Strengthening resilience in Mutoko farmers through agroecological research
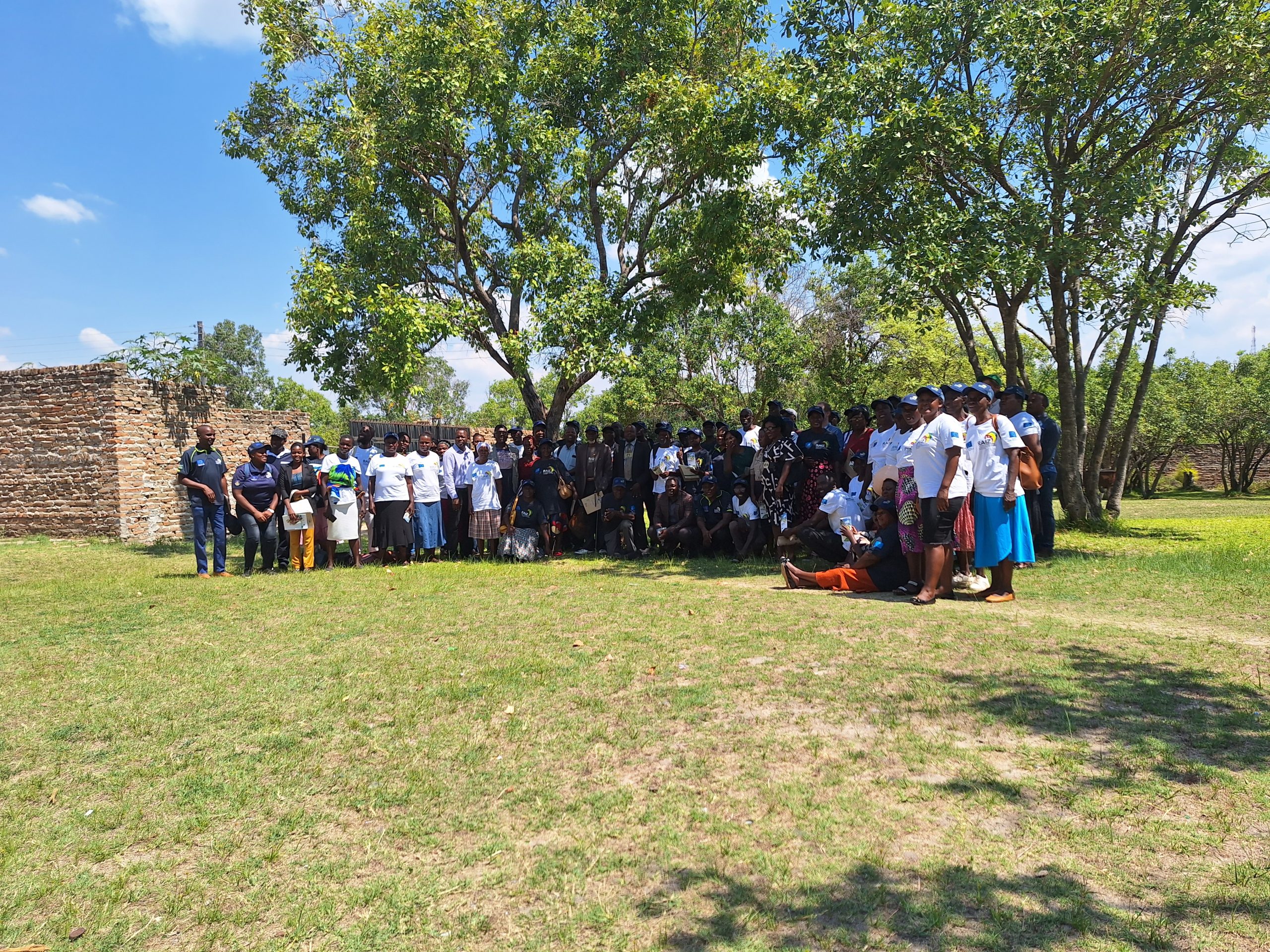

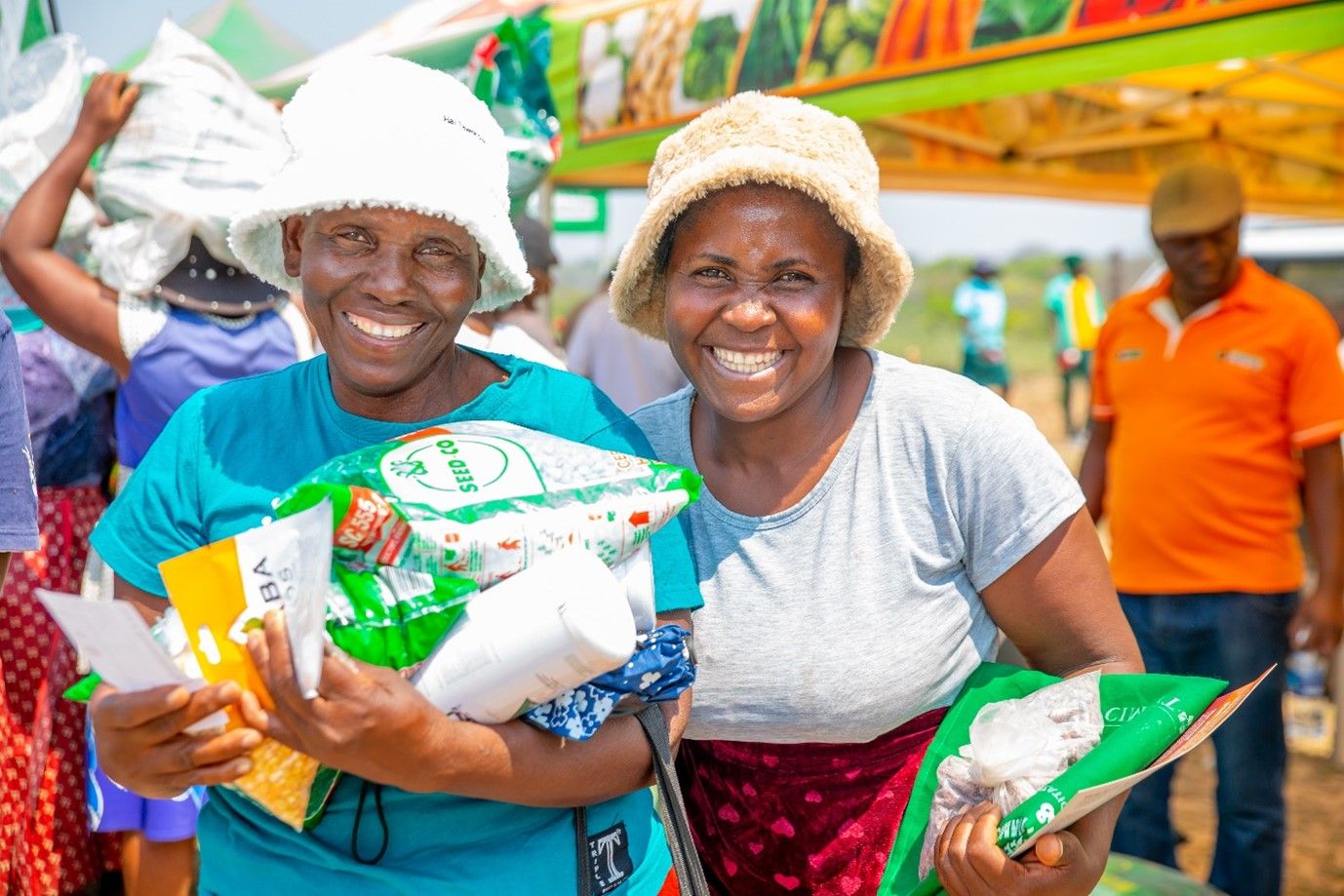
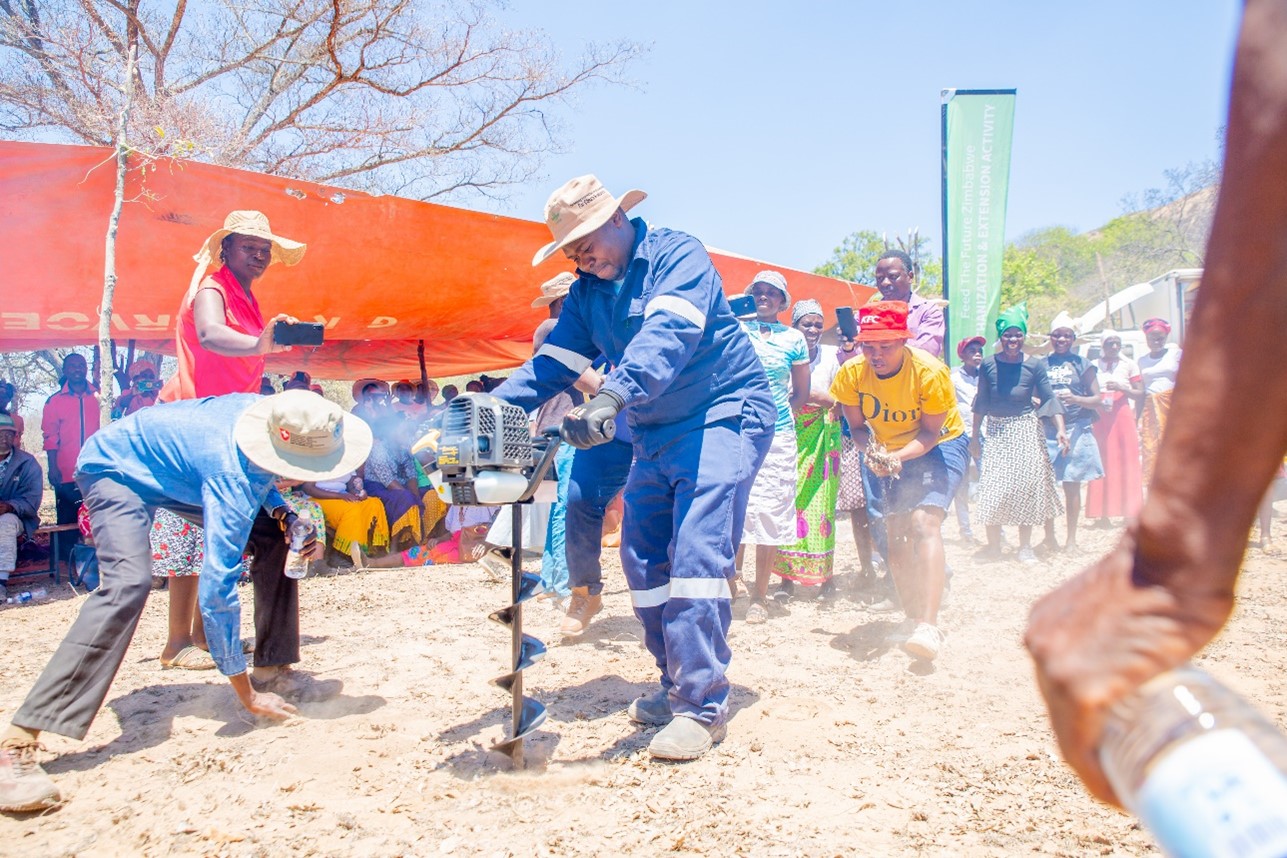
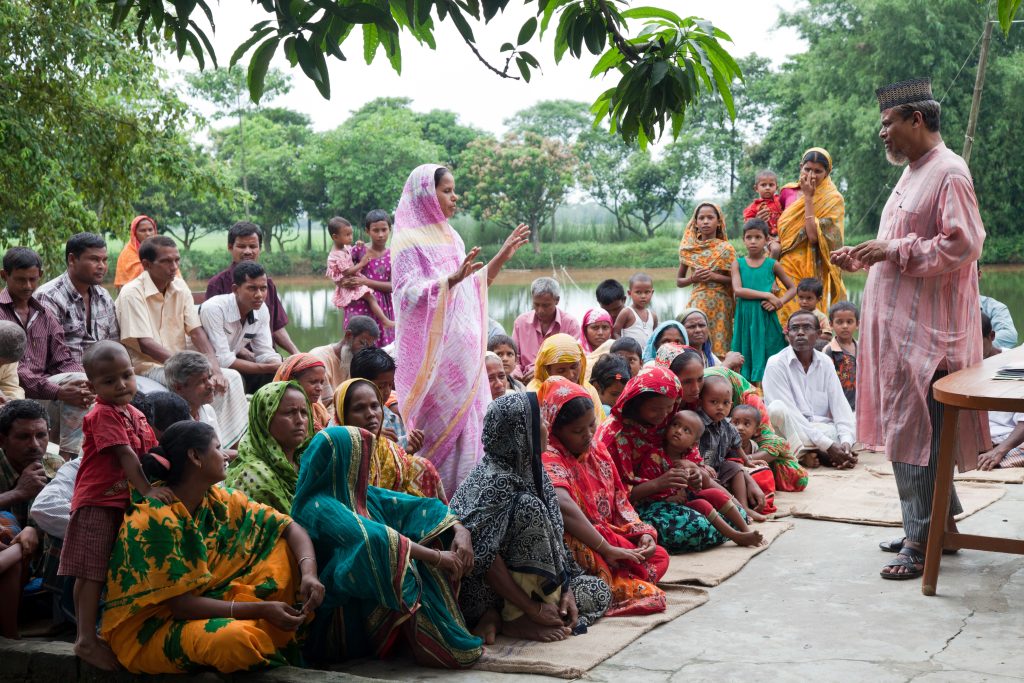
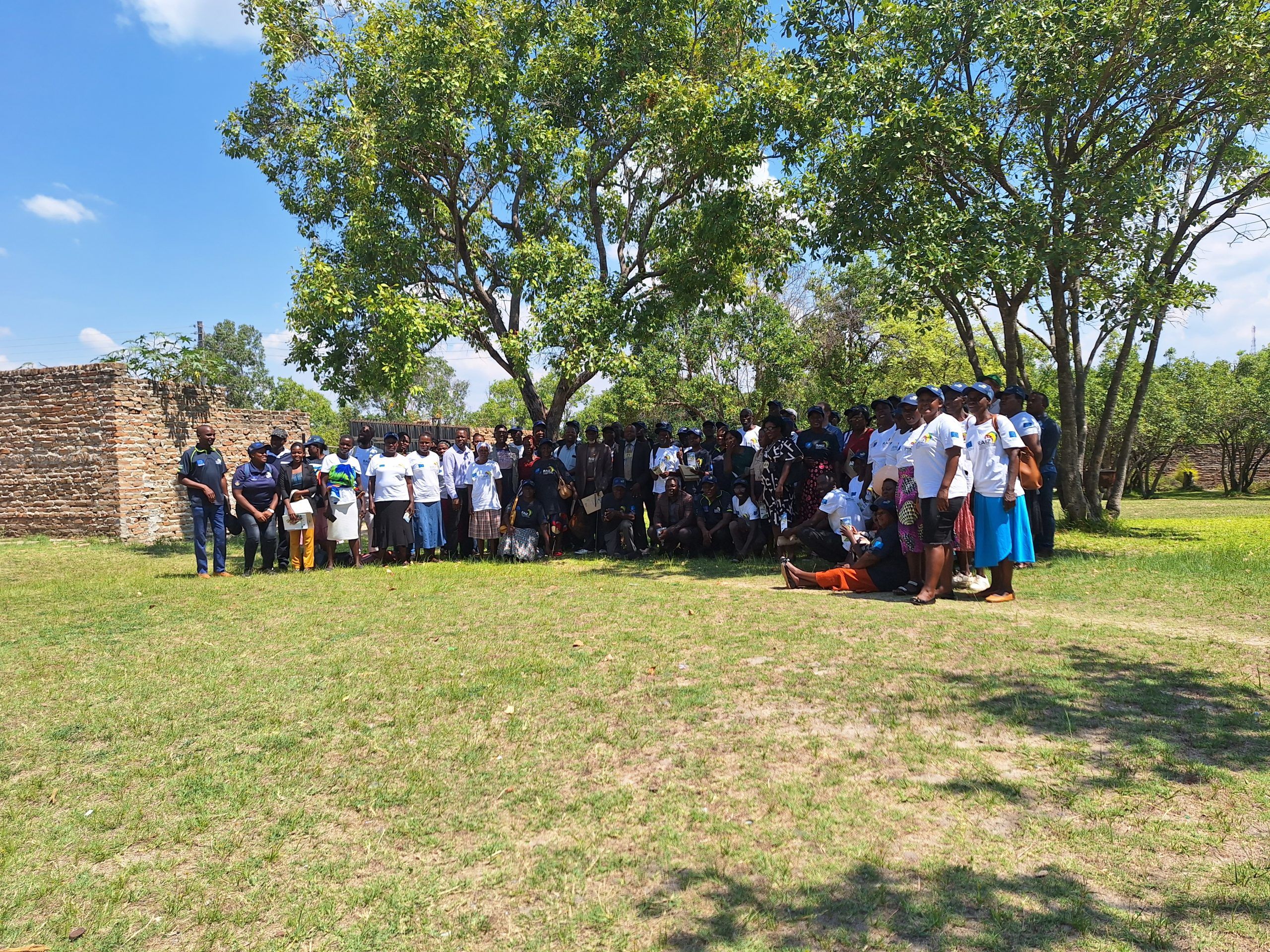
Mutoko, a semi-arid area located in Mashonaland east of Zimbabwe, is prone to droughts and unpredictable rainfall patterns. In an effort to tackle the challenges faced by local smallholder farmers in the region, partners of the Resilience Building through agroecological intensification in Zimbabwe (RAIZ) project organized a participatory workshop to amplify the project’s mandate and gather feedback from key stakeholders. The workshop at Mutoko brought together diverse participants from the Women Affairs, Youth, and Agriculture ministries from the government of Zimbabwe, local leaders and council, extension officers, students, and farmers from Wards 10 and 8. Attending farmers and stakeholders expressed interest in the project that would enable them to face challenges and improve agricultural practices in Mutoko.
Working towards climate-smart solutions: the RAIZ project
RAIZ is a collaborative effort between CIMMYT, the French Agricultural Research Centre for International Development (CIRAD), and the University of Zimbabwe. The project is funded by the European Union, and it focuses on recognizing the strategic role of agroecological approaches in tackling climate change and enhancing sustainable agriculture in arid areas. Research operations are underway in Mutoko to produce scientific evidence and contribute to agroecology policy.
Agroecology offers climate-smart solutions that help farmers adapt to changing conditions, mitigate greenhouse gas emissions, conserve natural resources, and promote food security and resilience in the face of climate uncertainties. RAIZ implements ‘Living Labs’ which strengthens collaboration between diverse stakeholders, including farmers and scientists, whose collective insights help develop demand-driven solutions.
During the Mutoko workshop, Professor and Systems Agronomist Regis Chikowo provided context of RAIZ and emphasized on its goal of helping build resilience in farmers through sustainable approaches. “The aim is not only to help farmers adapt to climate change but also to enable them to thrive in the face of adversity,” said Chikowo.
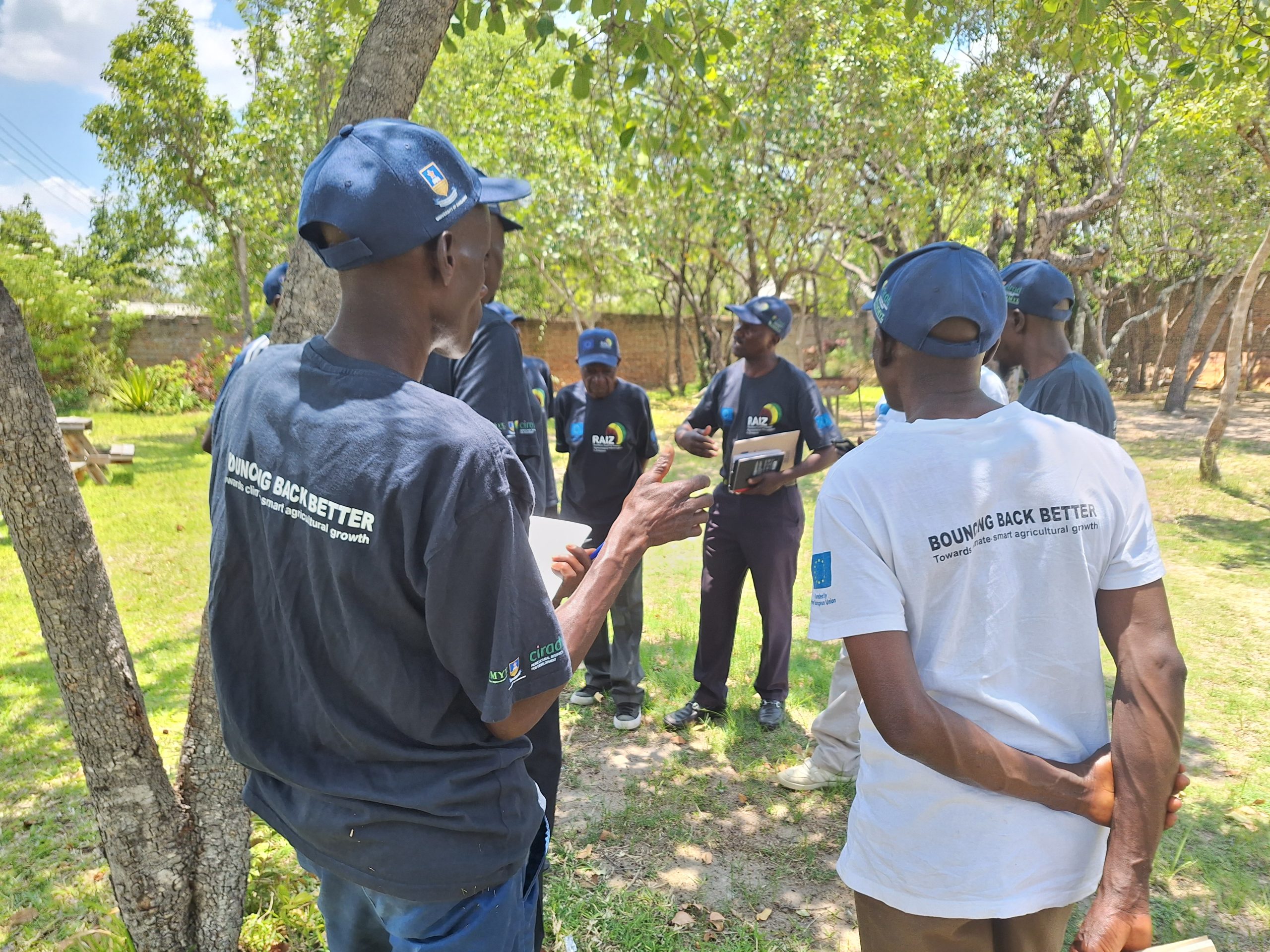

Building synergies between research and farmer realities
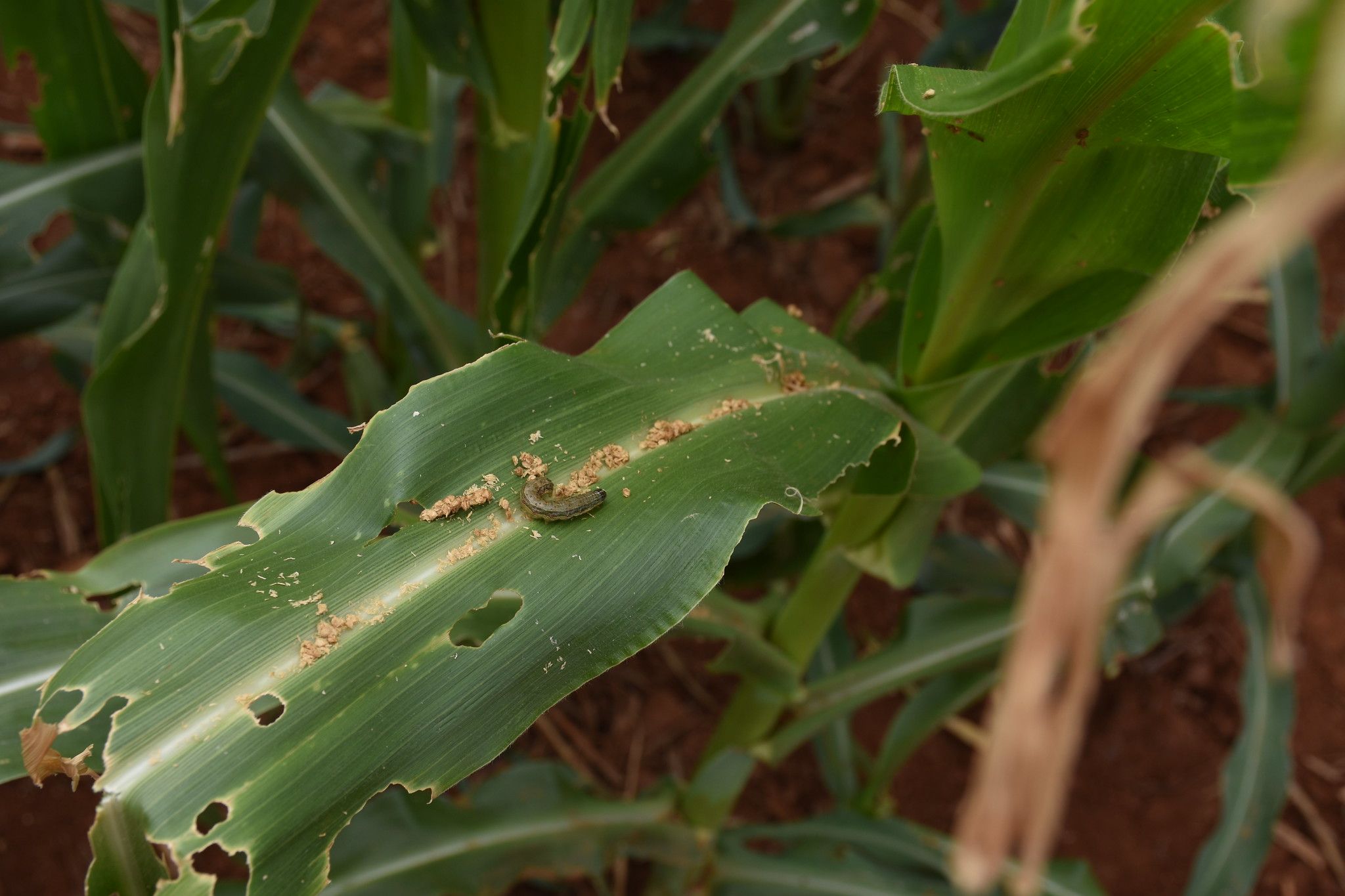
To bridge the gap between research and farmer realities, six student-researchers of RAIZ are working on various aspects of building farmer resilience based on agroecological principles. Their study areas comprise of weed control, climate-proofing with resilient small grain varieties, indigenous knowledge systems, and soil health among others. One student-researcher, in collaboration with farmers, is conducting research on weed control and its impact on crop yield. In all, they are set to articulate and tackle climate change in Mutoko.
“Through my research in weed control and how it affects yields, we are hosting trials with some farmers. We are putting into effect mulch practices gumbeze ramwari, and assessing how it affects yields. We are then intercropping maize with cowpea so that farmers spend less time fighting off weeds, while promoting crop diversification,” says Juliet Murimwa, a Ph.D. student.
Knowledge and sources of information on when to expect rains and average temperatures are vital for farmers to better plan the entire planting-to-harvesting operations. Recognizing this, research student Rejoice Nyoni is studying the types and usefulness of climate services information accessed by smallholder farmers in RAIZ project sites.
“My research is centered on understanding whether smallholder farmers are getting enough knowledge from available sources, including radio which is more prominent,” says Nyoni. Farmers have long relied on traditional knowledge systems to predict weather patterns and plan farming activities. However, with climate change, some of these traditional knowledge sources are being altered. “This season, I will be joining our farmers in Mutoko to discuss and understand which indigenous knowledge systems they use to gather information about weather patterns. We want to find ways to ensure that such wisdom does not get lost, as generations are slowly moving away from traditional cultures and norms,” she adds.
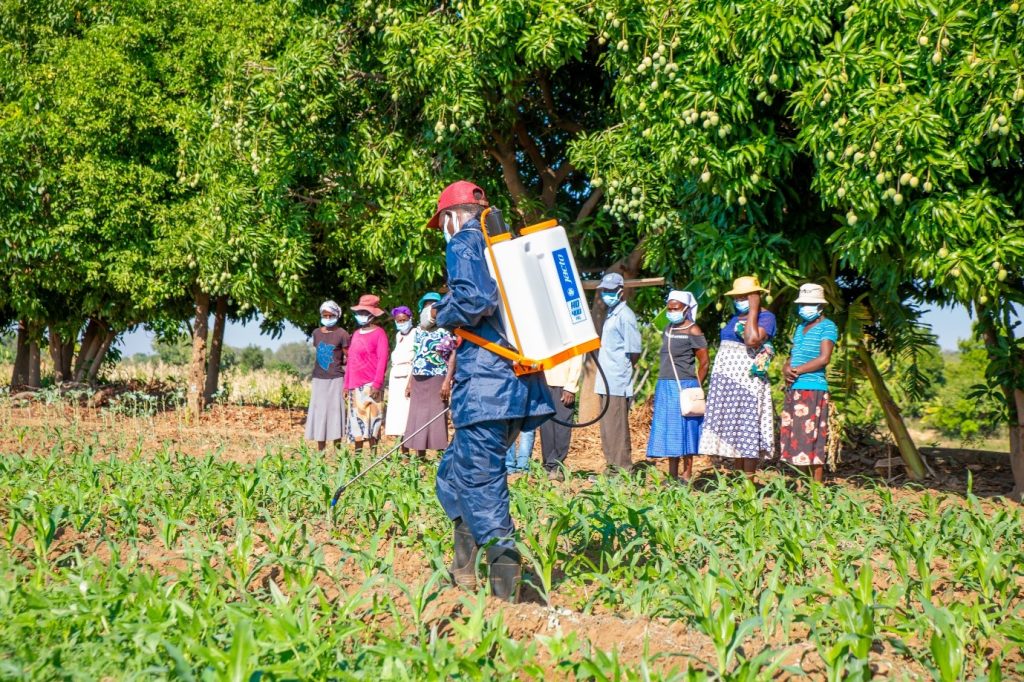
CIMMYT’s work in RAIZ operational areas supported by graduate students, is also testing the effectiveness of newly availed local commercial organic fertilizers and how they contribute to climate smartness when used along with conservation agriculture practices. CIMMYT is also leading the development of an agroecology handbook, set to be used by extension staff and other development practitioners.
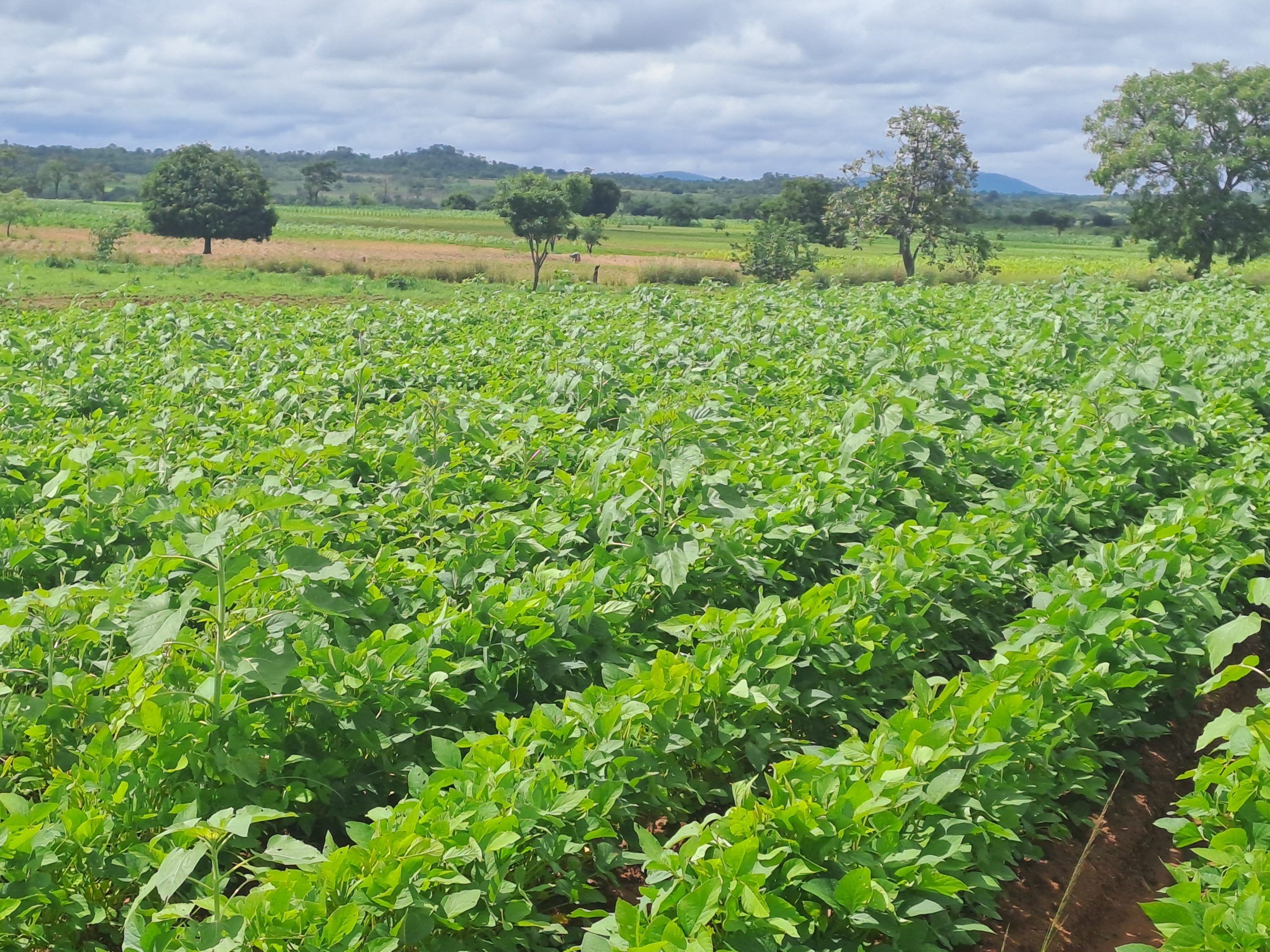
In line with the International Year of Millets in 2023, RAIZ actively promotes the cultivation of small grains to enhance the resilience of local farmers. As part of the project, a student researcher is conducting trials in Mutoko to assess the performance of different small grain varieties in the face of climate change. Farmers in Mutoko’s Ward 10 have started experimenting with small grains and have experienced promising yields. A farmer in Mutoko Ward 10, Mudzengera, shared his positive experience with growing sorghum, “Last year we grew three varieties of sorghum. We really liked the new variety as it was not prone to bird attack. On the other hand, the native variety we usually grow is prone to birds feasting on them. We realized good yields which improved household nutrition. I look forward to another farming season with such trials on sorghum,” he says.

A shared vision for a sustainable future
A visioning exercise conducted during the workshop, solicited views from the farmers on how they envision the future of agriculture. The session, facilitated by Isaiah Nyagumbo, senior agronomist at CIMMYT, and marking the initiation of Living Laboratories in the district, started with asking farmers what change and developments they would like to see in their ward after three to four years, with respect to agriculture. The farmers were disaggregated into four groups by gender and ward. The emerging aspirations revolved around the twin goals of safeguarding the environment and enhancing crop yields. Farmers from both wards 10 and 8, expressed a shared desire to improve agricultural marketing infrastructure, agroforestry, and the protection of forests, recognizing the critical role that trees play in mitigating climate change and preserving biodiversity. Mulching, which holds immense potential in conserving soil moisture, and adopting mechanized operations were among other aspirations. Furthermore, the participants expressed interest in cultivating small grains, drought-tolerant maize, use of renewable energy, and leveraging digital platforms.

 Delivery of HT maize hybrids to smallholder farmers in South Asia
Delivery of HT maize hybrids to smallholder farmers in South Asia