Training on quarantine pests of wheat in Ethiopia

Ethiopia’s loose quarantine system permits the introduction of foreign pests, which attack crops and hurt yields and farmer incomes, making understanding how to identify new pests vital; strengthening the national quarantine system is thus key to protecting crops.
To address these challenges, CIMMYT-Ethiopia hosted a training session on the quarantine of wheat pests in Ethiopia from 13-15 October at Holetta Agricultural Research Center, where seeds of the most commonly introduced germplasm are inspected before they are planted and further evaluated for foreign pests at isolation sites throughout the country. Attending the session were 13 trainees from Holetta and six other research centers, including Sinana, Kulumsa, Adet, Mekele, Werer, and Ambo.
Temesgen Desalegn, Holetta Agricultural Research Center Director, welcomed participants and delivered an orientation session about the center, staff, and the crop and livestock research conducted at the site. The center is the oldest quarantine site to receive and inspect seeds of introduced germplasm for foreign pests by further planting and evaluating at isolated sites, Desalegn said, explaining that his aims for the training included exploring various aspects of regulatory issues.
Bekele Abeyo, wheat breeder and country representative at CIMMYT’s Ethiopia office, highlighted the role of wheat in the Ethiopian economy, describing major growing regions and production trends. He also described the challenge of recurrent rust epidemics that cause significant yield losses, and how such losses affect the country’s growth and transformation plan aimed at achieving food security. Due to the significant yield losses caused by the rust epidemics, CIMMYT and its national counterparts, the Ethiopian Institute of Agricultural Research (EIAR) and Regional Agricultural Research Institutes (RARIs), developed a project, now in its first year, titled “Seed Multiplication and Delivery of High Yielding Rust Resistant Bread and Durum Wheat Varieties to Ethiopian Farmers.”
The project, which targets 51 districts in four regions, has two sub-components, five specific objectives, and several activities under each objective. It supports small-scale farmers with an emphasis on women, encourages private sector partners, and links farmers with industries. It also aims to build the capacity of national programs by acquiring field and laboratory equipment and conducting various types of short-term trainings sponsored by the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) and the CIMMYT/EIAR seed project.
Eshetu Derso, Deputy Director of crops research at EIAR, offered praise for such training and the long-lasting relationship and support CIMMYT has provided. He mentioned that CIMMYT staff are forging change by helping Ethiopia identify and bridge gaps. Eshetu detailed various components of phytosanitary/regulatory issues regarding quarantine and pests in Ethiopia, including recent phytosanitary proclamations in the country. Finally, he noted that awareness will be created and vigilant phytosanitary action taken to ensure no new foreign pests are introduced. All plant materials introduced into Ethiopia will be inspected by quarantine officials at international airports or seaports by establishing separate “plant quarantine counters” and a scanning system.

The government is trying to keep out quarantine diseases such as ergot, late potato blight, and Karnal bunt, Eshetu said, mentioning other risky diseases such as the wheat rusts, white rot in garlic, maize lethal necrosis, yellow mosaic virus in papaya, ginger bacterial leaf wilt, and fruit spot of citrus. All these diseases have either been introduced into Ethiopia or have the potential to be introduced, he said.
CIMMYT pathologist Monica Mezzalama conducted an introductory training course on seedborne diseases of wheat, including detection methods, diagnosis, epidemiology, and management of fungi, bacteria, and viruses. She coupled descriptions with hands-on practice observing fungal, bacterial, and viral diseases of wheat in quarantine fields; leaf sampling and sample preparation; and laboratory work on isolation techniques (leaf and seed). She also covered MLN, the major threat to maize production in recent years.
Mohammed Dawd, Head of quarantine at EIAR, and Bekele Kassa, plant pathologist at Holetta Agricultural Research Center, offered insights and conducted training on pests and quarantine diseases in Ethiopia.
Participants raised many concerns related to the skills gap that hinders proper handling of quarantine services, limited training opportunities, and the lack of guidance from senior scientists and management. They emphasized the importance of keeping up expertise on threats and risks posed by quarantine pests and concluded that current weak quarantine enforcement in Ethiopia should be bolstered by strictly implementing rules and regulations to prevent the introduction of unauthorized and uncertified germplasm.

 WPEPs Annual Planning Meeting-3The Wheat Productivity Enhancement Program (WPEP), funded by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), held its annual wheat planning meeting organized by Pakistan Agricultural Research Council (PARC) and CIMMYT on 8-10 September 2015 in Islamabad.
WPEPs Annual Planning Meeting-3The Wheat Productivity Enhancement Program (WPEP), funded by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), held its annual wheat planning meeting organized by Pakistan Agricultural Research Council (PARC) and CIMMYT on 8-10 September 2015 in Islamabad.


 Martin Kropff, CIMMYT Director General, emphasized CIMMYT’s achievements and new ways forward during a talk commemorating his first 100 days as DG, at CIMMYT headquarters in El Batбn, Mexico, on 20 October 2015.
Martin Kropff, CIMMYT Director General, emphasized CIMMYT’s achievements and new ways forward during a talk commemorating his first 100 days as DG, at CIMMYT headquarters in El Batбn, Mexico, on 20 October 2015.









 SYDNEY, Australia, October 9 (CIMMYT) – A recent gathering of more than 600 international scientists highlighted the complexity of wheat as a crop and emphasized the key role wheat research plays in ensuring global food security now and in the future.
SYDNEY, Australia, October 9 (CIMMYT) – A recent gathering of more than 600 international scientists highlighted the complexity of wheat as a crop and emphasized the key role wheat research plays in ensuring global food security now and in the future. EL BATAN, Mexico (CIMMYT) – Gains in China’s agricultural productivity over the past 30 years are due in large measure to smallholder farmers who have readily adopted innovative farming practices introduced by scientists, said a top wheat breeder during a speech at the country’s annual Friendship Awards.
EL BATAN, Mexico (CIMMYT) – Gains in China’s agricultural productivity over the past 30 years are due in large measure to smallholder farmers who have readily adopted innovative farming practices introduced by scientists, said a top wheat breeder during a speech at the country’s annual Friendship Awards.
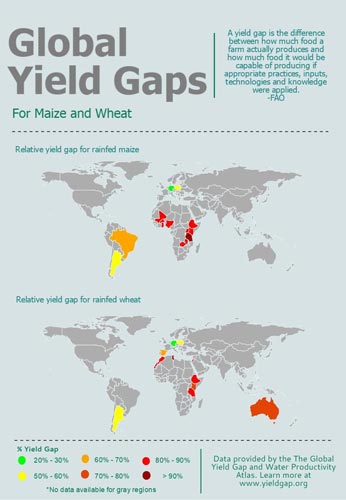 A
A 