Essential actions to mitigate the food crisis, stabilize supply and transition to greater agrifood system resilience

As the Russia-Ukraine war continues to degrade global food security, a new analysis lays out concrete actions that governments and investors must do now to mitigate near-term food security risks and stabilize wheat supplies, while transitioning toward long-term resilience.
The guidance, published in Nature Food by scientists from the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and partners, lays out short-, medium- and long-term steps to respond to the global food crisis and ultimately lead to a more resilient global agrifood system.
“The Russia-Ukraine war will impact global food security over months — if not years,” said CIMMYT Global Wheat Program Director and lead author Alison Bentley. “We now need to move beyond defining the problem to implementing practical actions to ensure stable supply, safeguard the livelihoods of millions of vulnerable people and bring resilience to our global agrifood system.”
The war in Ukraine and trade sanctions against Russia are triggering a level of volatility that could easily overwhelm existing mitigation mechanisms. More than 2.5 billion people worldwide consume wheat-based foods; those in lower- to middle-income countries dependent on imports from Russia and Ukraine are particularly affected. Some of the world’s poorest countries, such as Bangladesh, Sudan and Yemen, rely heavily on Russian and Ukrainian wheat. Given the highly interconnected nature of contemporary agrifood systems, few will remain unaffected by this new global food shock.
Mitigate the immediate crisis
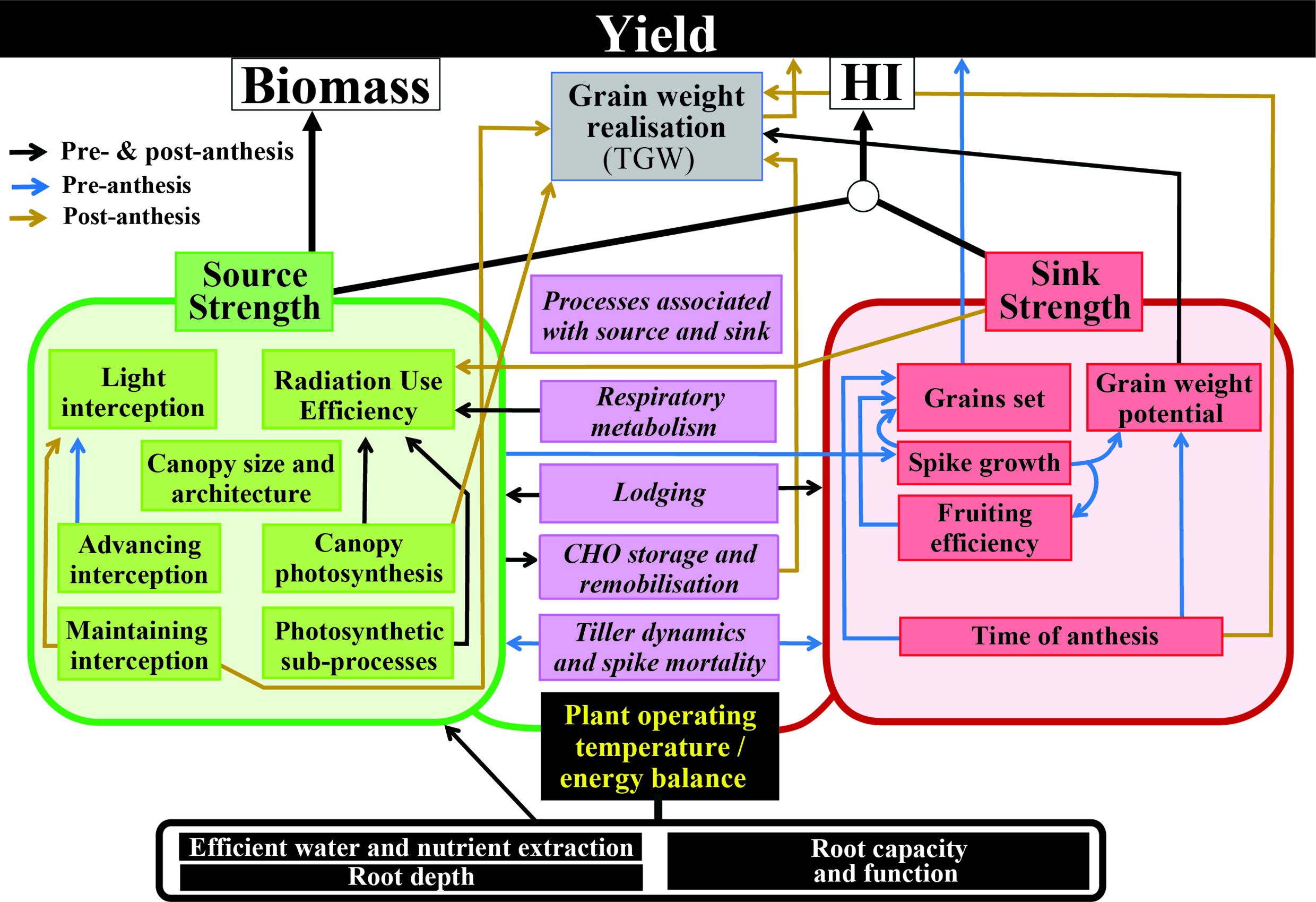
The first priority, according to the authors, is to mitigate the immediate crisis by boosting wheat production in existing high- and low-productivity areas, ensuring grain access and blending wheat flour with other low-cost cereals. Bundled agronomic and breeding improvements and sustainable farming practices can reduce dependence on imported grain and fertilizer, while coordinated, multilateral policies can help conserve grain stocks for human consumption and avert trade restrictions.
Increase the resilience of wheat supply
In the medium term, the authors emphasized the need to increase the local, regional, and global resilience of the wheat supply. This can be done by expanding production within agro-ecological boundaries, supporting national wheat self-sufficiency and providing technical assistance, to increase the production of high-yielding disease-resistant wheat and to mainstream capacity for pest and disease monitoring.
Transition to system-level resilience
Finally, to reach crucially needed resilience in the world’s agrifood system, long-term measures must be taken that encompass agroecosystem diversity, address gender disparities in agriculture and rural communities and sustain increased investment in a holistic, agrifood transition.
“The current global food crisis underscores and compounds existing inequalities in our global food system,” Bentley said. “A transition to agrifood system resilience requires us to urgently balance global food supply needs with the multi-layered challenges of climate change, achieving gender equity, nutritional sufficiency and livelihood security.”
RELATED RESEARCH PUBLICATIONS:
Near- to long-term measures to stabilize global wheat supplies and food security
This research is supported by CGIAR Trust Fund Contributors.
INTERVIEW OPPORTUNITIES:
Alison Bentley – Director, Global Wheat Program, International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT)
FOR MORE INFORMATION, OR TO ARRANGE INTERVIEWS, CONTACT THE MEDIA TEAM:
Marcia MacNeil, Head of Communications, CIMMYT. m.macneil@cgiar.org, +52 5558042004 ext. 2019.
Rodrigo Ordóñez, Communications Manager, CIMMYT. r.ordonez@cgiar.org, +52 5558042004 ext. 1167.
Ricardo Curiel, Communications Manager, CIMMYT. r.curiel@cgiar.org, +52 5558042004 ext. 1144.
ABOUT CIMMYT:
The International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) is an international organization focused on non-profit agricultural research and training that empowers farmers through science and innovation to nourish the world in the midst of a climate crisis.
Applying high-quality science and strong partnerships, CIMMYT works to achieve a world with healthier and more prosperous people, free from global food crises and with more resilient agrifood systems. CIMMYT’s research brings enhanced productivity and better profits to farmers, mitigates the effects of the climate crisis, and reduces the environmental impact of agriculture.
CIMMYT is a member of CGIAR, a global research partnership for a food secure future dedicated to reducing poverty, enhancing food and nutrition security, and improving natural resources.
For more information, visit staging.cimmyt.org.