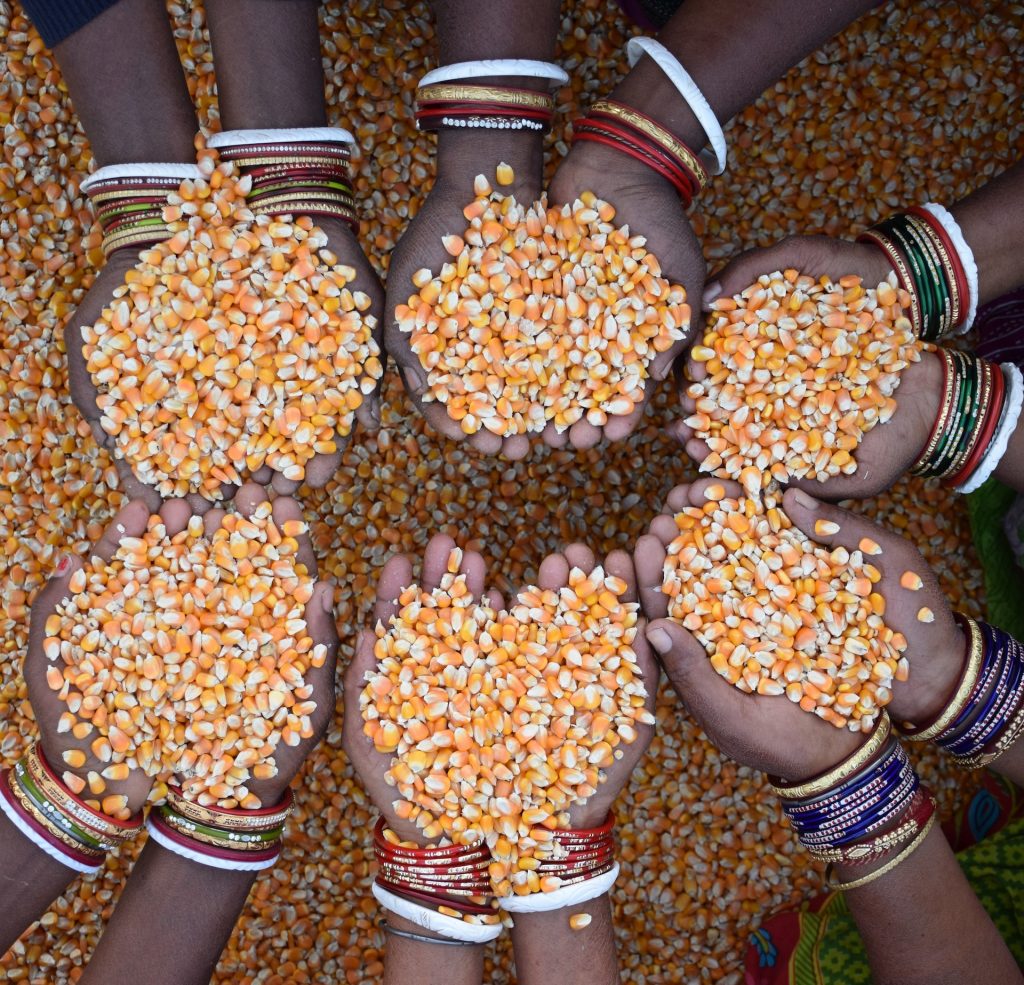The transformative value of maize
The state of Odisha, in the east of India, ranks sixth in rice production in the country. Agriculture in Odisha’s tribal-dominated plateau region, however, is characterized by depleted soils along with low and variable rice yields. During the monsoon season, more than 60,000 hectares of land are left fallow, due to lack of knowledge and to farmers’ low risk tolerance.
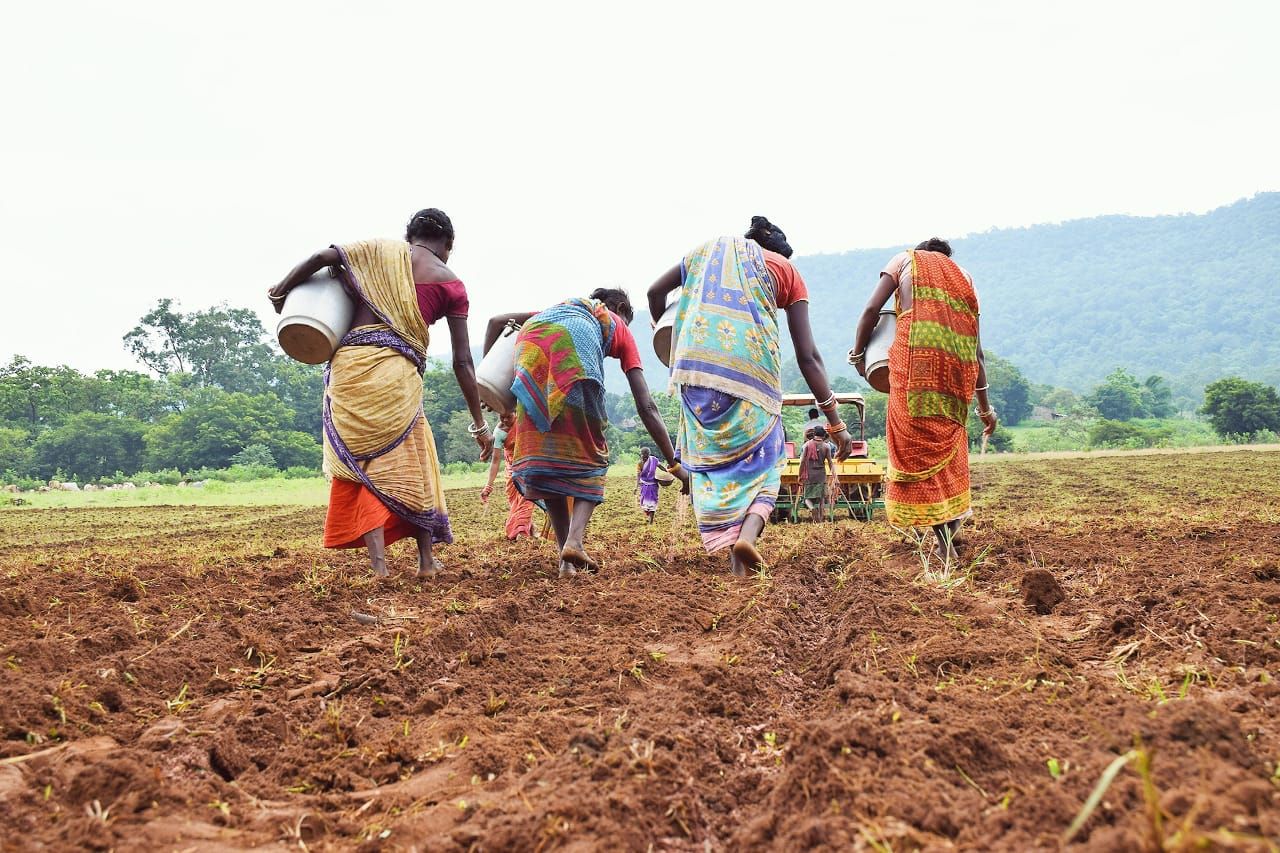
In districts like Mayurbhanj, over 50% of the population belongs to tribal groups. Women there are mostly engaged in traditional roles: being at home looking after family, farm and livestock while their men are away as migrant laborers or with menial jobs. Women working on farming used to be considered daily wage laborers, as if they were only supporting their husband or family who were officially the farmers.
The last few years, with the introduction of maize cultivation and its promotion predominantly for women farmers, a significant change in the perception of women’s role is unfolding in the region.
In 2013, the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) began working in the plateau region through the Cereal Systems Initiative for South Asia (CSISA), improving farming systems for higher yields and providing sustainable livelihood options for tribal farmers. Since then, farmers in the region have achieved considerable production of maize in the monsoon season — and women have particularly led this transformation.
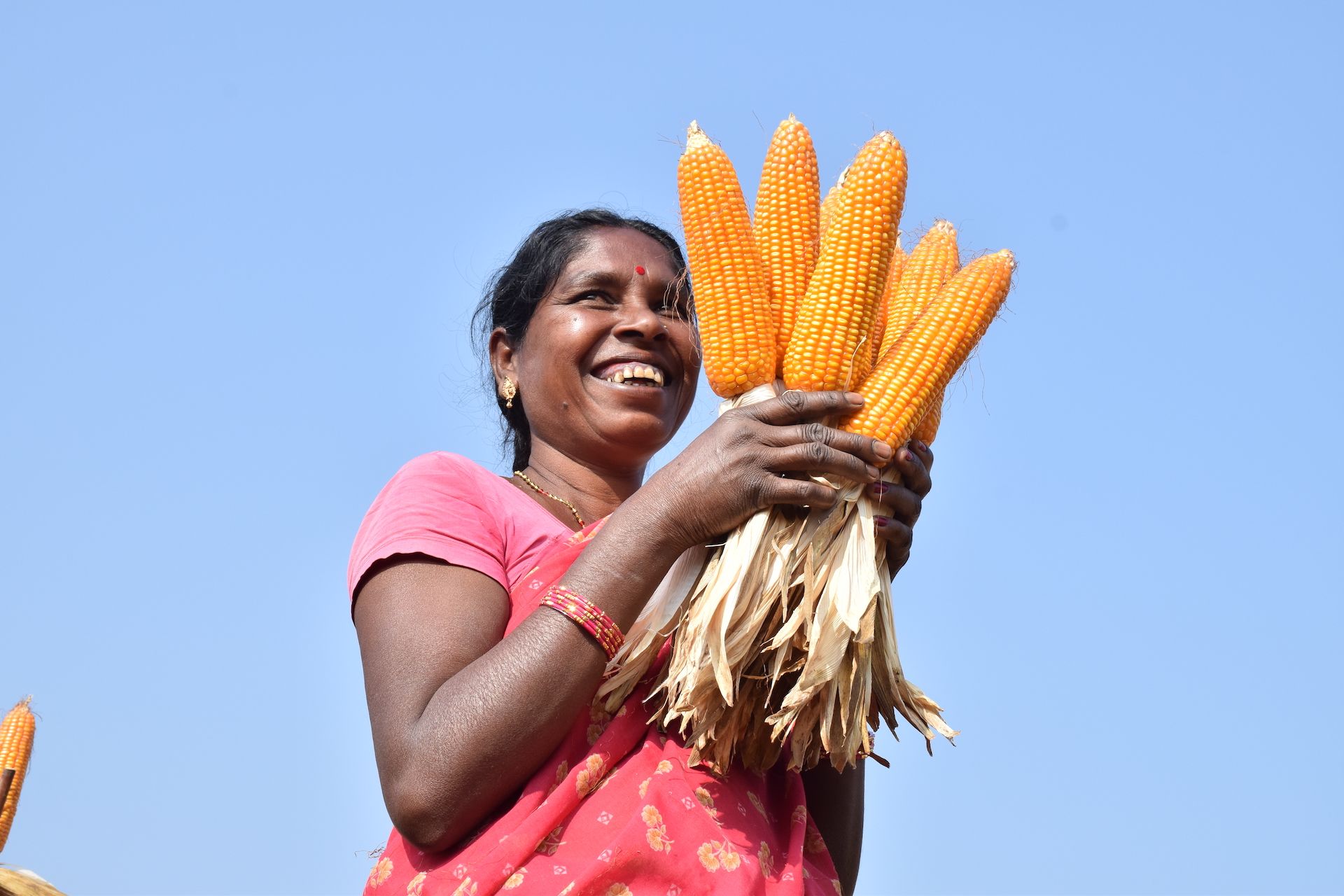
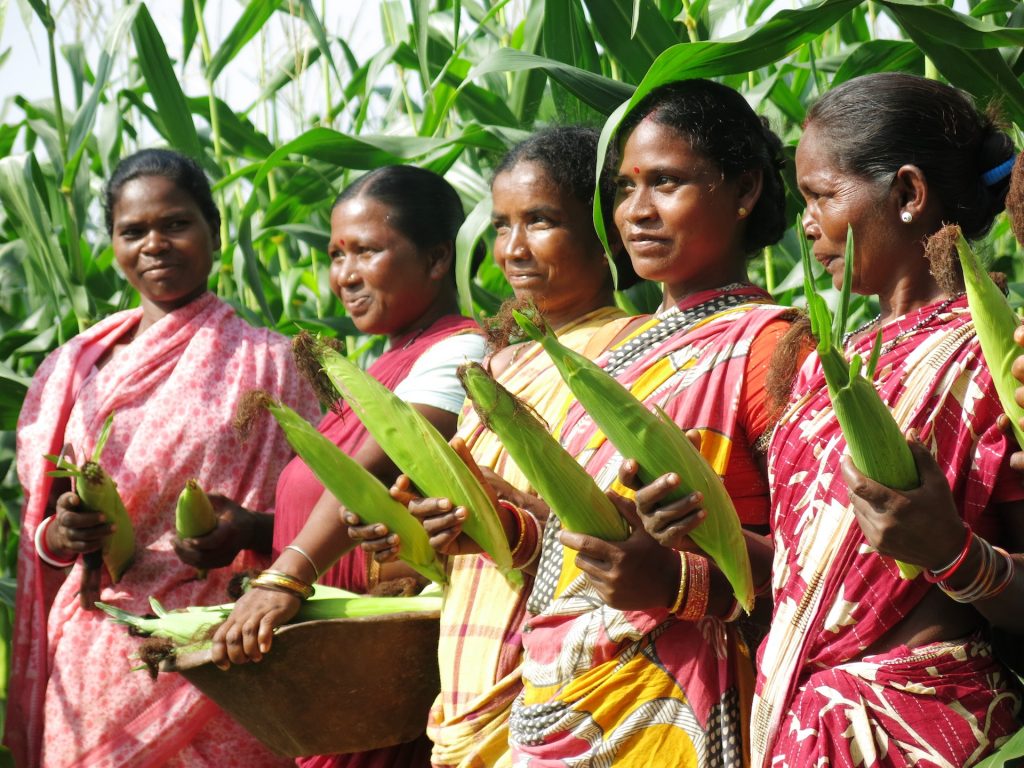
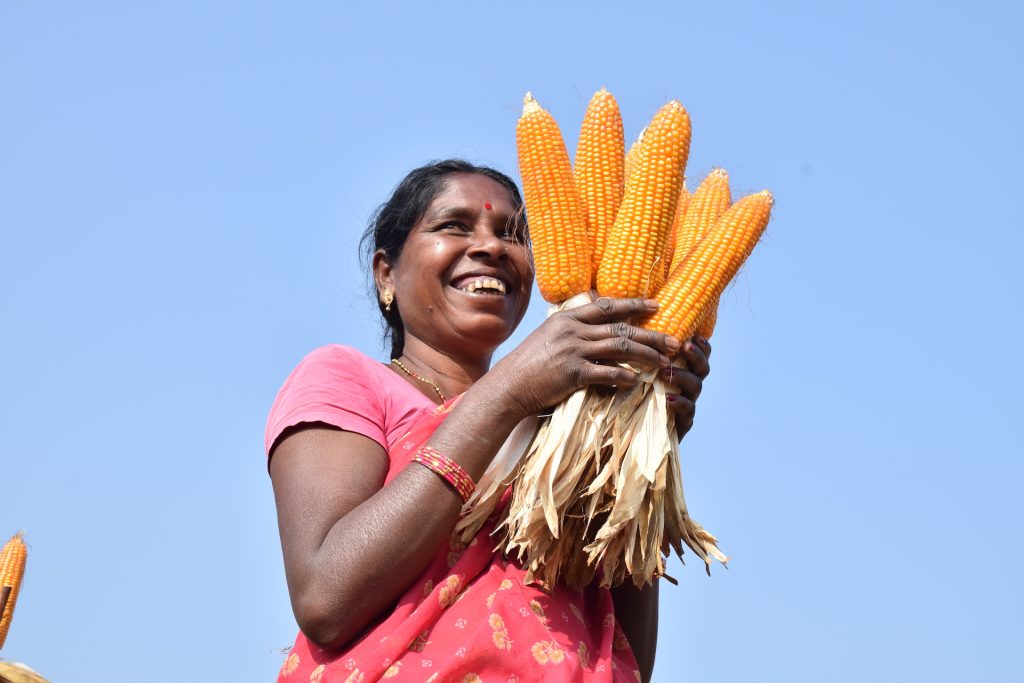
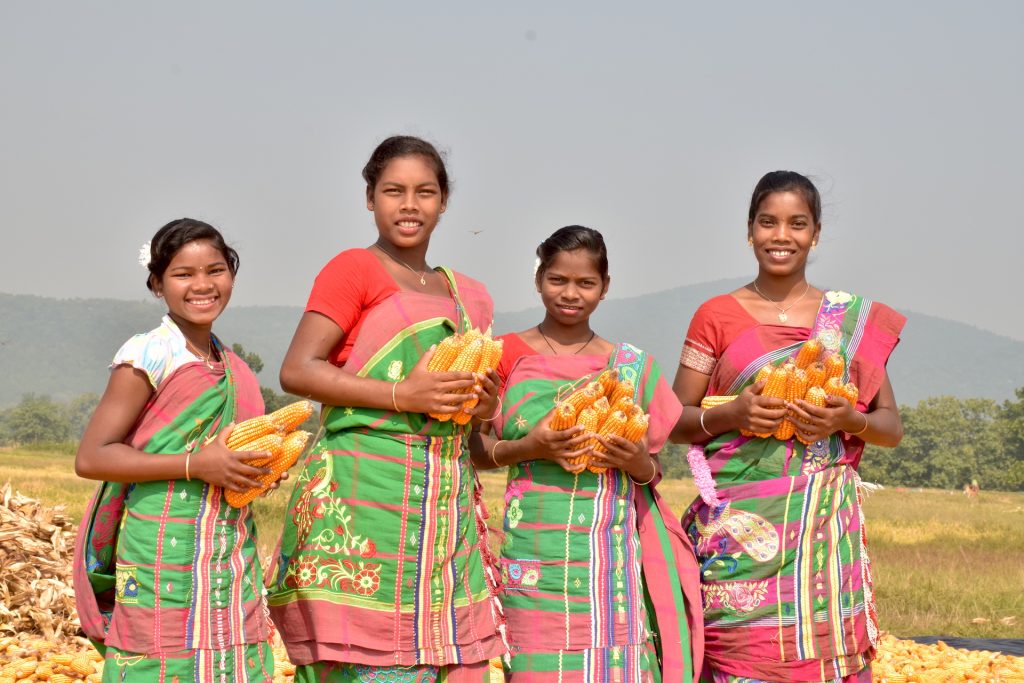
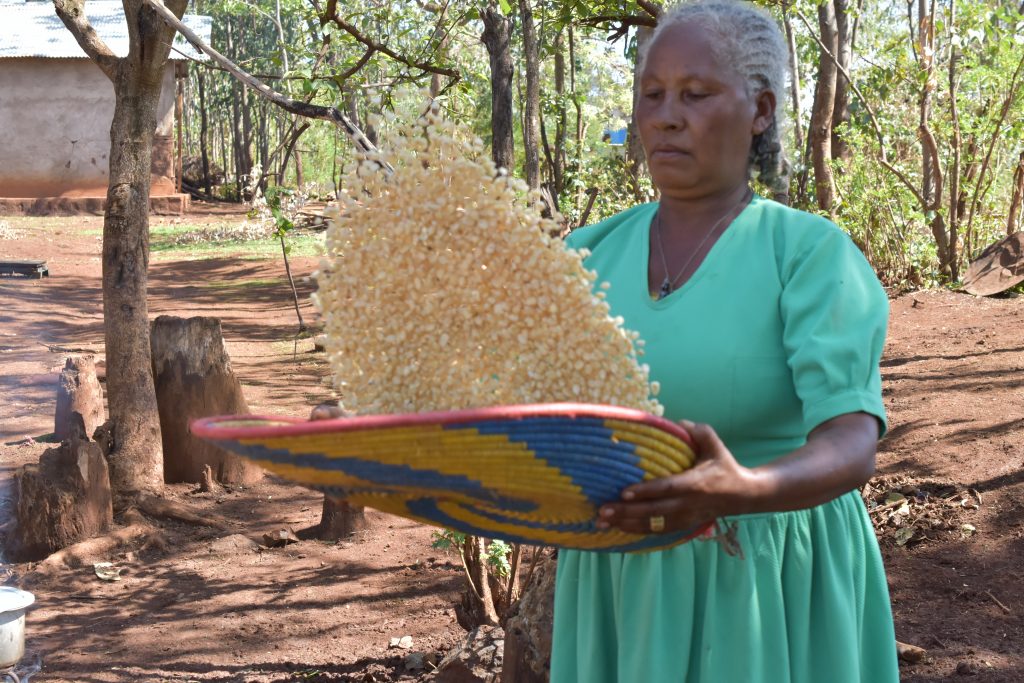
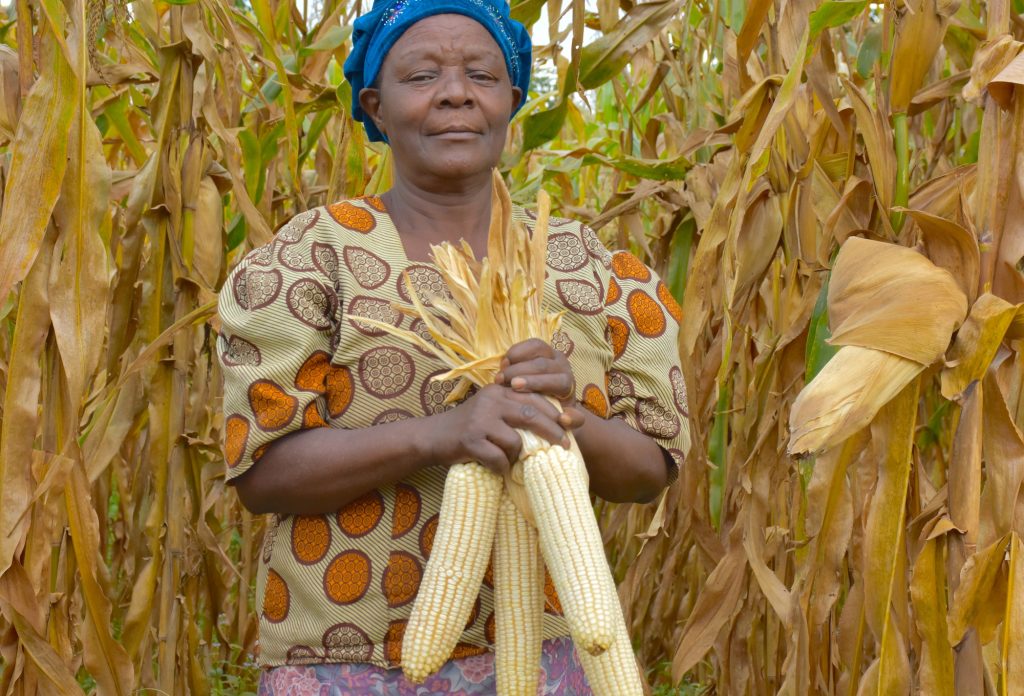
Farmers from this region — 28% of which were women — converted 5,400 hectares of fallow lands into successful maize cultivation areas. Not only has this new opportunity helped improve family income, but also women’s identity as resilient and enterprising farmers.
This impact was possible through the applied research efforts of the CSISA project along with partners like Odisha’s State Department of Agriculture, the Odisha Rural Development and Marketing Society (ORMAS), the Integrated Tribal Development Agency (ITDA) and two federations of women’s self-help groups supported by PRADAN.
On International Women’s Day, we share the story of these successful farmers who have made maize cultivation a part of their livelihoods and a tool for socioeconomic development.
Transforming fallow lands into golden maize fields
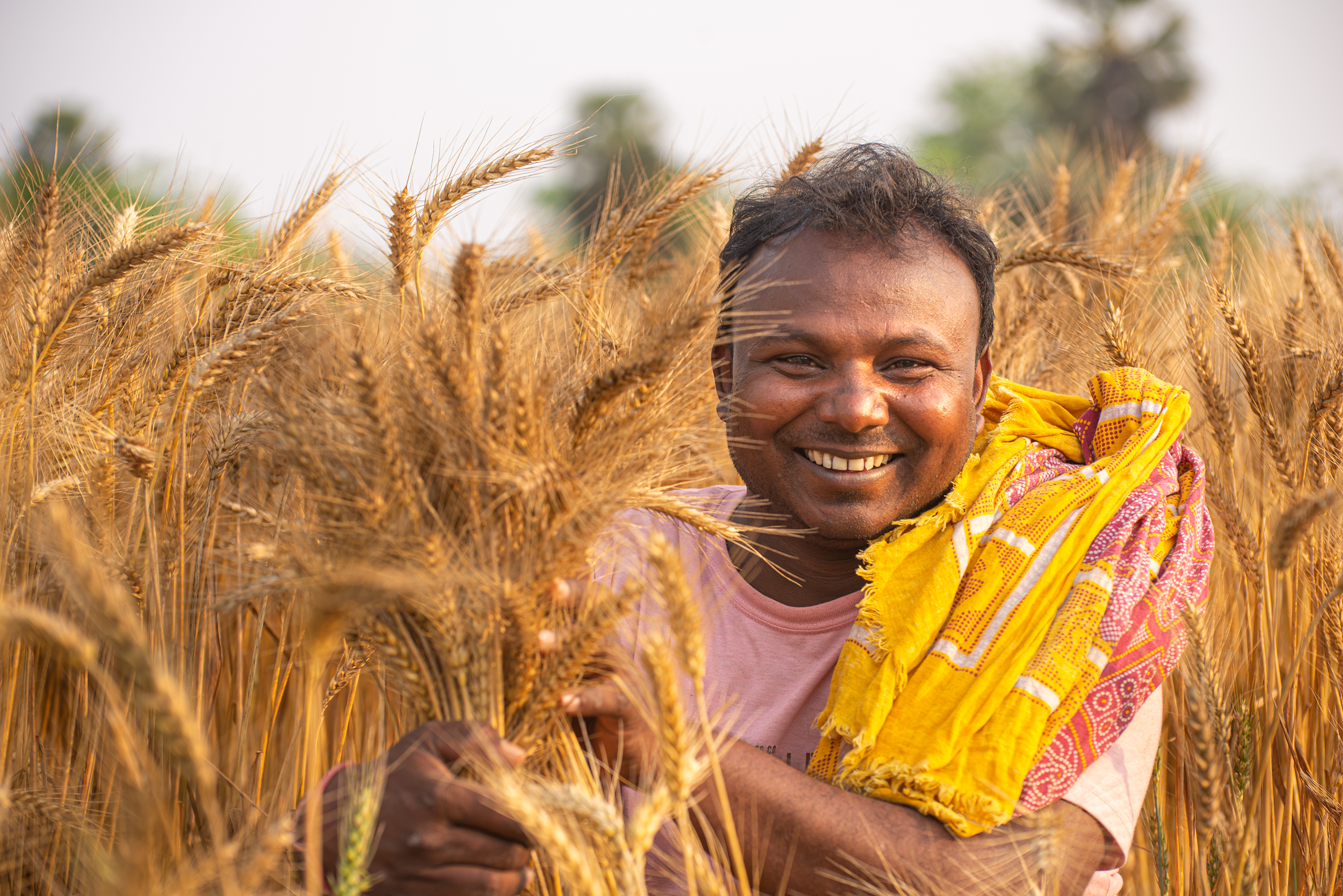
Women working in the fields used to be considered daily wage laborers, but today they are acknowledged as enterprising farmers who transformed fallow lands into golden maize fields.
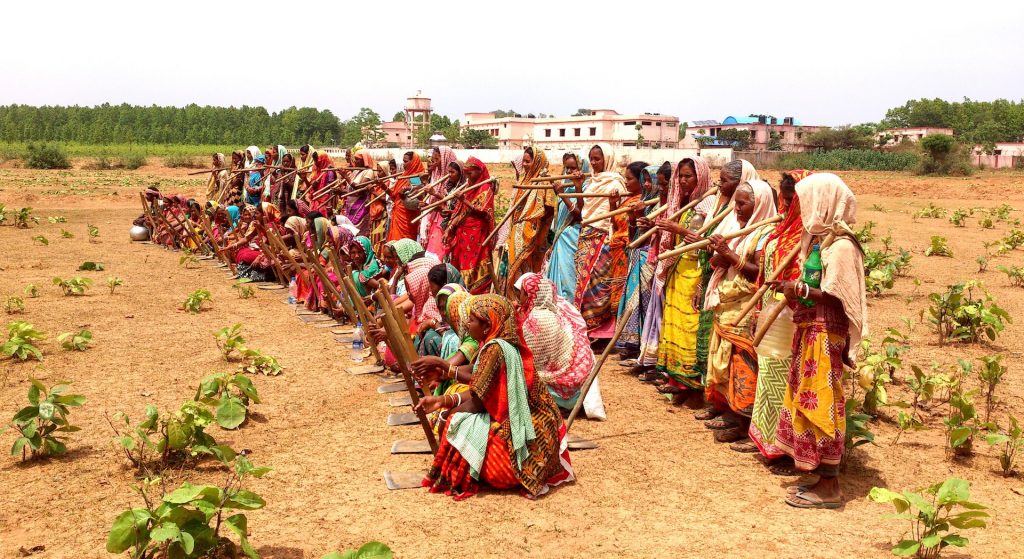
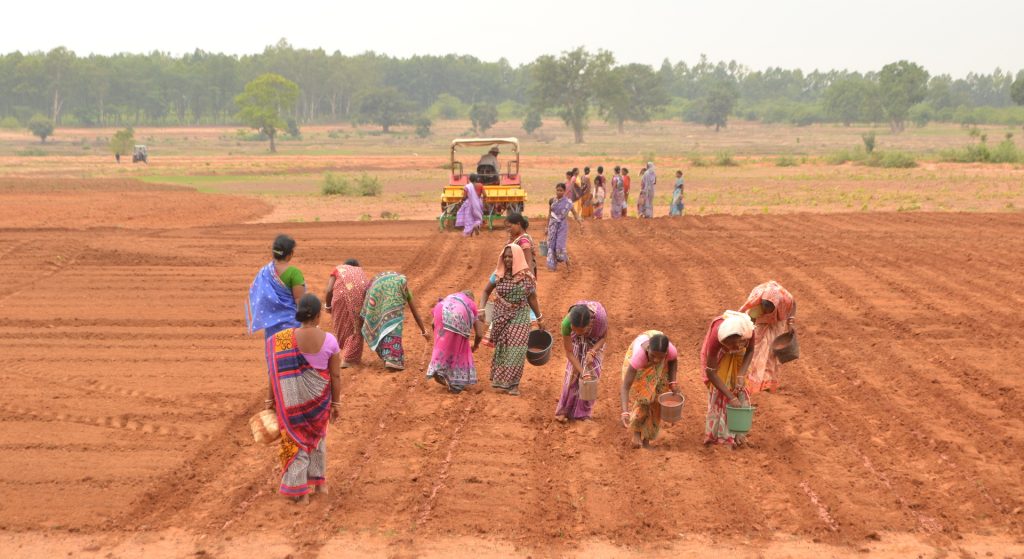
In the season 2019/2020 alone, in all four districts where CSISA is actively engaged — Bolangir, Keonjhar, Mayurbhanj and Nuapada — improved maize cultivation was adopted by 7,600 farmers — 28% of which were women — in 5,400 hectares of fallow land, resulting in considerable production of quality maize in the region. Since many of the women in the districts are smallholder farmers or without agriculture land, farming also happens on leased land through self-help groups.
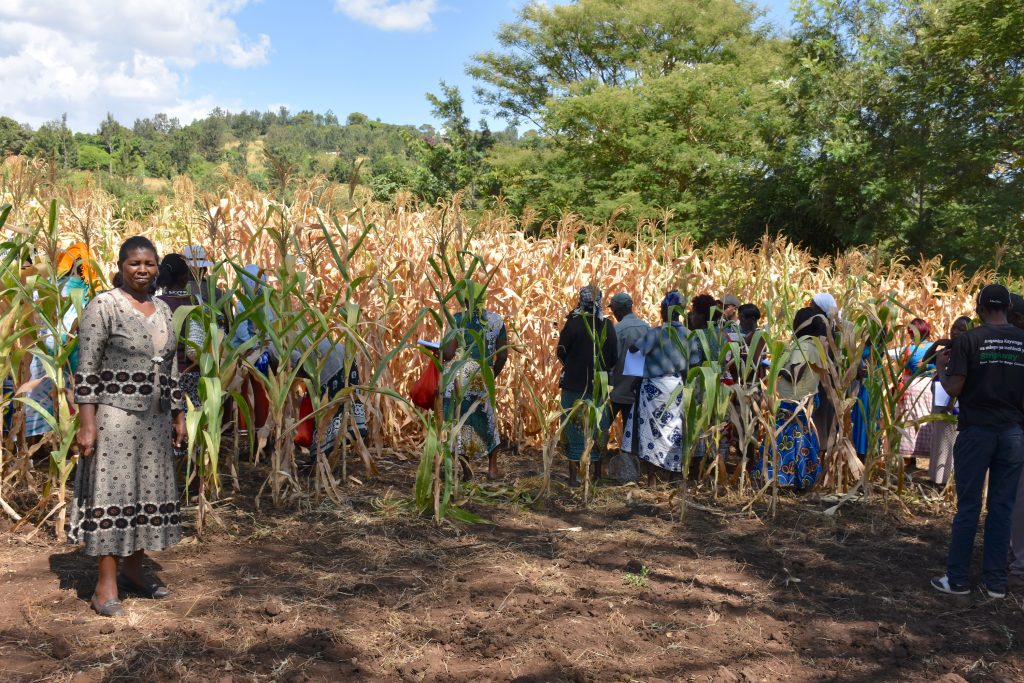
Learning and implementing best maize cultivation practices
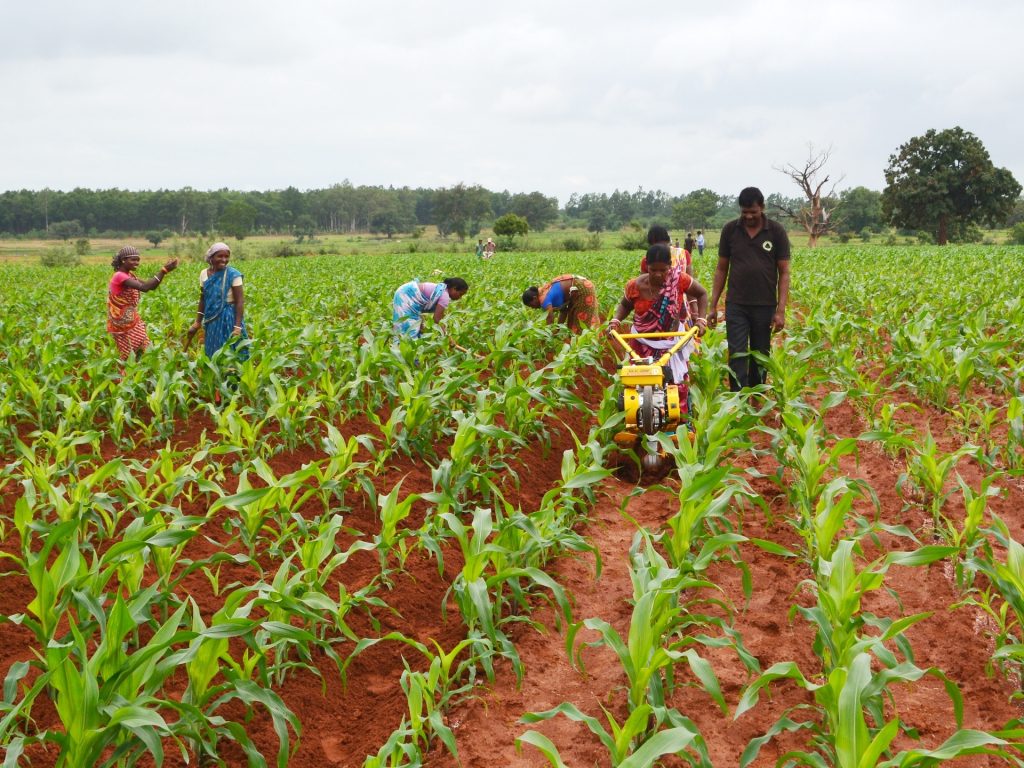
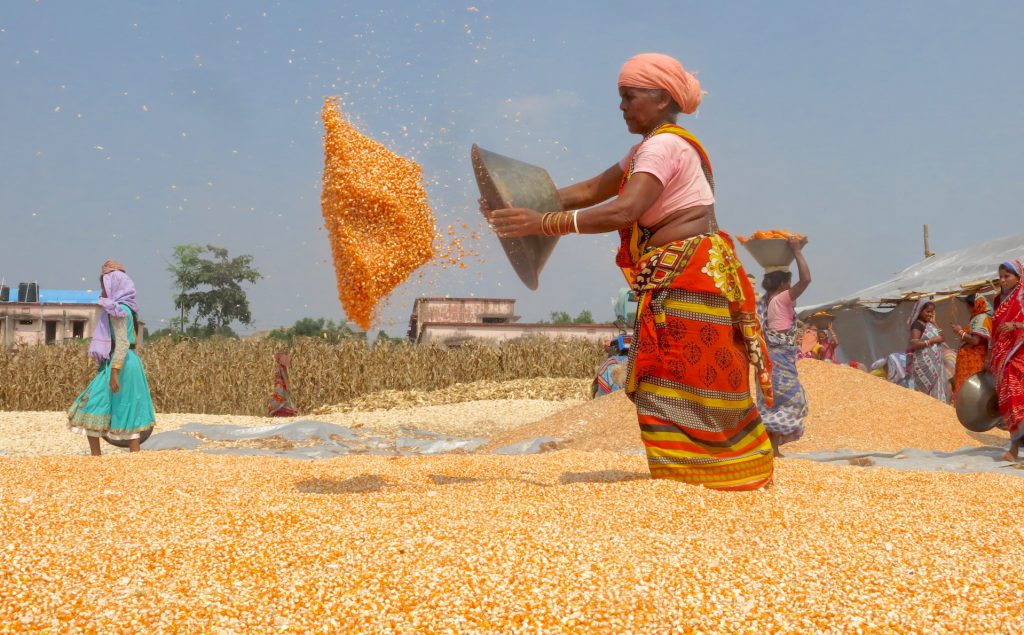
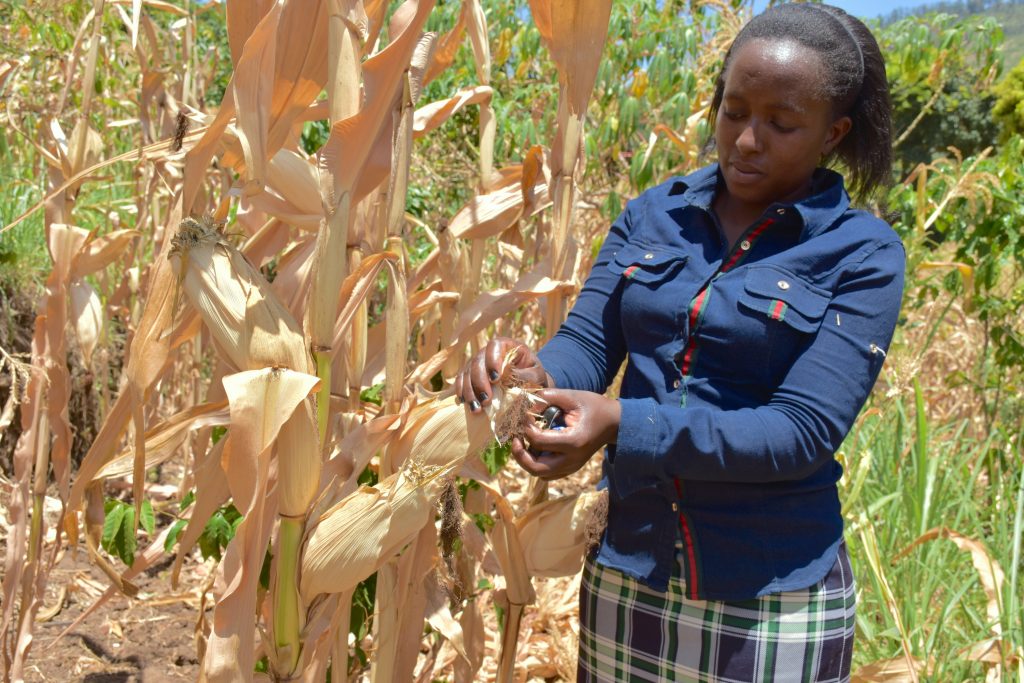
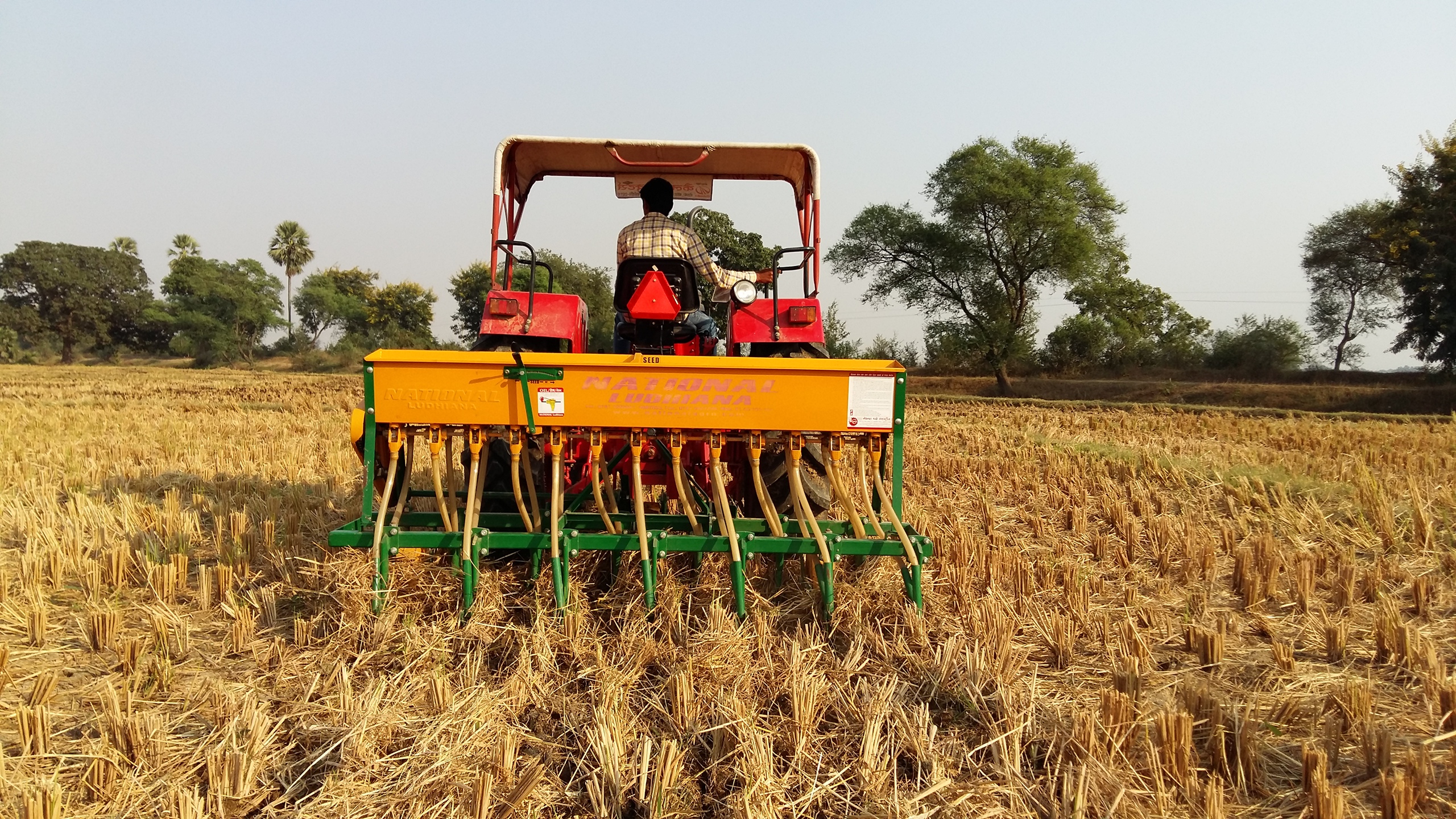
CSISA supports the farmers all the way from sowing to crop harvesting, ensuring the produce is shiny and golden. Through self-help groups, farmers have access to fertilizers and machines to weed and earth-up their fields. Researchers have introduced seed cum fertilizer drills for maize sowing, which make fertilizer placement more uniform and crop establishment easier, saving time and helping these women manage both household responsibilities and the farm.
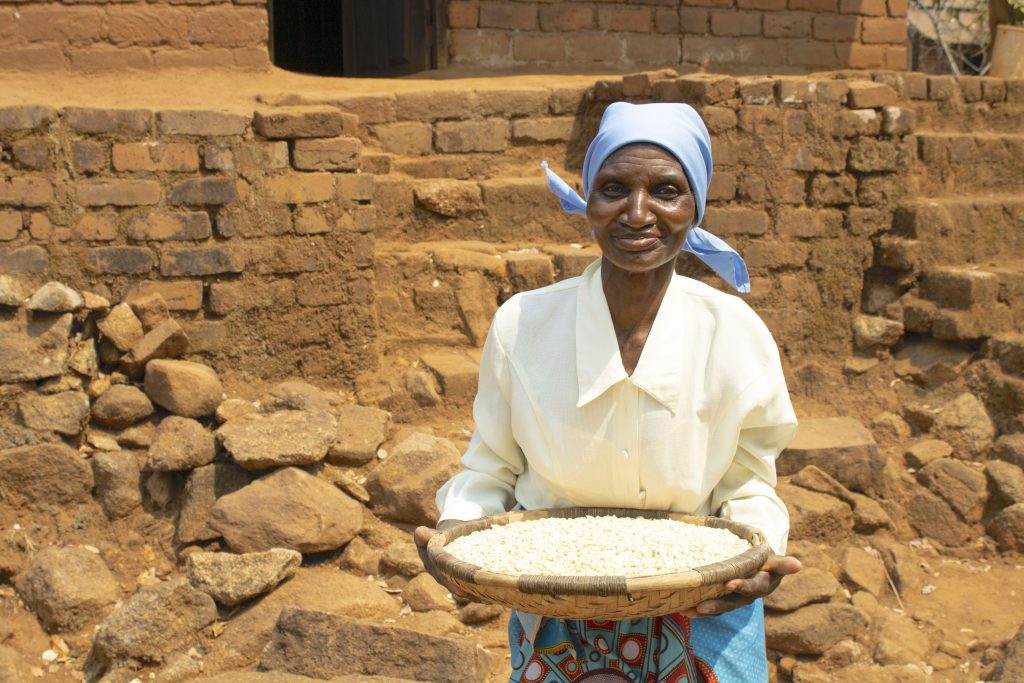
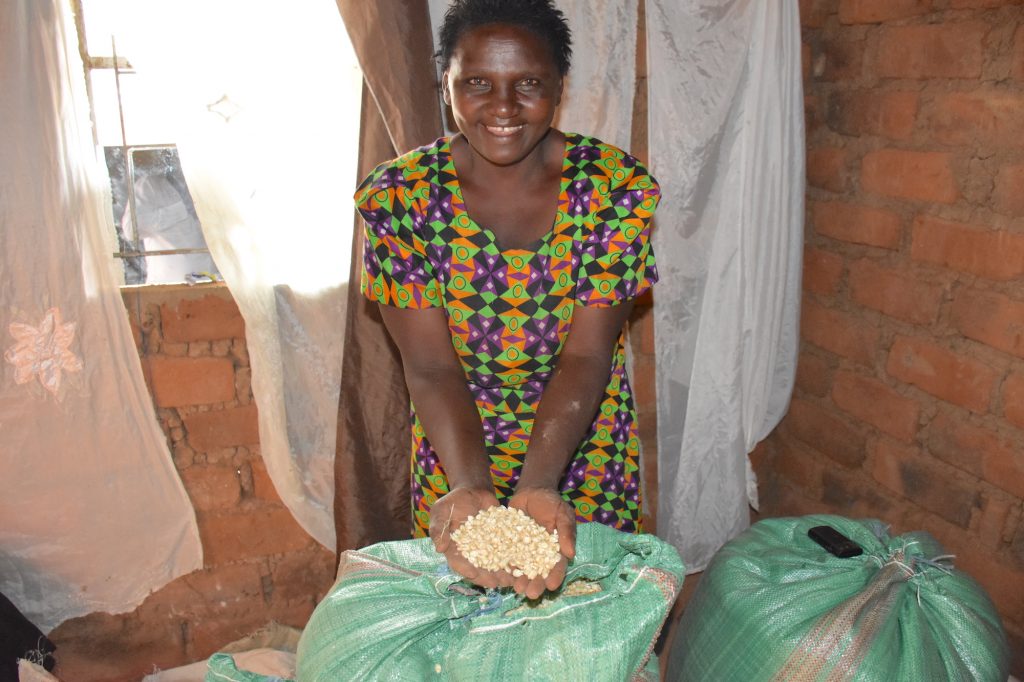
Quality knowledge for quality grain
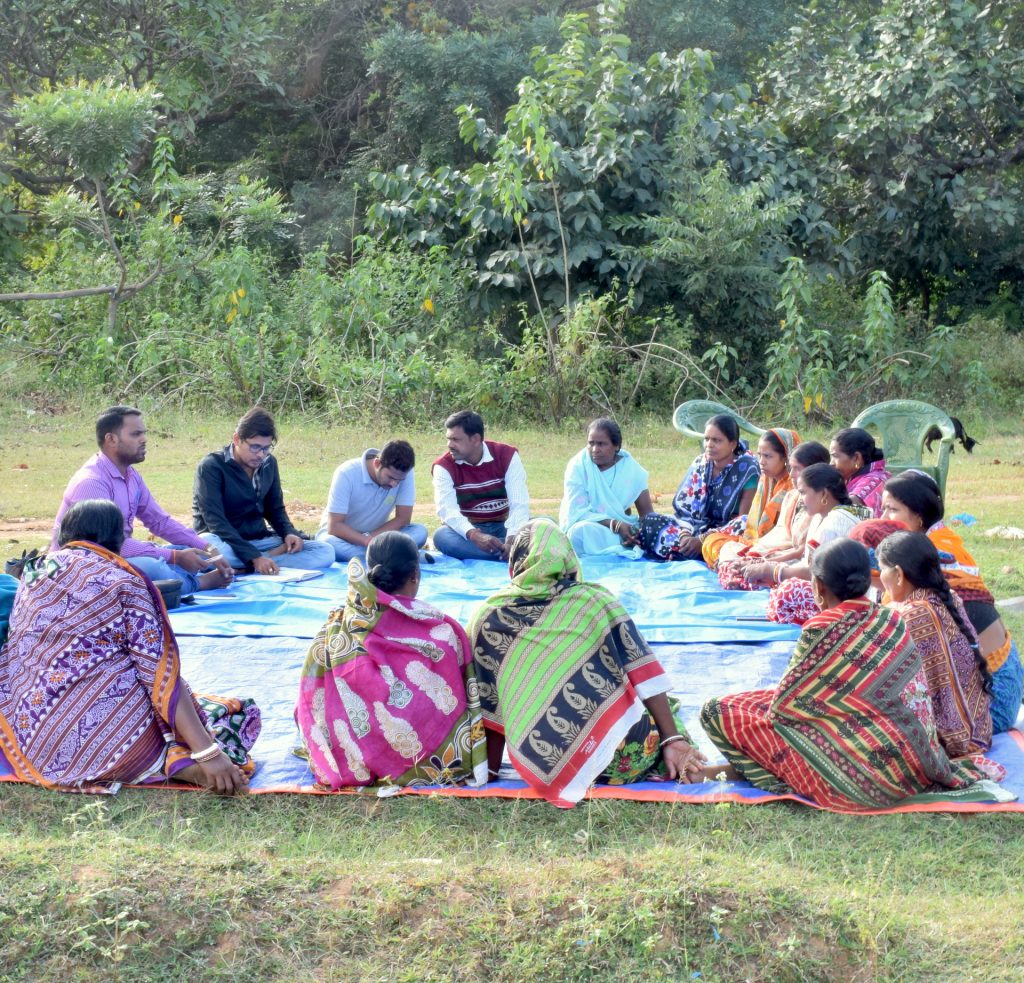
To strengthen the capacity of farmers, the project team trains them continuously on grain quality parameters like moisture level, foreign matters, infestation rate. Most of the participants are farmers from women collectives and self-help groups. They have gradually advanced in their knowledge journey, going from general awareness to subject-specific training.
Marketing gurus
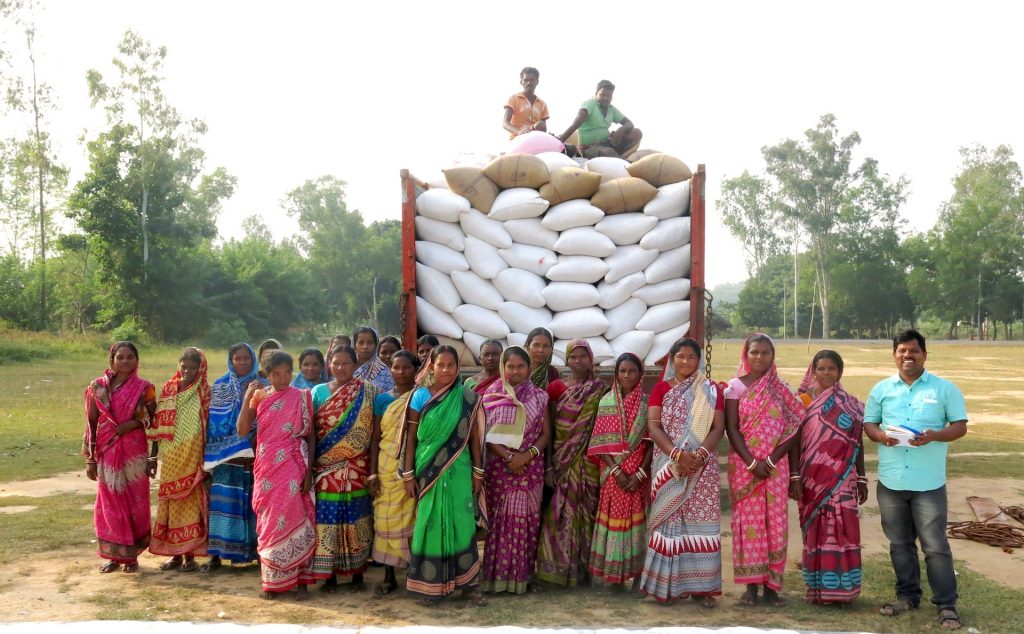
Even though many large poultry feed mills operate in Odisha, most of their maize comes from outside the state. Women self-help groups are bridging that gap. In collaboration with the State Department of Agriculture and Farmers’ Empowerment, the CSISA project has cultivated a network of market actors including producers, providers of agricultural inputs and development partners. Market access to these value chains will help women, all the way from planting to produce marketing.
Extending the collaboration, in the four districts of Odisha and beyond
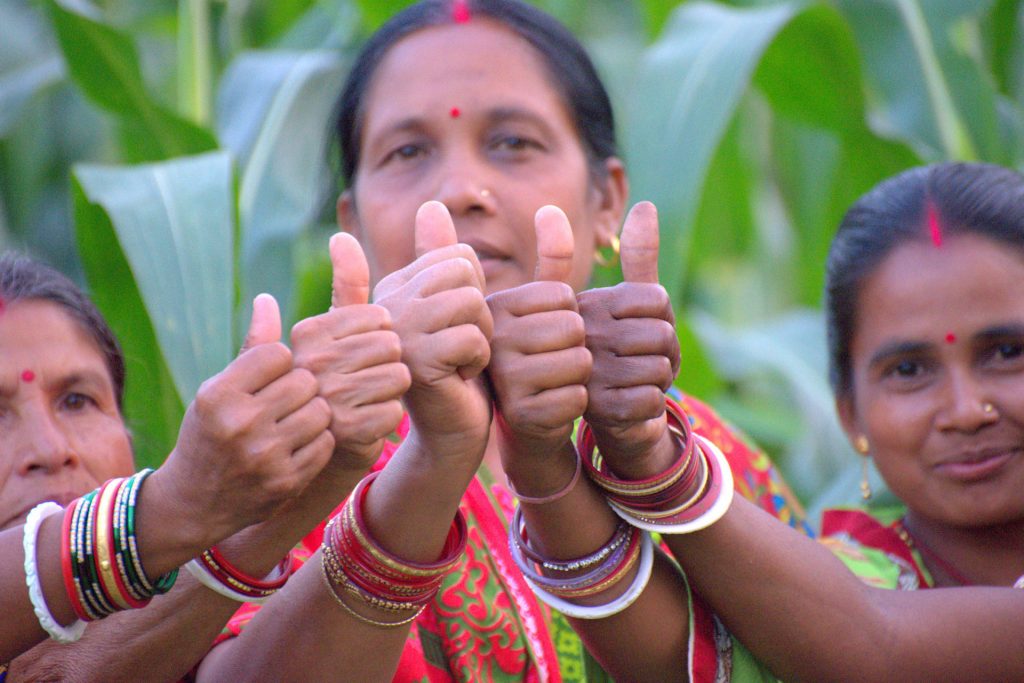
A considerable increase in maize production has improved incomes for families across the regions, as well as their food security. It has also created opportunities for women to raise their social and economic standing.
There are opportunities for CSISA and its partners to continue collaborating in the project region and beyond. CIMMYT has worked with Odisha’s State Department of Agriculture, the Odisha Rural Development and Marketing Society (ORMAS), the Integrated Tribal Development Agency (ITDA), women’s self-help groups, farmers’ producer groups, private seed companies and many other collectives.
Weathering the crisis
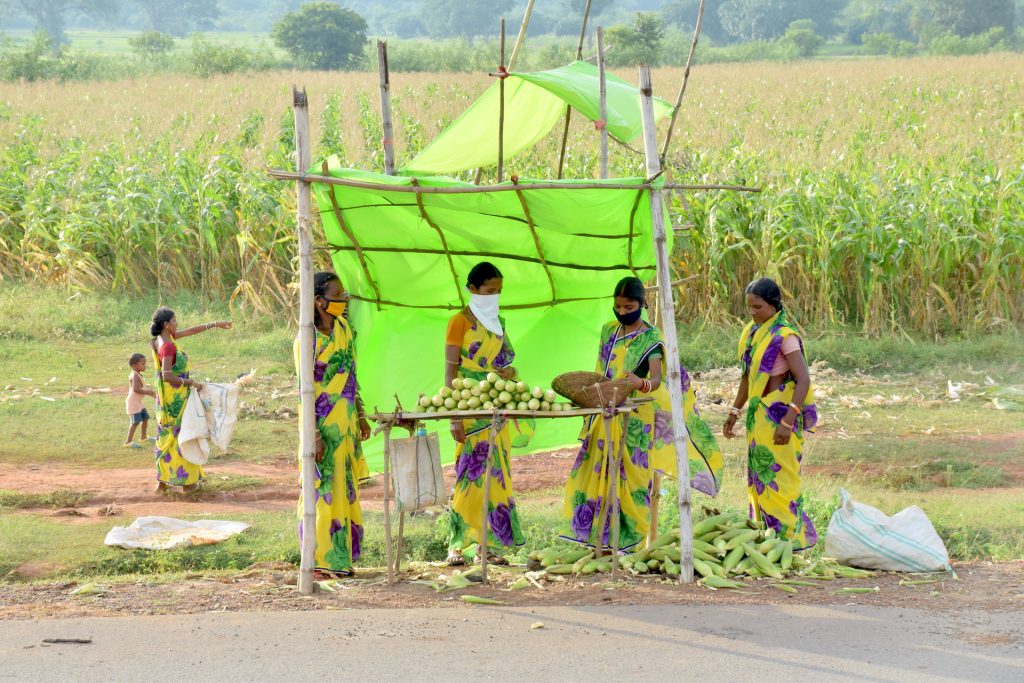
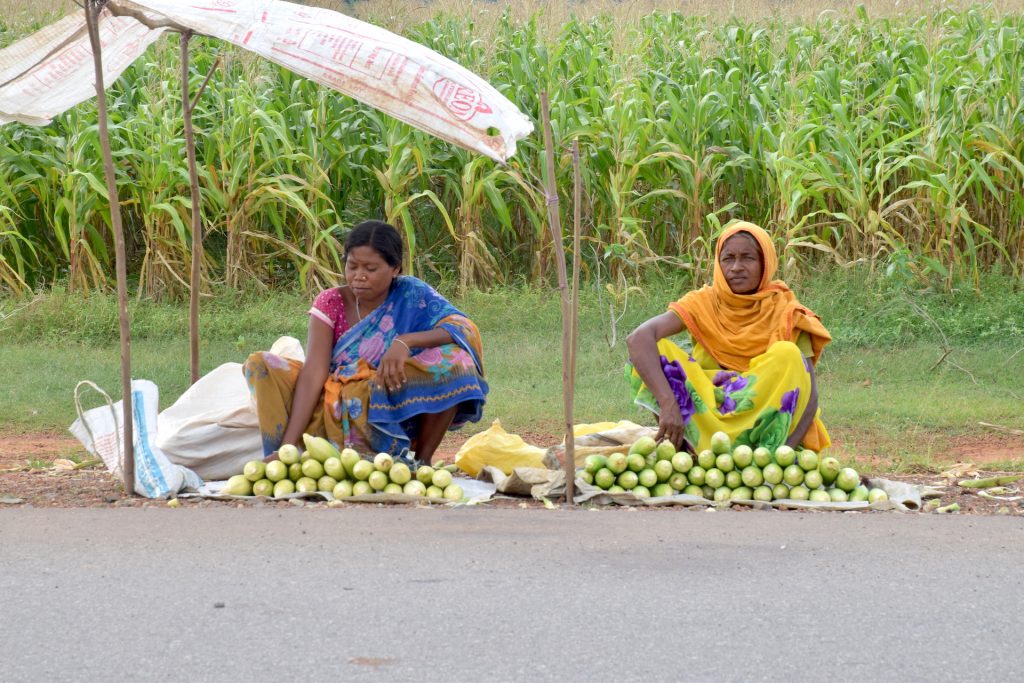
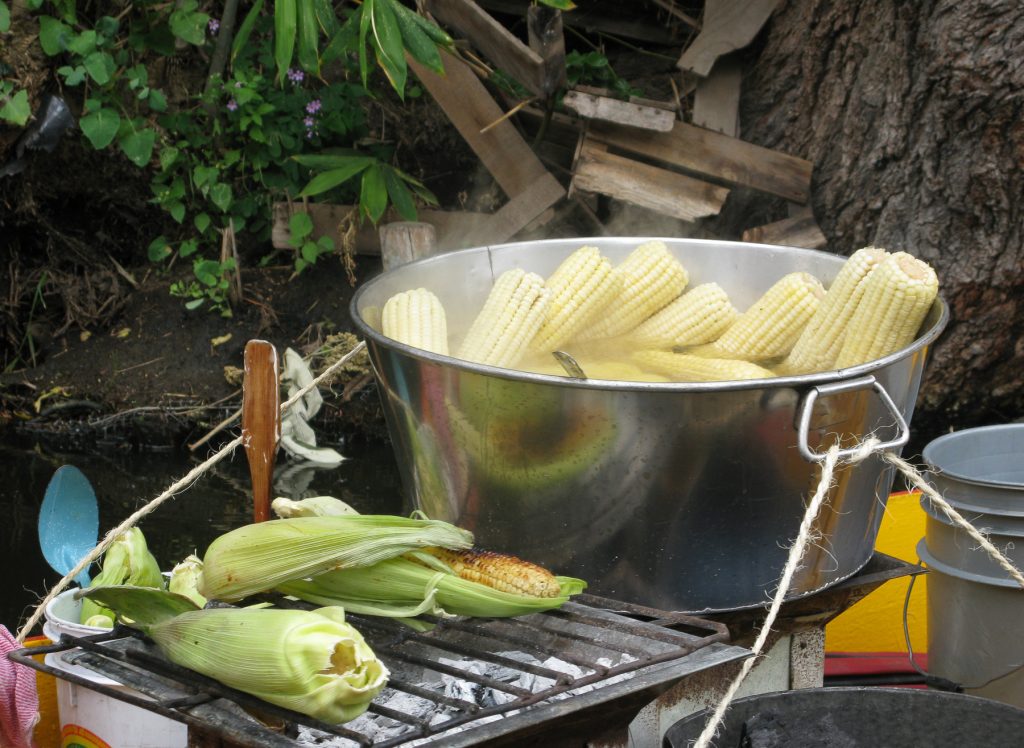
Women have shouldered the responsibility and led their families out of the COVID-19 crisis. When men were left jobless and stranded as migrant workers during lockdown, many women associated with the CSISA project began generating income by selling green corn. This small income helped ensure food to feed their families and wellbeing in this critical period.
The road ahead
With the purpose of advocating this positive transformation in similar conditions, CSISA is committed to expand maize intensification in the plateau region of Odisha and engaging more farmers. Ongoing research and studies are focusing on improving the outreach, to help women increase their maize area and productivity with better-bet agronomy. This will contribute to secured income in coming years and the sustainability of the initiative.