Money-making machines
A new small-mechanization pilot initiative launched in July is equipping farmers with the business and technical skills they need to provide mechanization services to communities in six wards of Masvingo district, Zimbabwe.
With funding from the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC) managed by the United Nations World Food Program (WFP), the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) is leading implementation of the pilot in collaboration with Kurima Machinery and the Zimbabwe Agriculture Development Trust (ZADT), who are supporting the technical training and financial management, respectively.
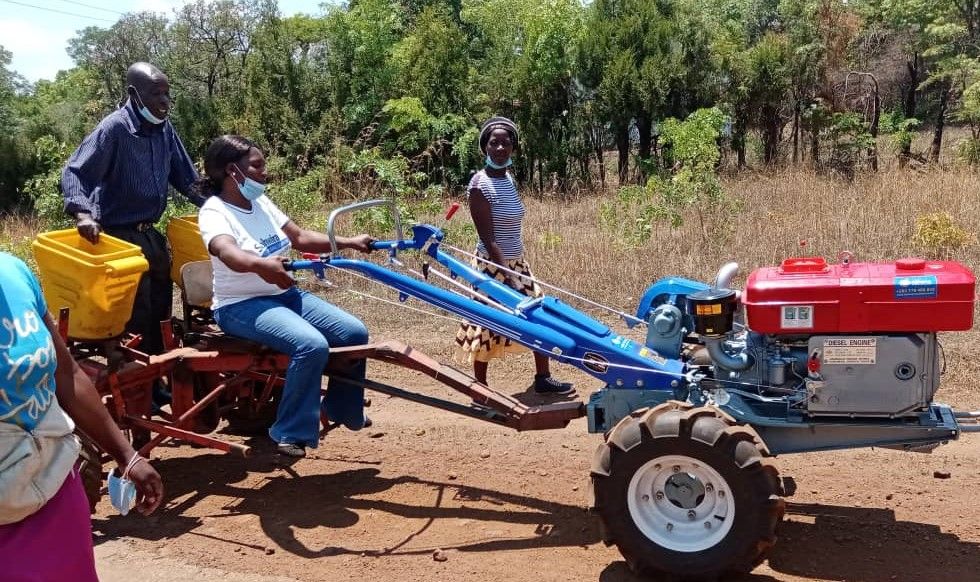
Anchored on a strong business model, 15 farmers have signed up to become service providers and invested an initial deposit of $500 to access the mechanization package comprising a two-wheel tractor and trailer, a direct planter and a maize cob sheller. Through a “lease-to-own” credit facility, eligible service providers will have 24 months to pay the remaining balance for the set of equipment.
“This approach addresses re-payment challenges in past interventions, where equipment was distributed without a firm commitment from the service providers and without putting in enough effort to establish a viable business,” says Christian Thierfelder, a cropping systems agronomist at CIMMYT. “An advantage of this new form of financial commitment by the service providers is that it guarantees full participation and a change in their perception towards farming as a business.”
Since 2013, smallholder farmers in Zimbabwe have been exposed to the benefits of combining small-mechanization with conservation farming systems to improve productivity — land preparation, planting and harvesting to achieve higher yields while reducing production costs. Besides making farming tasks more efficient for individuals, this set of equipment can be used to provide critical services to other farmers in their wards.
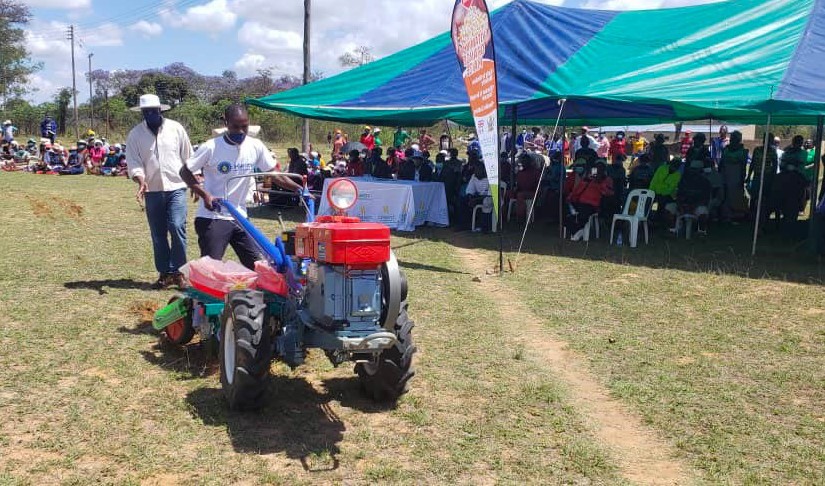
The two-wheel tractor can have various implements attached to it for services such as planting, transportation and shelling. It can also be used to run other important implements such as water pumps, mills or threshers.
This mechanization pilot therefore presents an additional pathway out of poverty and into sustainable production and income generation at household level, while boosting the local economy and rural employment in Masvingo district.

Training for local service provision
Eligible service providers were recently invited to attend a one-week specialized business and technical training course at Gwebi Agricultural College, just outside of Harare. The training package consisted of two main components: business management; and two-wheel tractor operation, maintenance and repair.
Elliot Zvovovo, a participating service provider, explains how the balanced training approach equipped him fully with all the knowledge and skills he needs to run his business. “I learned different ways of record keeping, managing income and treating my clients professionally,” he says.
“On the machinery side, I learned about of all the parts of a two-wheel tractor and practiced assembling the engine so that maintenance and repair will be easy for me.”
Julius Shava, another participating service provider, agrees, adding that knowing how to maintain the two-wheel tractor and troubleshooting will also minimize costs of hiring external mechanics to attend to faults. “I realized the importance of routine checks for oil and water levels, how to crank-start the tractor and hitch the planter all by myself.”
Supporting agricultural extension in line with service providers is critical to mainstreaming transformational change in rural areas. As such, seven local extension officers — key partners in the implementation of small-mechanization activities — were also invited to participate in the training.
“The training proved to be very effective, particularly the emphasis on mastering business principles and on the technical side, integrating service providers’ existing knowledge of conservation farming with small-mechanization,” says Canaan Zhakata, an extension officer for Ward 15.
Through the practical sessions, all service providers have now learned how to operate a two-wheel tractor, calibrate the direct planter for seed and fertilizer rates and use the sheller — giving them full technical skills and knowledge,” explains Dorcas Matangi, a research associate at CIMMYT.
The certification they have received will increase farmers’ confidence as they return to Masvingo to commence service delivery, with continued on-site support from their local extension officers. “Once we return to Masvingo, we can assist the new service providers by monitoring their service delivery to ensure full compliance with the technical requirements for operating the machinery,” says Tsvakai Dumbu, an extension officer for Ward 17.
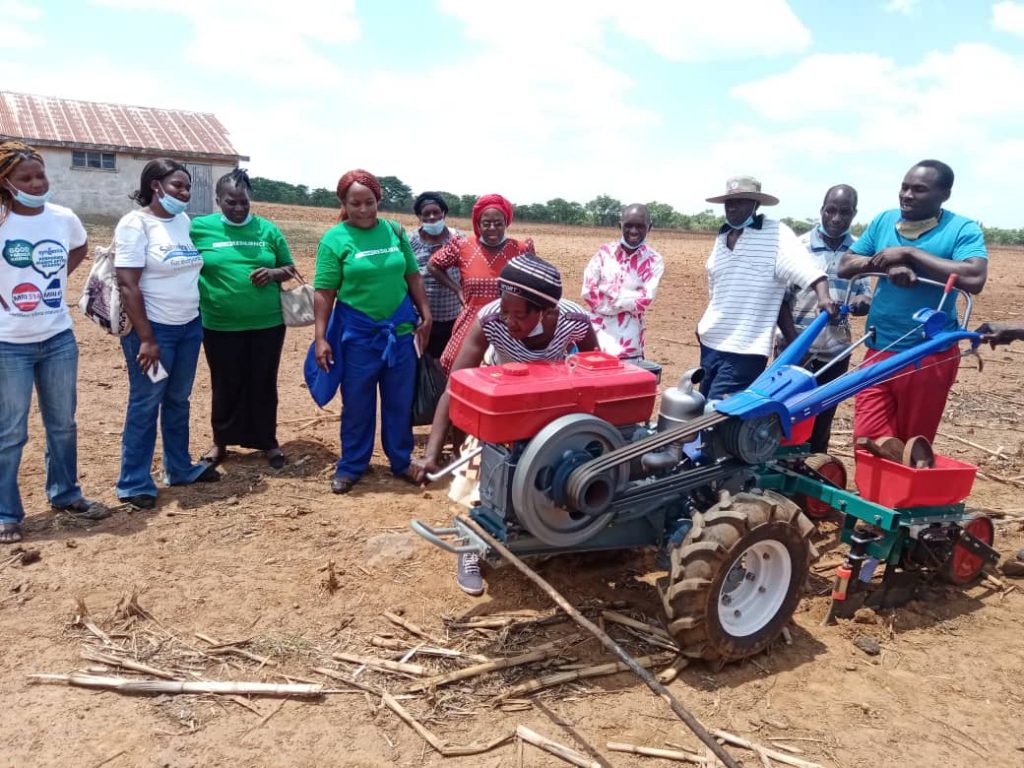

A profitable business for the local economy
This mechanization pilot is poised for success as it draws on existing positive results gained by the women and youth service providers in western Zimbabwe, who are running successful mechanized enterprises following the recently completed Farm Mechanization and Conservation Agriculture for Sustainable Intensification (FACASI) project.
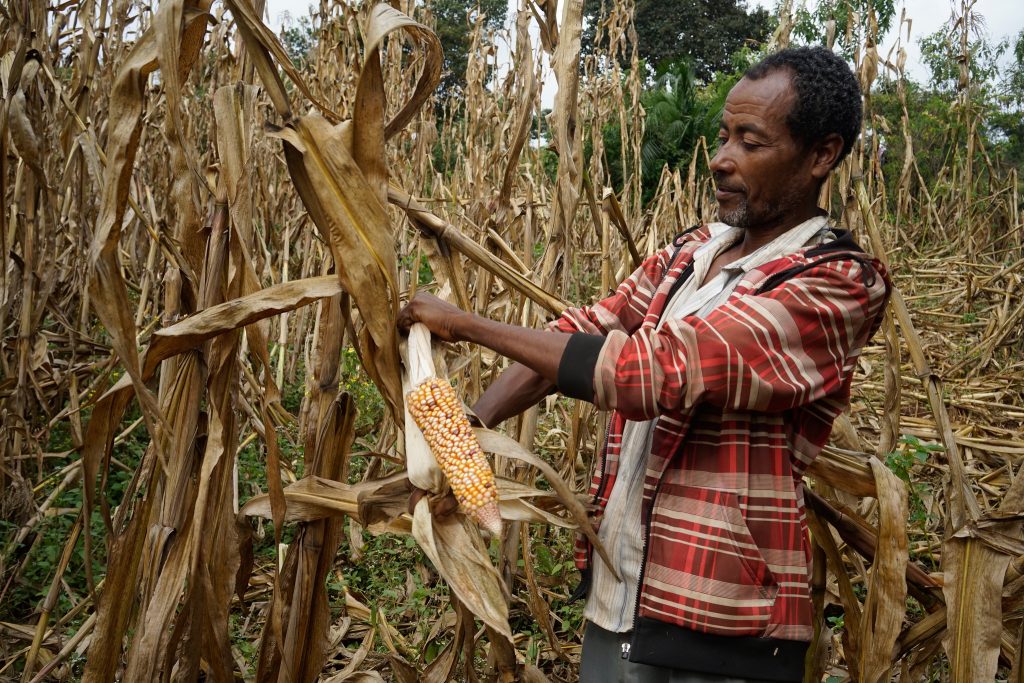
“During a recent seed fair, we heard of a youth group in Makonde that is making up to $7,000 just from maize shelling services,” says Zvovovo. “Knowing that it takes just one day to shell up to three tons of maize with the sheller, I now know that reaching such an income is achievable.”
This pilot will prove that there is scope for small-mechanization to expand on productivity through the two-wheel tractor, trailer and sheller, as shown in other parts of eastern and southern Africa. It will explore leverages on the opportunities and demand for services in Masvingo.
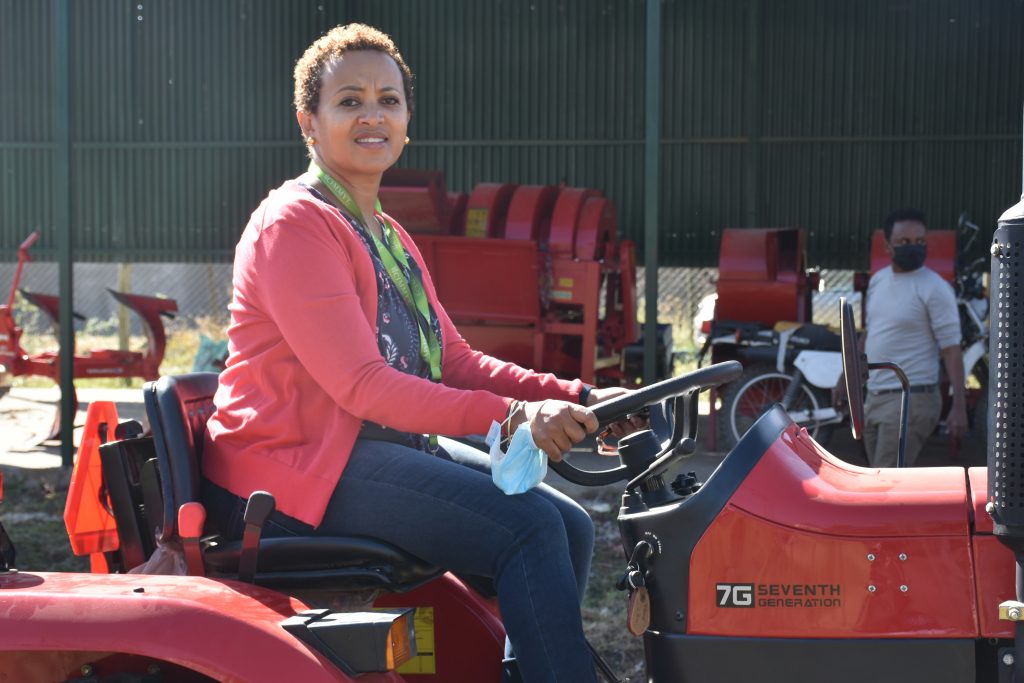
Cover image: An extension officer from Masvingo district drives a two-wheel tractor during a training for service providers and extension officers at Gwebi Agricultural College, Zimbabwe. (Photo: Shiela Chikulo/CIMMYT)