The perilous life of aphids fascinates South Asian crop scientists

Among the world’s most destructive and hated crop pests, the sap-sucking insects known as aphids are engaged in dramatic evolutionary battles with predators that include wasps whose larvae hatch and pupate in aphid bodies, devouring them from inside.
Rather than a new science fiction/horror film, this scenario is actually the basis for innovative pest control, as described by topic experts at two presentations of their interactive program “Aphids and their biological control on wheat, barley and maize” for wheat scientists in India and Nepal on 24 and 26 November 2014.
“The 34 participants, including 26 in Nepal and 8 in India, heard short lectures on maize and wheat aphids and other insect pests, followed by videos on aphid biology and their biological control,” said Arun Joshi, CIMMYT wheat breeder based in Nepal who helped organize the programs, in conjunction with the Indian Institute of Wheat and Barely Research (IIWBR) of the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) at Karnal and the Nepal Agricultural Research Council (NARC). “They learned about the special traits of the biological control agents that can be used in South Asia, as well as how to rear and spread them in crop fields, with the idea of training farmers in these skills.”

The main presenter, Prof. Urs Wyss, Institute of Phytopathology, University of Kiel, Germany, has produced over 70 films on insect pest biology and bio-control. Prof. Chandra Prakash Srivastava, Head, Department of Entomology, Banaras Hindu University, India, spoke to both groups about maize and wheat insect pests and their management.
“This is the first program on wheat insect pest management and biological control at IIWBR (former DWR, Karnal) in two decades,” said Dr. Indu Sharma, IIWBR project director. Joshi said that NARC colleagues made similar comments in praise of the program.
The training program was organized in response to mounting evidence of crop damage from aphids in Peninsular and northwestern India and the Terai and Midhills of Nepal. It was conducted at IIWBR, Karnal, through Dr. Indu Sharma and Dr. M.S. Saharan and in Nepal through Dr. Yagya Prasad Giri, Head, Entomology, NARC.
Other institutions represented in India included:
- Chandra Shekhar Azad University of Agriculture and
Technology, Kanpu. - Agriculture Research Station, Niphad, Maharashtra.
- Agriculture Research Station, Durgapura, Rajasthan.
- Centre of Excellence for Research on Wheat, S.D.
- Agriculture University, Vijapur, Gujrat.
- Punjab Agriculture University, Ludhiana.
- G.B. Pant Univ. of Agriculture and Technology,
Pantnagar. - Assam Agricultural University, Shillongani, Nagoan.
Uttar Banga Agriculture University, West Bengal.
In Nepal participants came from:
- The Department of Entomology, National Agriculture
Research Institute, Khumaltar. - National Wheat Research Program (NWRP),
Bhairahwa. - National Maize Research Program (NMRP), Rampur.













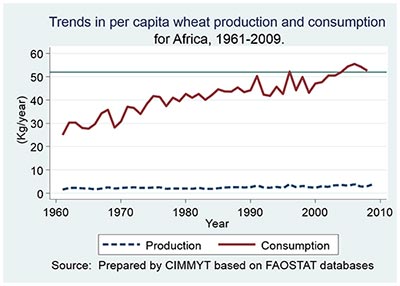







 The CIMMYT community celebrates the illustrious life and mourns the passing on 11 December of Wilfred M. Mwangi, distinguished Kenyan scholar, statesman and researcher who dedicated his career to improving the food security and livelihoods of farmers in sub-Saharan Africa. In 27 years at CIMMYT, Mwangi made significant contributions both as a principal scientist and distinguished economist with authorship on nearly 200 publications, as well as country and regional liaison officer, associate director of the global maize program, leader of the Drought Tolerant Maize for Africa (
The CIMMYT community celebrates the illustrious life and mourns the passing on 11 December of Wilfred M. Mwangi, distinguished Kenyan scholar, statesman and researcher who dedicated his career to improving the food security and livelihoods of farmers in sub-Saharan Africa. In 27 years at CIMMYT, Mwangi made significant contributions both as a principal scientist and distinguished economist with authorship on nearly 200 publications, as well as country and regional liaison officer, associate director of the global maize program, leader of the Drought Tolerant Maize for Africa (
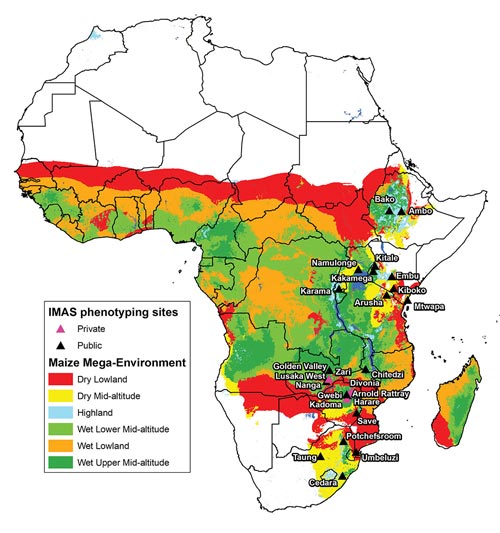 A public-private partnership that, along with CIMMYT, involves national research organizations such as the Kenya Agricultural & Livestock Research Organization (
A public-private partnership that, along with CIMMYT, involves national research organizations such as the Kenya Agricultural & Livestock Research Organization (