental materials from NARO, which works very closely with the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) to obtain improved stress tolerant maize.
“Besides the parental materials we receive from CIMMYT through NARO, we are trained on best practices in quality seed production, and receive materials and financial support for some of our operations,” Lusige said.
In the first year, the company produced about 120-150 tons of the Longe 5D variety, which has remained their flagship product over the past decade. Currently, the variety has up to 65 % share of the company’s annual seed production capacity, which stands at about 1,200 tons. The annual capacity is poised to reach 2,400 by 2025 due to growing demand from farmers. The first stress tolerant hybrid, UH5053, was introduced in 2013 and two more hybrids have since gone into commercial production.
“The hybrids have much higher yield than the OPVs and other varieties in the market in this region. They are stress tolerant and some are early maturing,” Lusige said “But, the advantage with the Longe 5D is that it is much cheaper, with a seed packet going for less than its hybrid equivalent. So, it is best suited for the resource-constrained farmers who may not have the funds to buy artificial fertilizer. However, under normal farmer conditions, it yields between 1.5-1.8 tons per acre compared to a hybrid that can produce about 3 tons or more.”
The Longe 5D is also a quality protein maize (QPM) variety, which combats hidden hunger by providing essential amino acids that children and lactating mothers need, according to Godfrey Asea, director of the National Crops Resources Research Institute at NARO.
“One of the initiatives we have been working on is nutritious maize, with some of the OPVs that we have released in the past being QPM varieties,” Asea said. “We are thinking of integrating more nutrient qualities such as vitamin ‘A’ in new varieties, some of which are in the release pipeline. We have also acquired genetic resources that are rich in zinc. QPM varieties, as well as varieties that are biofortified with vitamin A and zinc are very important in improving household nutrition in the future for resource-constrained maize-dependent communities.”
To make farmers aware of available seed and important attributes, marketing and promotional activities through radio, flyers, banners, field days and on-farm demonstrations come in handy. For some newer varieties, the company goes as far as issuing small seed packs to farmers so they can see for themselves how the variety performs.

From a regional outfit to the national stage
In the beginning, growth was slow for Masindi Seed due to capacity and financial constraints to sustain promotional activities. Around 2013 and 2015, the company received support from the Alliance for a Green Revolution in Africa (AGRA) to scale-up its marketing and promotional efforts, which greatly enhanced Masindi Seed’s capacity and visibility. From then on, Masindi Seed went from being just a small regional-focused outfit to a nation-wide seed firm, marketing seed as far as northern and eastern Uganda.
By working closely with farmers, Masindi Seed Company puts itself at a strategic position to understand farmers’ preferred traits better. They have found that farmers prefer traits that allow them to earn more, such as higher yield, which allows them to harvest much more maize and sell the surplus for much-needed income.

Seed that farmers can trust
Alinda Sarah, who doubles up as both a contract farmer for Masindi Seed and a large-scale grower for maize grain, agrees that obtaining the right seed that is guaranteed to germinate and offers a higher yield is a major boost to her trade.
“All I require is seed that I trust to have the attributes I want. What works for me is the seed that offers a higher yield, and can tolerate common stresses including drought, diseases and pests. This way, I can sustain my farming business,” she says.
The second attribute the farmers keep mentioning to Masindi agricultural extensionists is the maturity period, with farmers inclined to prefer faster maturing varieties, such as varieties that mature in 90 days. Ultimately, beyond some of these desirable and beneficial traits, the farmer is, before anything else, interested in the germinability of the seed they buy.
“By confirming the attributes that we tell them regarding our varieties with what they see at demo farms, the farmers trust us more,” Lusige said. “Trust is good for a business like ours and we try our best to preserve it. In the past, we have seen how some companies who lost the trust of their customers quickly went out of business.”
“Besides offering improved seed to farmers, we encourage our partner seed companies to support and teach the farmers good agronomic practices such as proper fertilizer requirements and application rates, early planting, appropriate spacing, weed control, integrated pest management and intercropping with legumes,” said Daniel Bomet, maize breeder at NARO.
Cover photo: Alinda Sarah demostrates how happy she is with the maize cob due for harvest on the farm she owns with her husband in Masindi, mid-western Uganda. (Photo: Joshua Masinde/CIMMYT)