Sustaining Conservation Agriculture initiatives: lessons from Malawi
Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) has experienced the worst impacts of climate change on agriculture over the past decades and projections show such effects are going to intensify in the coming years. Diminished agricultural production has been the primary impact channel given the high reliance on rainfed agriculture in the region. Combined with a growing population, food security for millions of people is threatened.
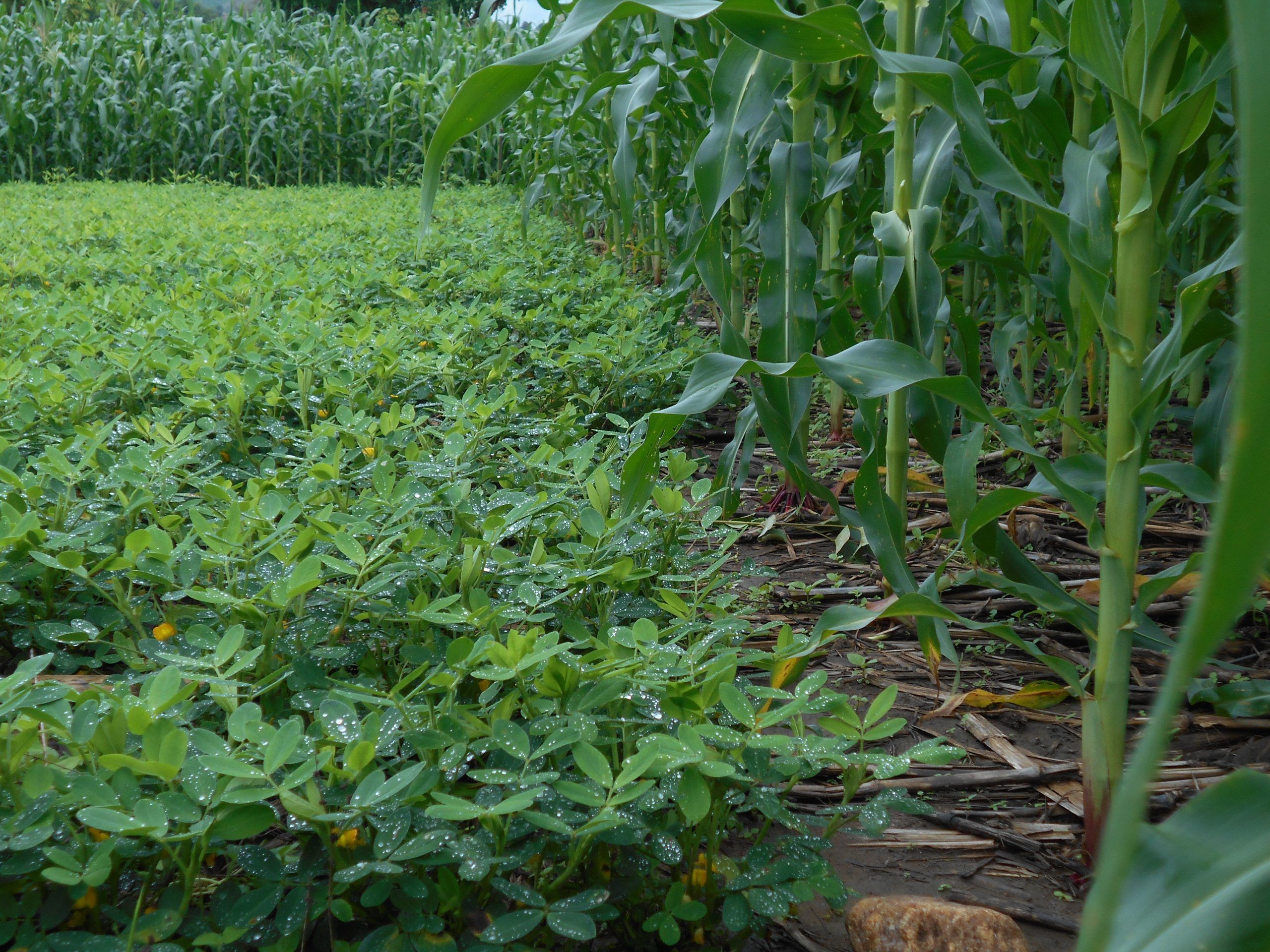
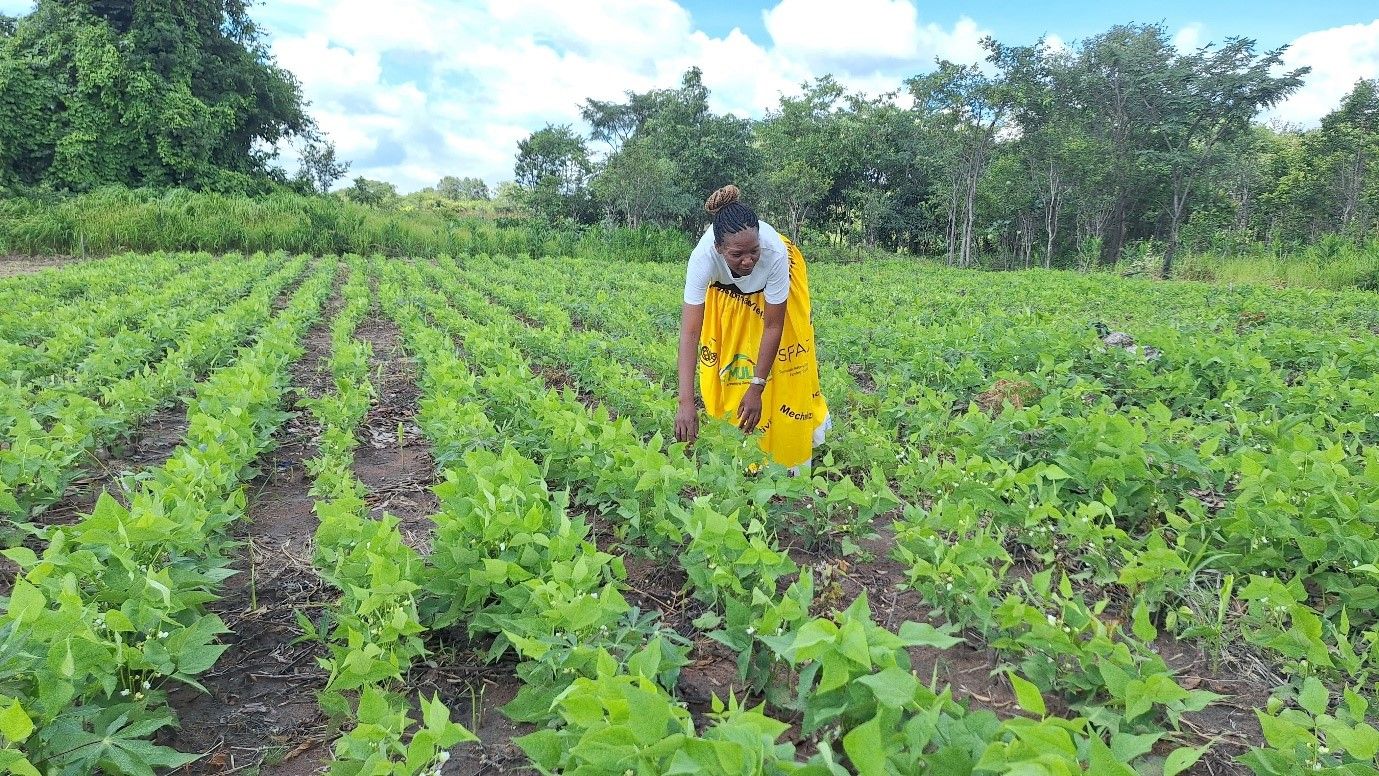
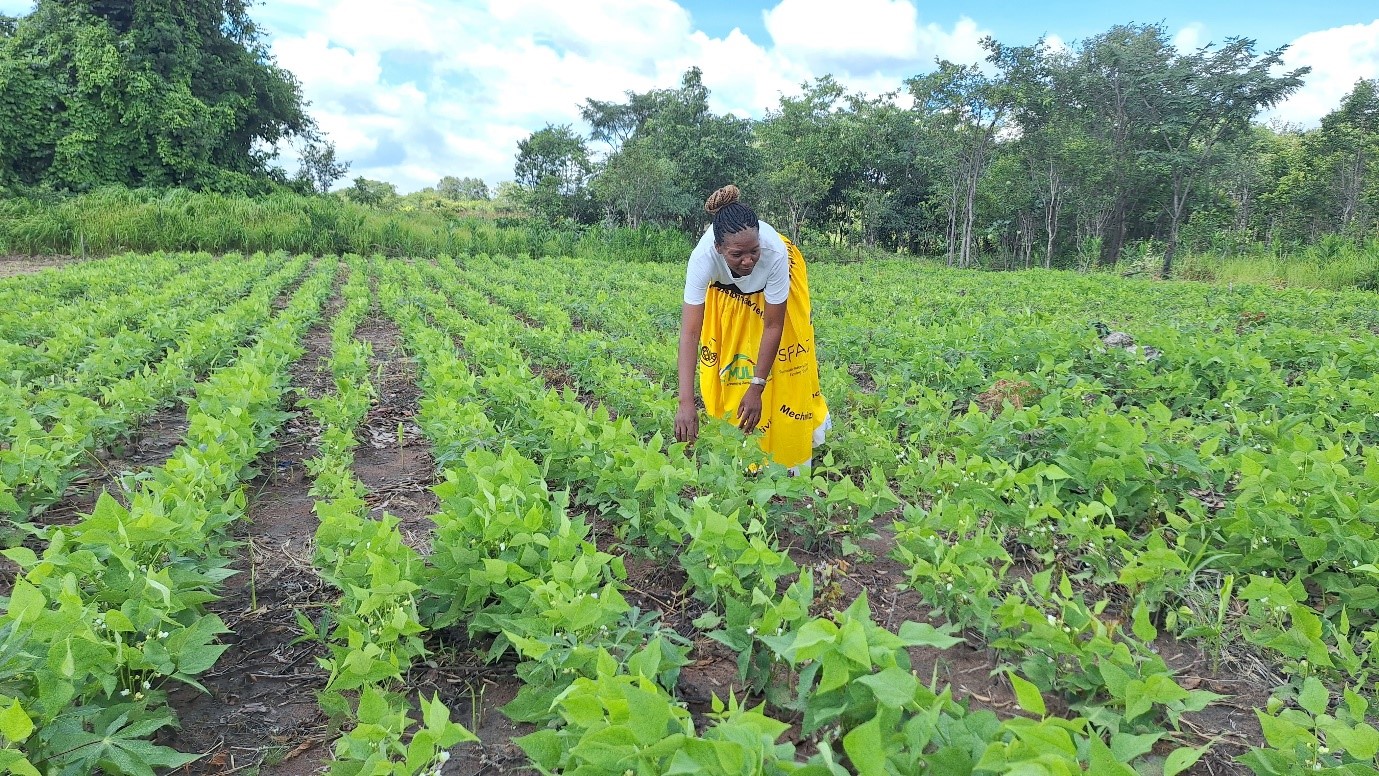
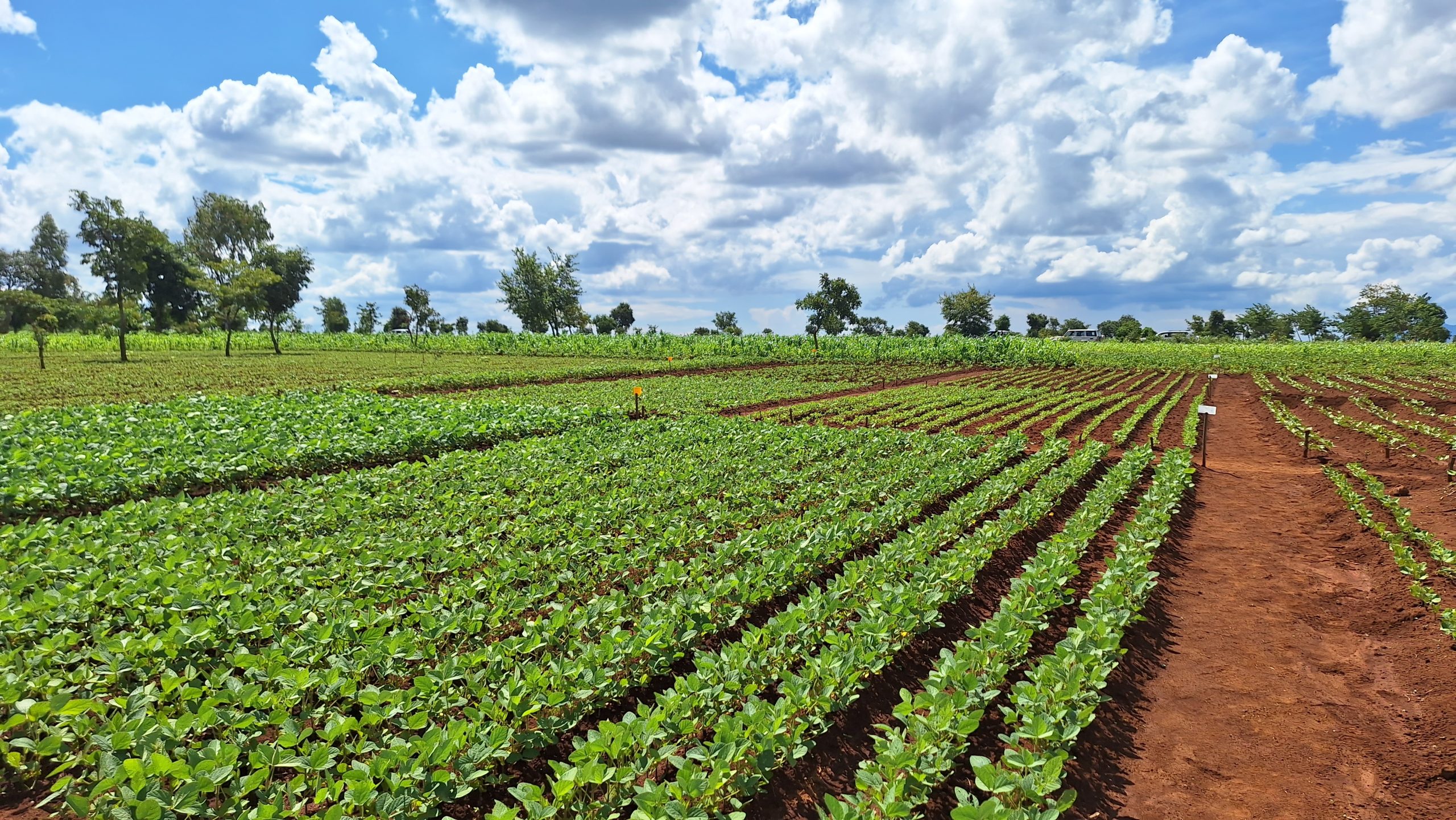
Conservation Agriculture (CA) is a sustainable cropping system that can help reverse soil degradation, augment soil health, increase crop yields, and reduce labor requirements while helping smallholder farmers adapt to climate change. It is built on three core principles of minimum soil disturbance, crop residue retention, and crop diversification.
CA was introduced in southern Africa in the 1990s, but its adoption has been patchy and often associated with commercial farming. A group of researchers, led by Christian Thierfelder, principal cropping systems agronomist at CIMMYT, set out to understand the reasons why smallholder farmers adopt CA, or why they might not or indeed dis-adopt. Their results were published in Renewable Agriculture and Food Systems on March 12, 2024.

“Conservation Agriculture can cushion farmers from the effects of climate change through its capacity to retain more soil water in response to high water infiltration and increased soil organic carbon. It is therefore a viable option to deal with increased heat and drought stress,” said Thierfelder. However, even with these benefits, adoption of CA has not been as widespread in countries like Malawi.
“There are regions within Malawi where CA has been promoted for a long time, also known as sentinel sites,” said Thierfelder. “In such places, adoption is rising, indicating that farmers are realizing the benefits of CA over time. Examining adoption dynamics in sentinel sites can provide valuable lessons on scaling CA and why some regions experience large rates of non- or dis-adoption.”
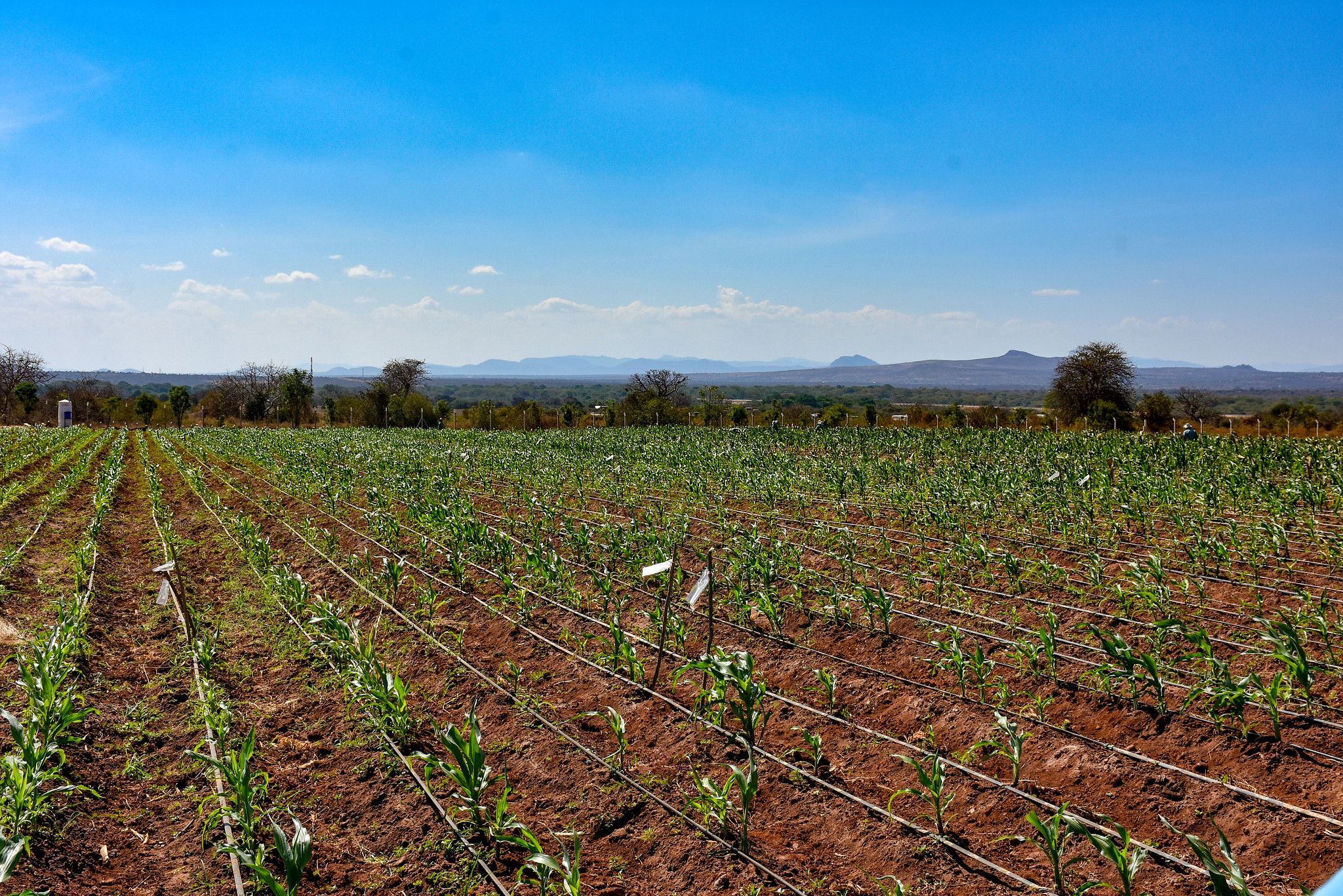
Thierfelder and his co-authors, Innocent Pangapanga-Phiri of the Center for Agricultural Research and Development (CARD) of the Lilongwe University of Agriculture and Natural Resources (LUANAR), and Hambulo Ngoma, scientist and agricultural economist at CIMMYT, examined the Nkhotakota district in central Malawi, one of the most promising examples of widespread CA adoption.
Total LandCare (TLC), a regional NGO working in Malawi has been consistently promoting CA in tandem with CIMMYT in the Nkhotakota district since 2005.
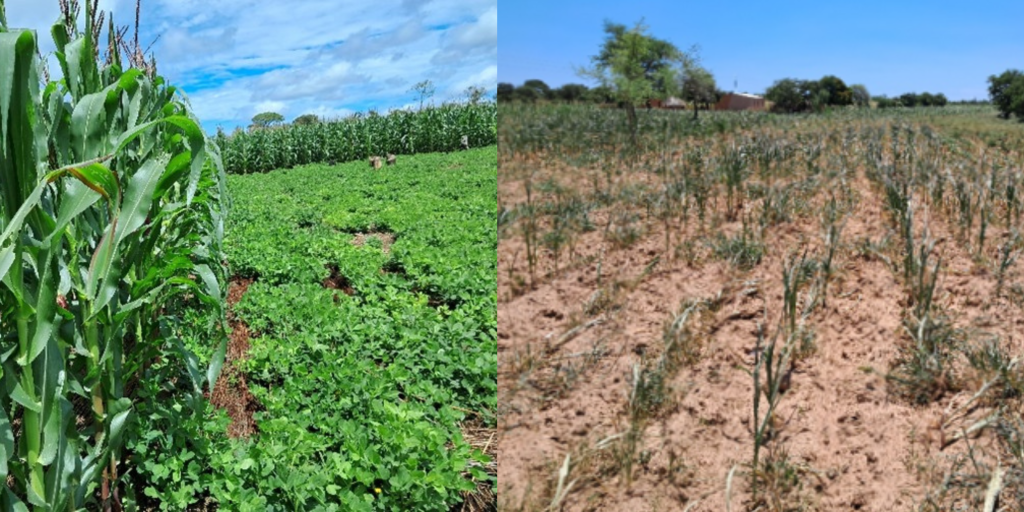
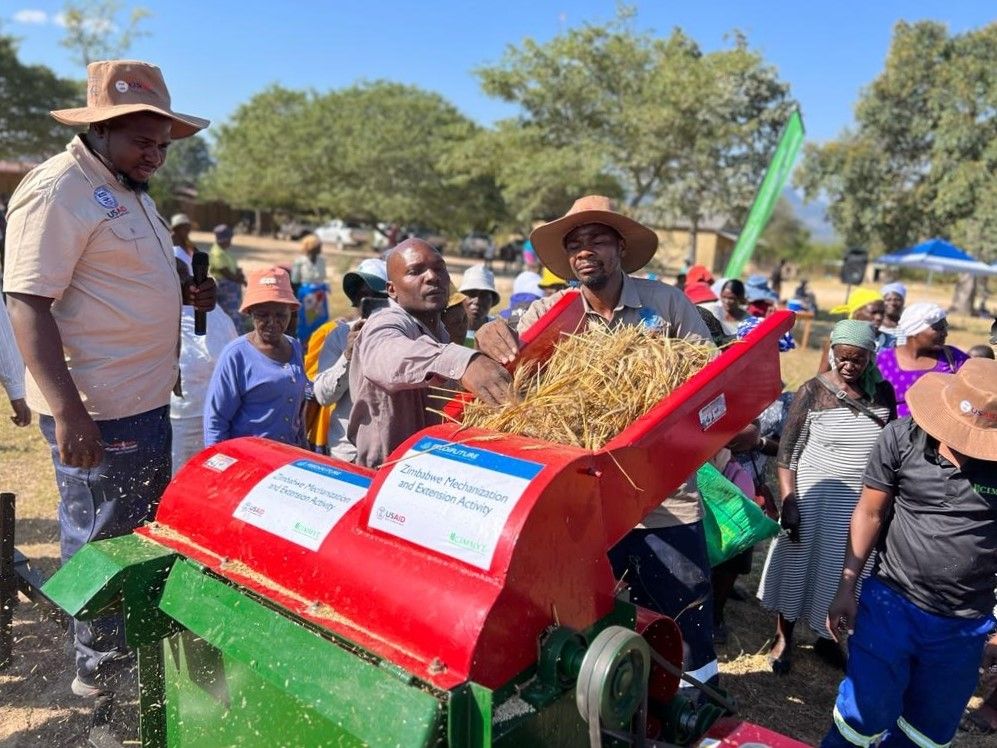
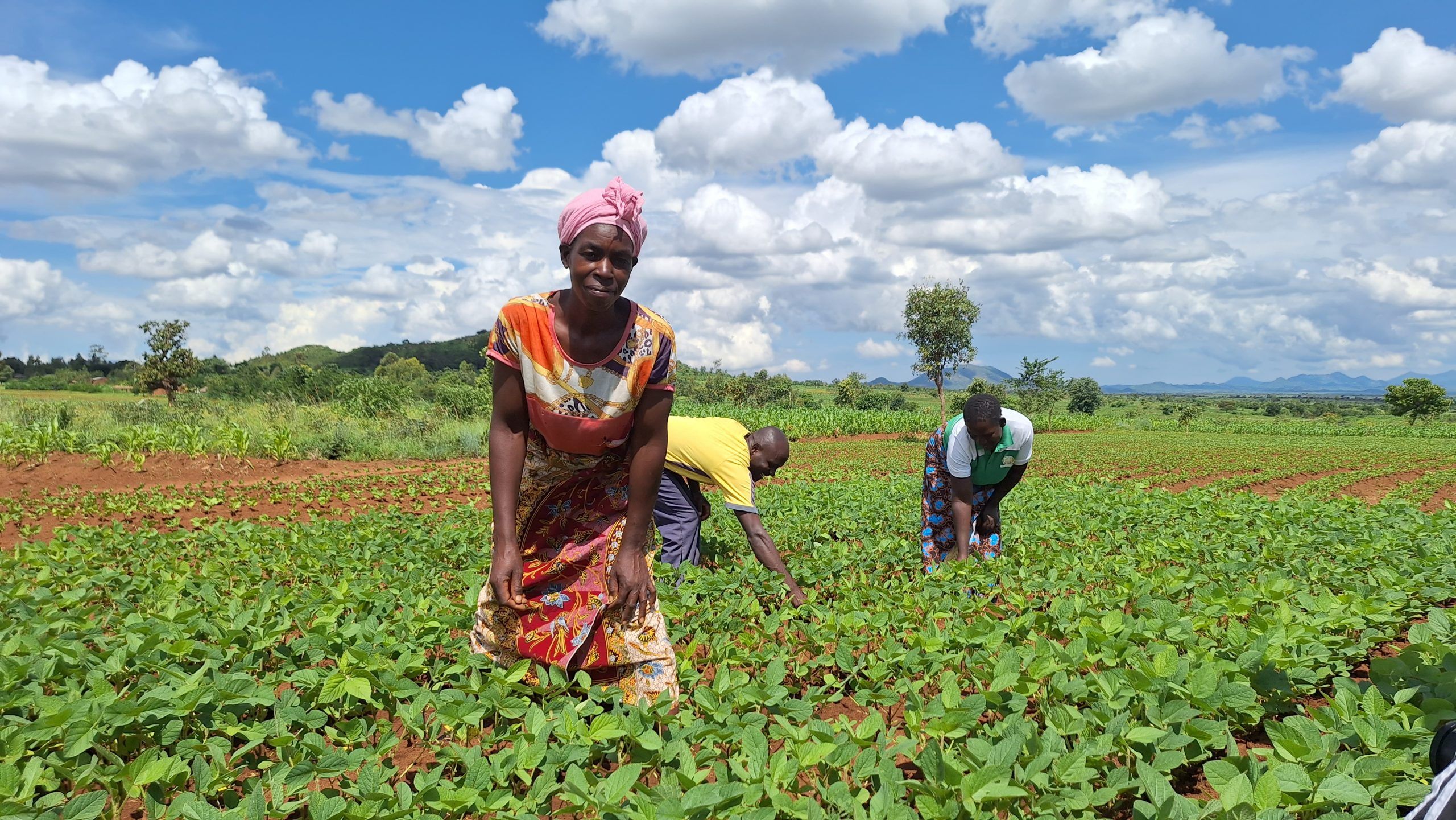
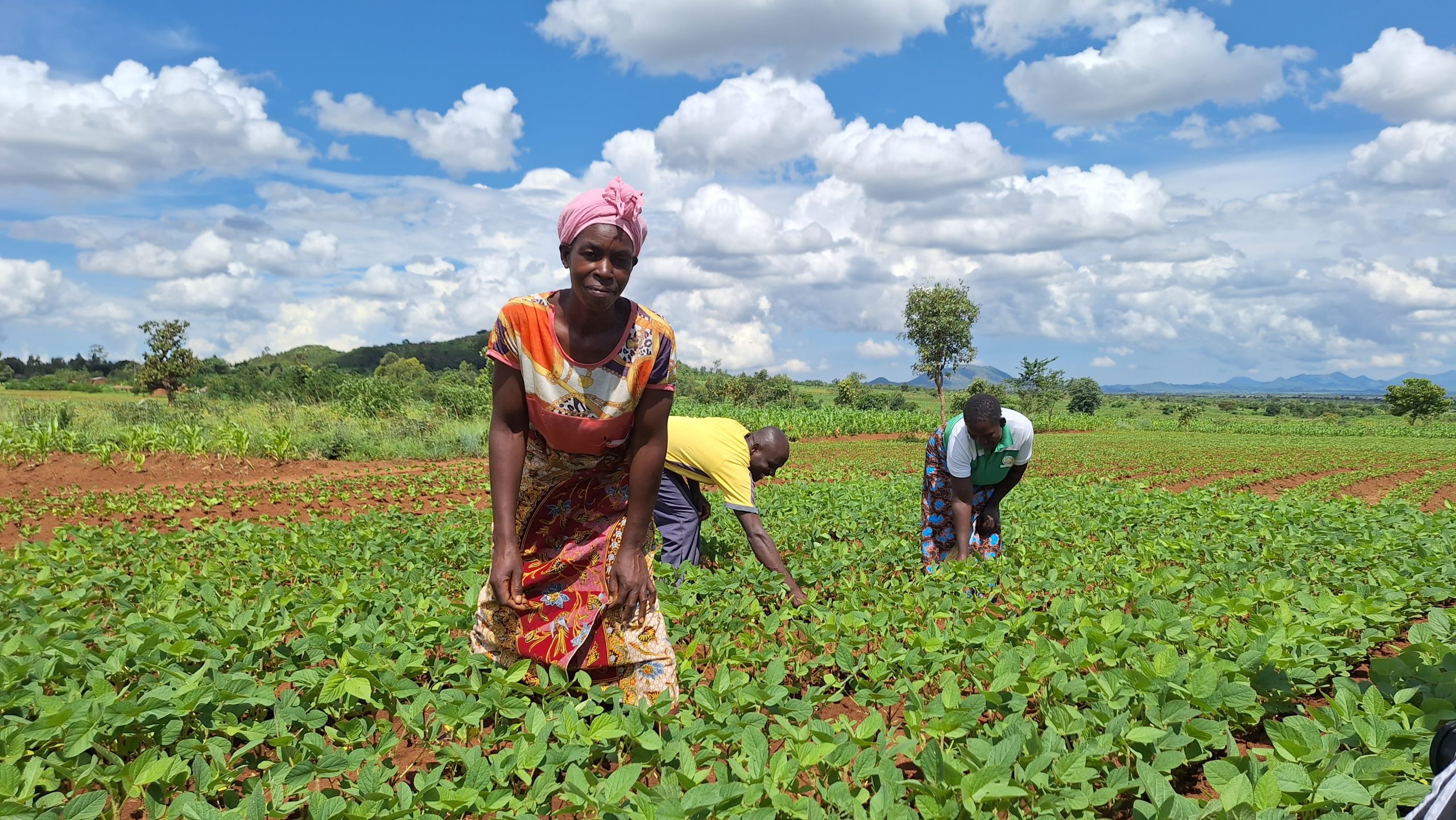
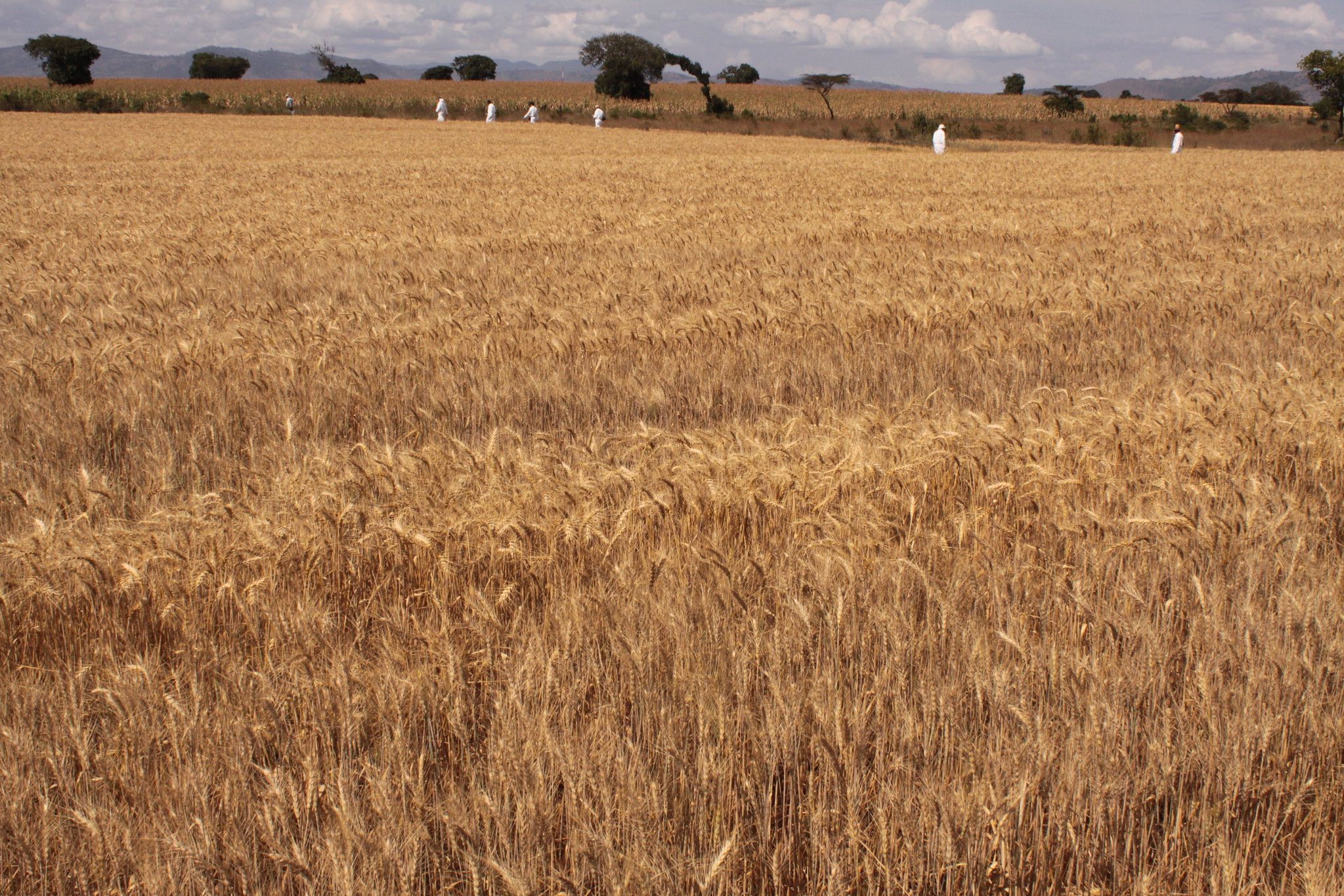
Results from both individual farmer interviews and focused group discussions revealed that farmers that implement CA saw higher yields per hectare than those who practiced conventional tillage practices. In addition, farmers using CA indicated greater resilience in times of drought, improved soil fertility, and reduced pest infestation.
Why adopt CA?
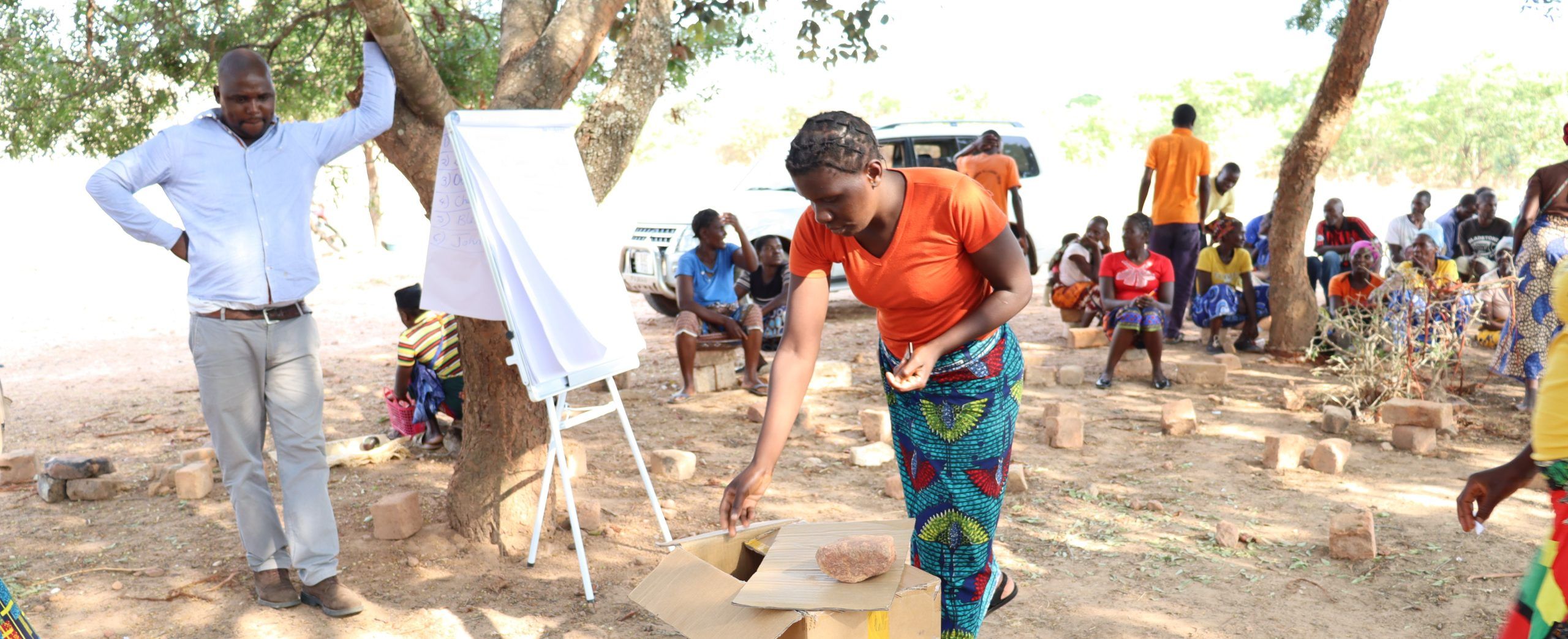
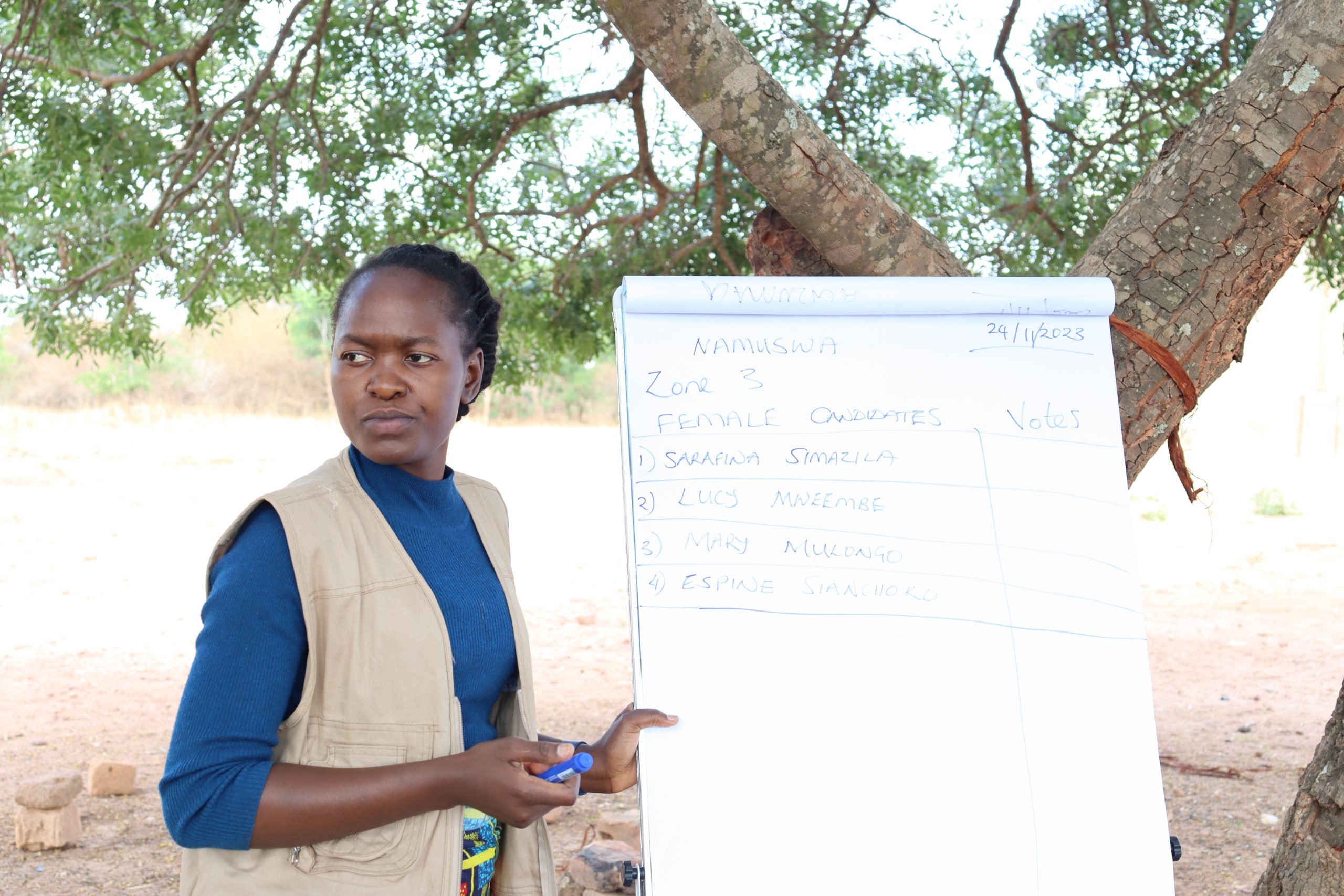
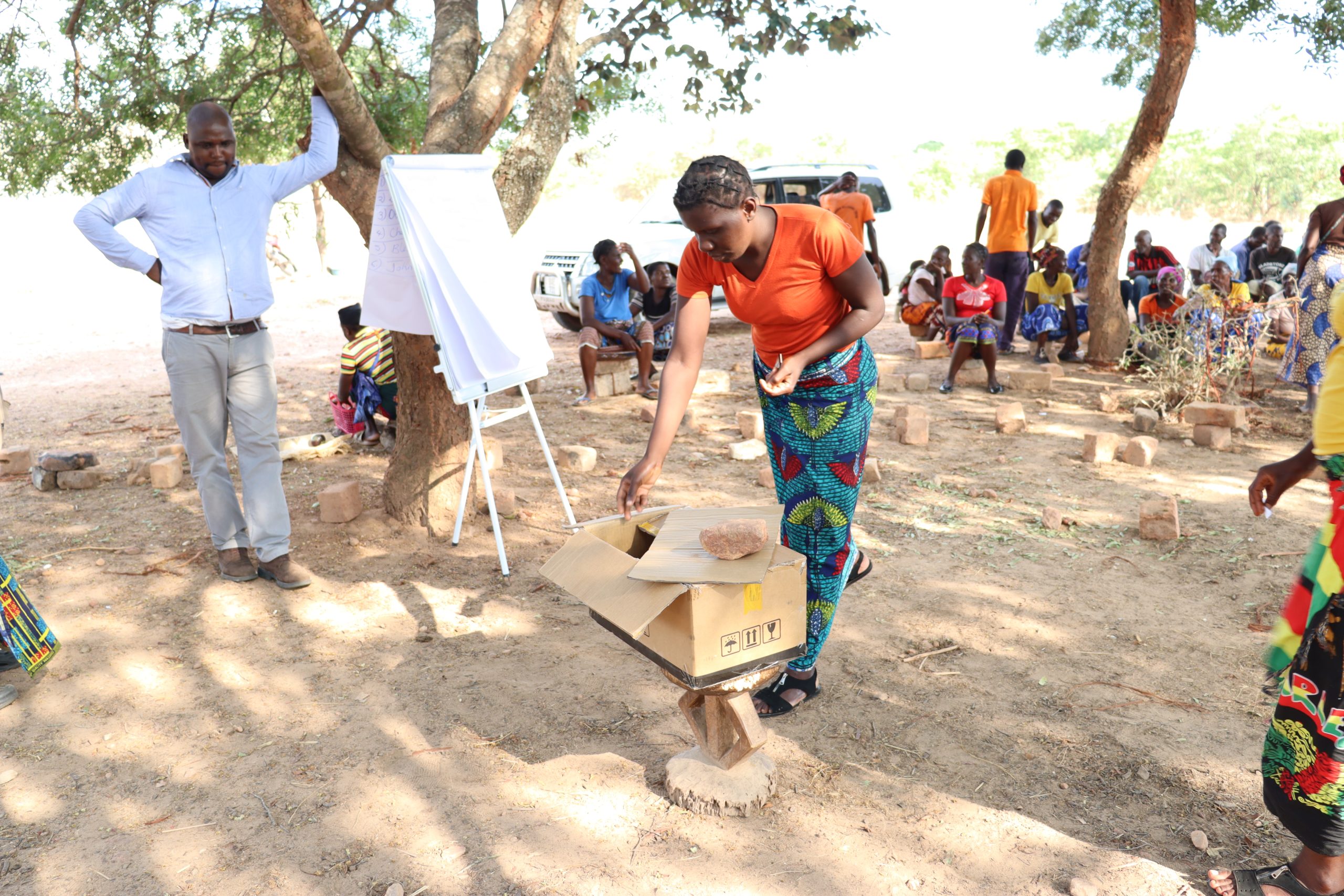
The primary factors enhancing CA adoption in the Nkhotakota district were the availability of training, extension and advisory services, and demonstration plots by the host farmers. Host farmers are farmers that have been trained by a TLC extension officer and have their own plot of land to demonstrate CA methods. In addition, host farmers train other farmers and share knowledge and skills through farmer field days and other local agricultural exhibitions.
“Social networks among the farmers serve a vital role in CA adoption,” said Ngoma. “Seeing tangible success carries significant weight for non-adopter farmers or temporal dis-adopters which can persuade them to adopt.”

During focus group discussions facilitated by the authors, farmers indicated that demonstration plots also removed fear for the unknown and debunked some myths regarding CA systems, for example, that practitioners show ‘laziness’ if they do not conventionally till their land.
“This suggests that CA uptake could be enhanced with increased, targeted, and long-term promotion efforts that include demonstration plots,” said Ngoma.
Similarly, the longer duration of CA exposure positively influenced farmers’ decisions to adopt CA methods as longer exposure might allow farmers to better understand the benefits of CA practices.
Why not adopt CA?
Farmers reported socioeconomic, financial, and technical constraints to adopt CA. An example is that farmers might not have the labor and time available for weed control, a necessary step in the first few years after the transition to CA.
“Weed control is an important challenge during the early years of CA adoption and can be seen as the ‘Achilles heel’ of CA adoption,” said Thierfelder. CIMMYT scientists therefore focused a lot of research in recent years to find alternative weed control strategies based on integrated weed management (IWM) using chemical, biological, and mechanical control options.

In most cases, the benefits of CA adoption are seen only after 2 to 5 years. Having such a long-term view is not always possible for smallholder farmers, who often must make decisions based on current conditions and have immediate family obligations to meet.
As a contrast to adopters of CA, non-adopters reported a lack of knowledge about CA as a whole and a lack of specific technical knowledge needed to transition from more traditional methods to CA.
This scarcity of technical support is often due to the lack of strong agriculture extension support systems. Since CA adoption can be complex, capacity building of both farmers and extension agents can therefore foster adoption and implementation of CA. This reinforces that farmer-to-farmer approaches through host farmers could complement other sources of extension to foster adoption.
Next steps
The authors identified three policy recommendations to accelerate CA adoption. First, there is a need to continue promoting CA using farmer-centric approaches more consistently, e.g., the host farmer approach. Using a farmer-centered approach facilitates experiential learning and can serve as a motivation for peer-to-peer exchange and learning and can reduce misinformation. The host farmer approach can be augmented by mega-demonstrations to showcase CA implementation at scale. In addition, rapid and mass extension delivery can be enhanced by using digital technologies.
Second, CA promotion should allow farmers the time to experiment with different CA options before adoption. What remains unclear at the policy level is the types of incentives and support that can be given to farmers to encourage experimentation without creating economic dependence. NGOs and extension workers could help farmers deal with the weed pressure soon after converting from full to minimum tillage by providing herbicides and training.
Third, there is a need to build and strengthen farmer groups to facilitate easier access to training, to serve as conduits for incentive schemes such as payments for environmental services, and conditional input subsidies for CA farmers. Such market-smart incentives are key to induce initial adoption in the short term and to facilitate sustained adoption.