FFAR’s food security webinar at COP27 highlights need for genebank collection diversity research

As part of the Agriculture Innovation Mission for Climate (AIM for Climate) Roadshow at the 27th annual UN Climate Change Conference of the Parties (COP27), the Foundation for Food & Agriculture Research (FFAR) and its partners are hosting a webinar on November 11, 2022 to highlight the Fast Tracking Climate Solutions from CGIAR Genebank Collections program and the importance of crop improvement research for building climate resilient supply chains.
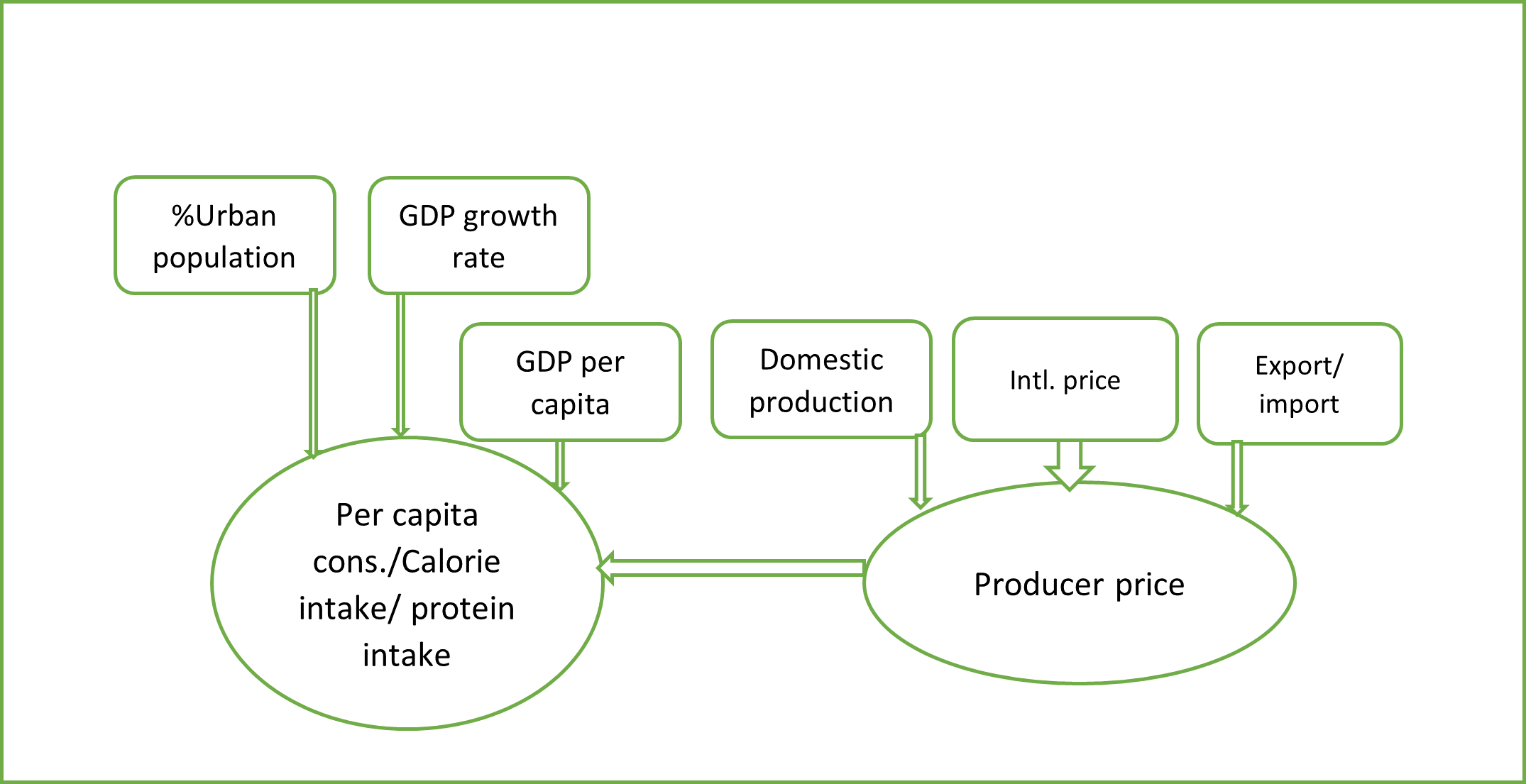
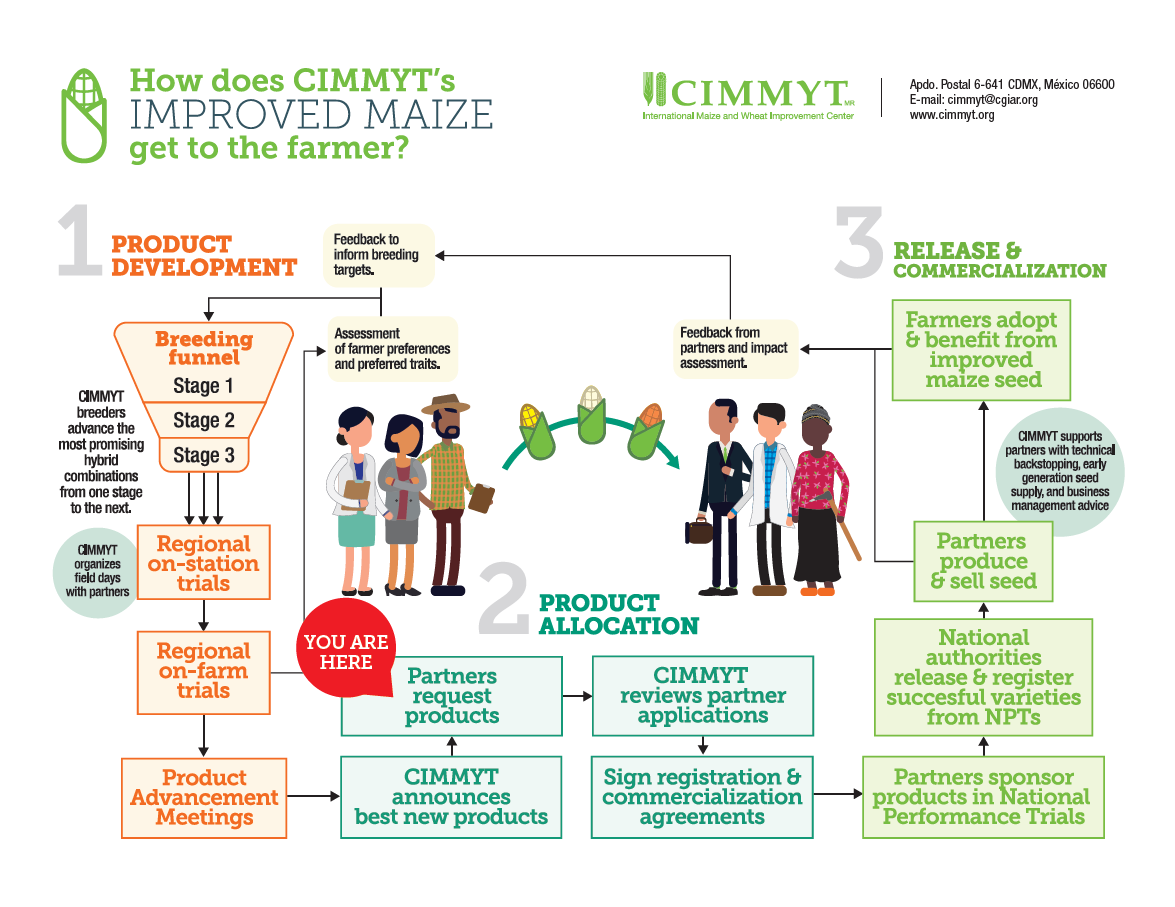
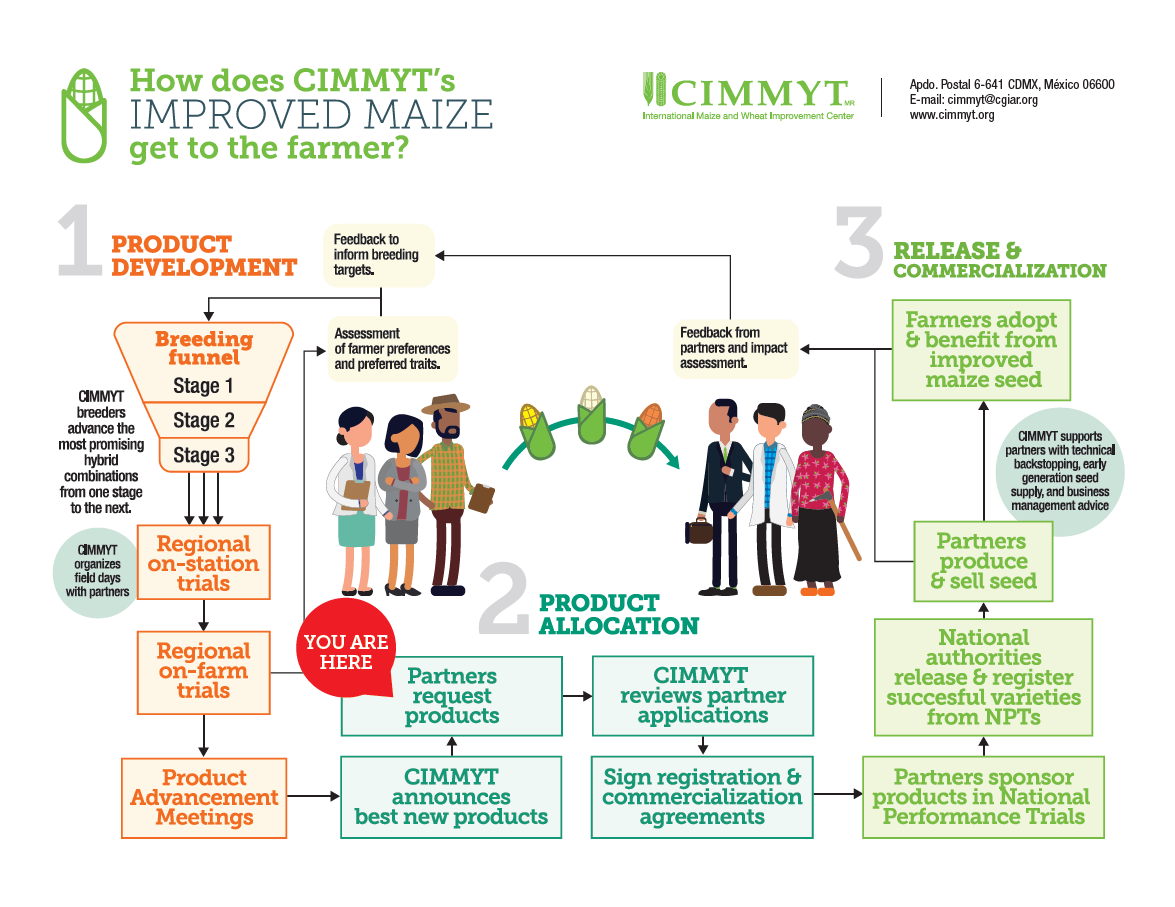
Fast Tracking Climate Solutions from CGIAR Genebank Collections is expanding CGIAR’s and other organizations’ crop improvement research. This initiative is key to developing new crop varieties adapted to the stresses of climate change, including disruptions caused by drought, heat and flooding. Through this ambitious research program, scientists have already developed critical traits using the genebanks, strengthening the identification of high-value genetic diversity from germplasm collections and more efficiently leveraging this diversity to develop new varieties of climate-resilient crops.
Join virtually to learn more about this program’s pioneering research, the value of collaboration in this research and opportunities to engage further.
WHEN: November 11, 2022, from 11 a.m. to 12 p.m. EST
WHO: Jeffrey Rosichan, FFAR (moderator)
Bram Govaerts, director general a.i. (secretary general and CEO), the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), CGIAR
Éliane Ubalijoro, member of the Global Diversity Crop Trust executive board, Global Crop Diversity Trust
Gary Atlin, senior program officer in the agricultural development initiative, Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation
Sarah Hearne, principal scientist, CIMMYT, CGIAR
RSVP: Please register for the webinar to receive call-in information. This event is free and open to the public.
AIM for Climate is a joint initiative by the United States and United Arab Emirates seeking to address climate change and global hunger. The initiative brings together partners to increase investment in climate-smart agriculture and food systems innovation. Specifically, AIM for Climate is advancing research through Innovation Sprints. As an AIM for Climate Knowledge Partner and an Innovation Sprint Partner, FFAR has two other Innovation Sprints in addition to the genebanking project: AgMission and the Greener Cattle Initiative.
For more information, contact Jamie Nickel, communications & legislative affairs associate, at jnickel@foundationfar.org.
About the Foundation for Food & Agriculture Research
The Foundation for Food & Agriculture Research (FFAR) builds public-private partnerships to fund bold research addressing big food and agriculture challenges. FFAR was established in the 2014 Farm Bill to increase public agriculture research investments, fill knowledge gaps and complement USDA’s research agenda. FFAR’s model matches federal funding from Congress with private funding, delivering a powerful return on taxpayer investment. Through collaboration and partnerships, FFAR advances actionable science benefiting farmers, consumers and the environment.
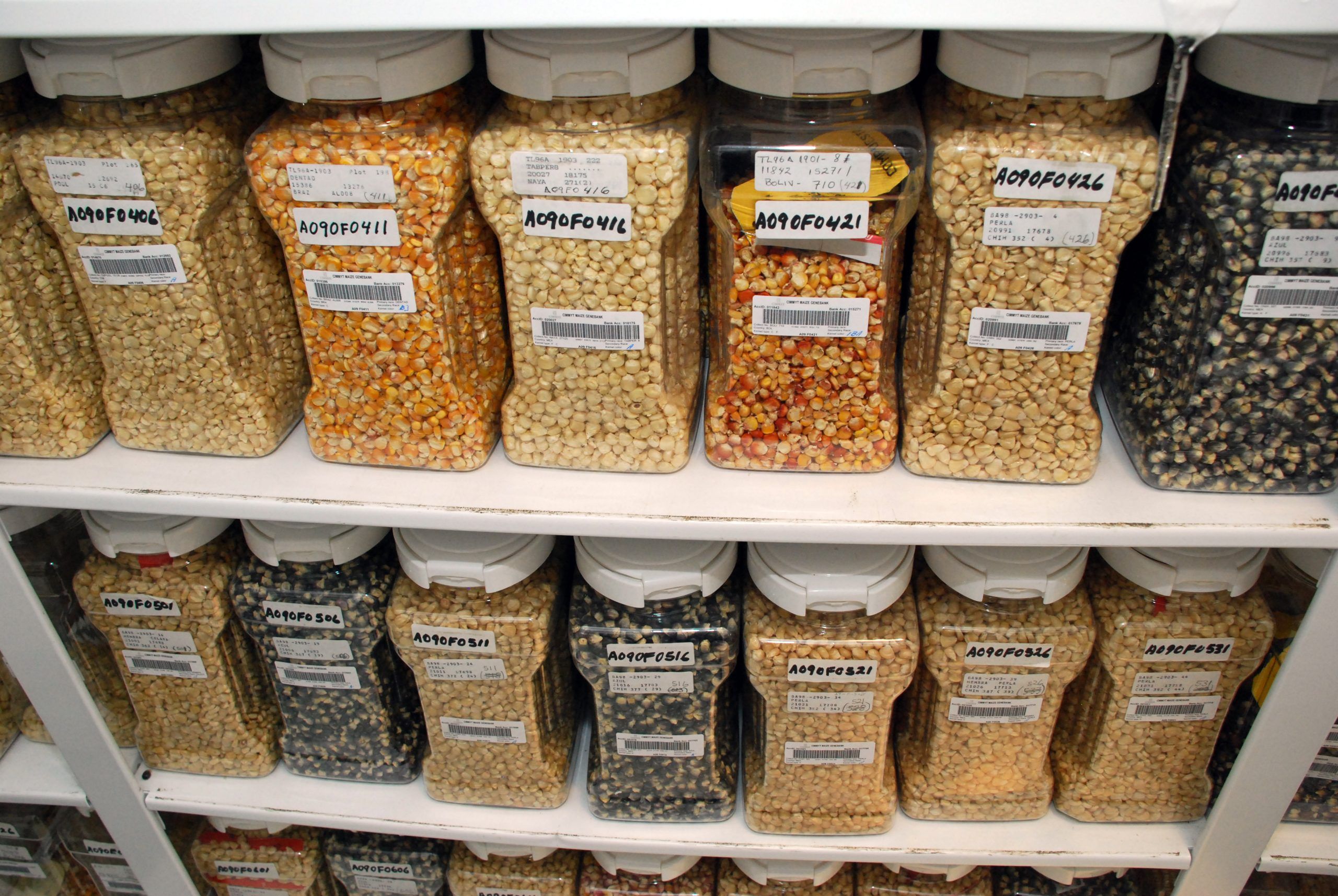
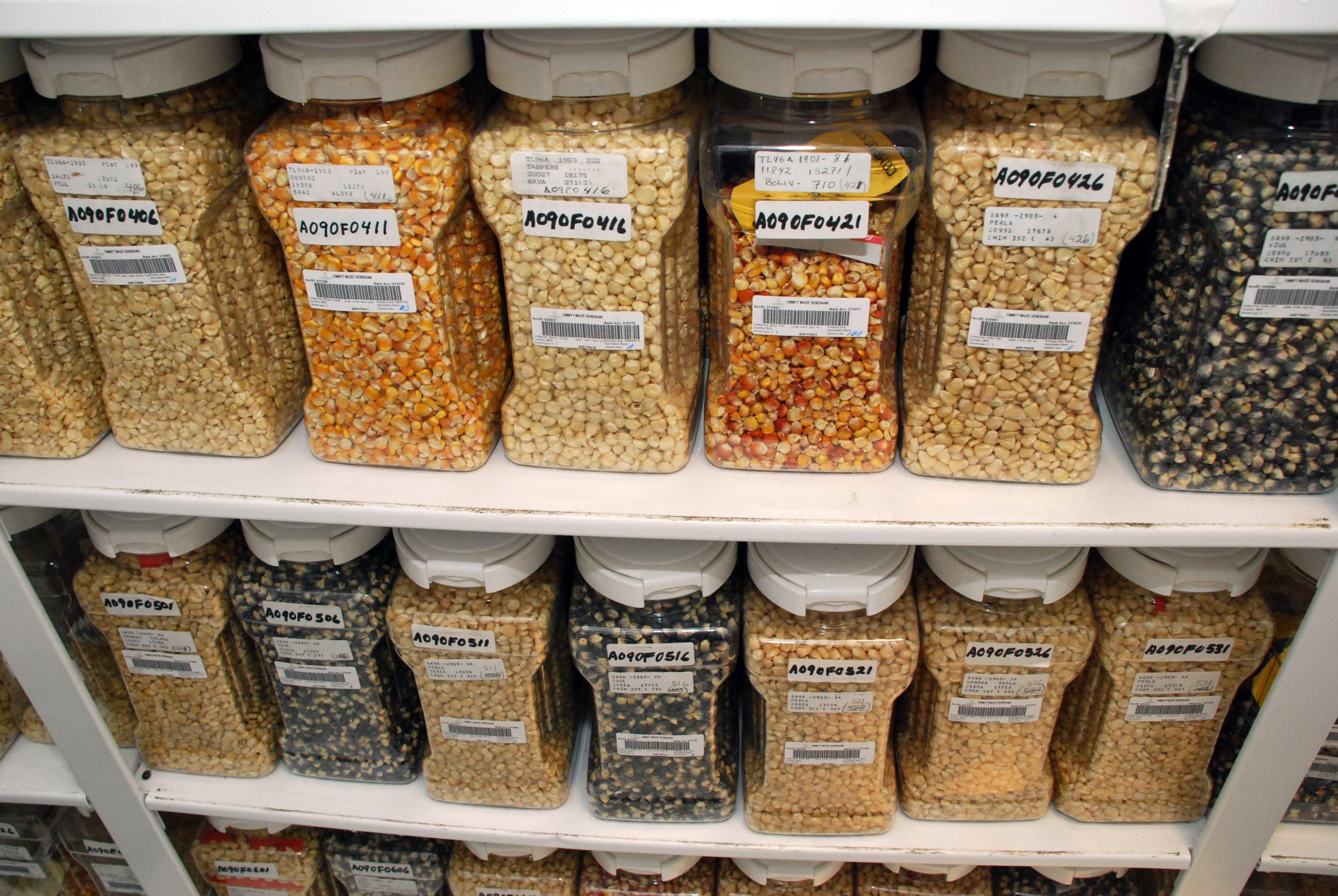
Cover photo: Shelves filled with maize seed samples make up the maize active collection in the Wellhausen-Anderson Plant Genetic Resources Center at CIMMYT’s El Batán headquarters, Mexico. (Photo: Xochiquetzal Fonseca/CIMMYT)