New partnership announced to protect Gorongosa National Park in Mozambique by improving agricultural livelihoods and crop systems
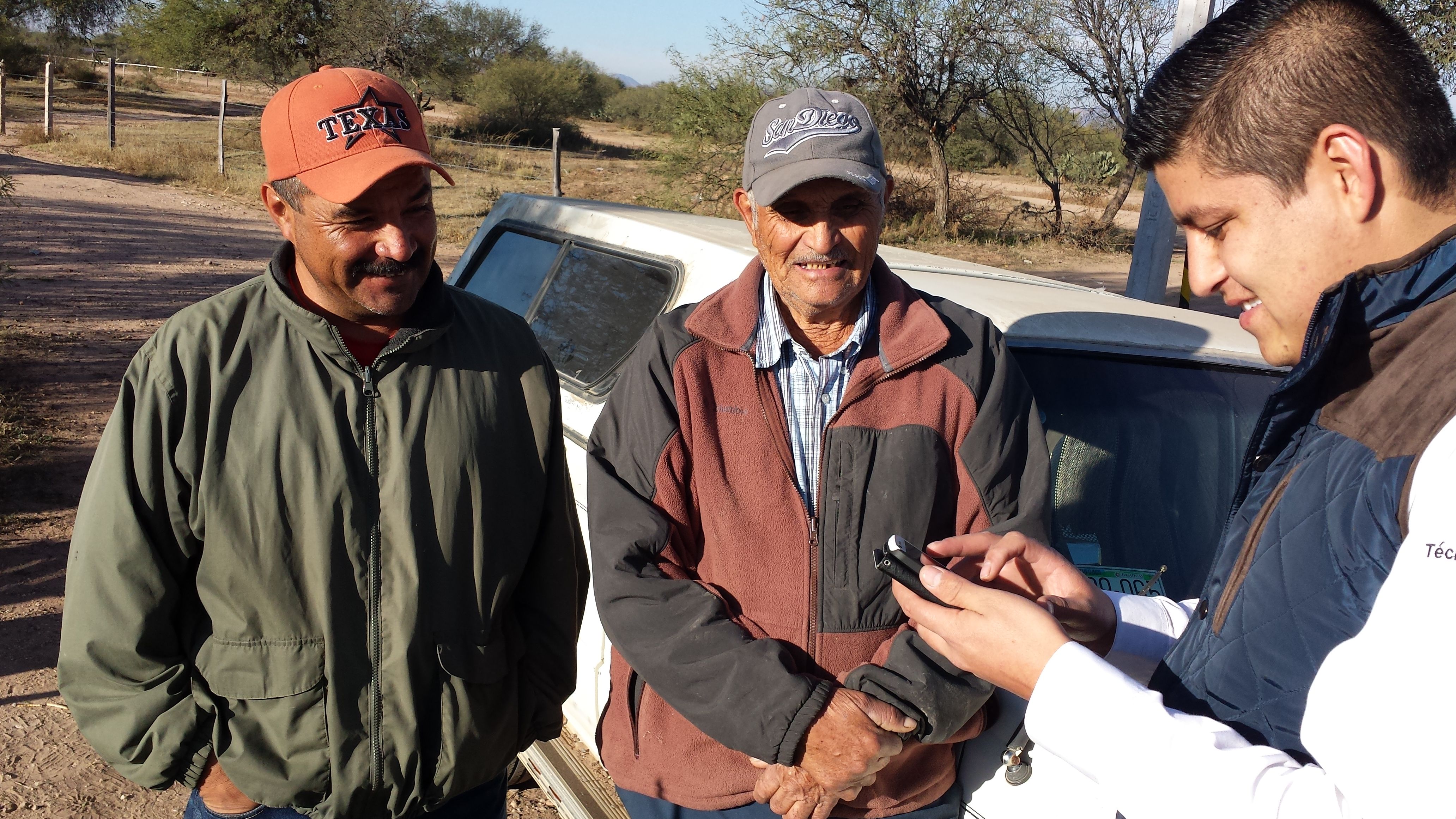
A collaboration scheme launched between the Gorongosa Restoration Project (GRP) and CIMMYT seeks to improve climate resilience, food security and nutrition in Mozambique’s Gorongosa National Park by facilitating the adoption of sustainable practices and giving local farmers access to formal markets and improved value chains.
The partner organizations aim to develop more resilient agrifood systems that contribute to conserve resources and improve the livelihoods of farmers inhabiting the protected area in Mozambique’s Sofala Province.
“Our primary objective is to establish an evidence-based, scalable and replicable model for developing sustainable and resilient agrifood systems in Mozambique that enhance food and nutrition security and climate resilience of local farmers and communities,” said Gregory C. Carr, GRP President.

The parties will explore collaboration opportunities to give local farmers access to drought tolerant and disease resistant varieties and improved seeds by building capacities of local seed systems.
“We are very excited to contribute to protect Gorongosa National Park by restoring soil health, accelerating a transition to resilience and sustainability and improving, as a result, the yields and living standards of local farming communities,” said Bram Govaerts, Director General at CIMMYT.
The new projects will also aim to promote agriculture conservation-based intensification practices that will increase yields sustainably and limit the expansion of the agricultural frontier in the buffer zone neighboring the protected area.
“If you bring two world class organizations together and create critical mass, it is possible to succeed and show that agriculture is not the enemy of biodiversity,” said the U.S. Special Envoy for Global Food Security, Cary Fowler.

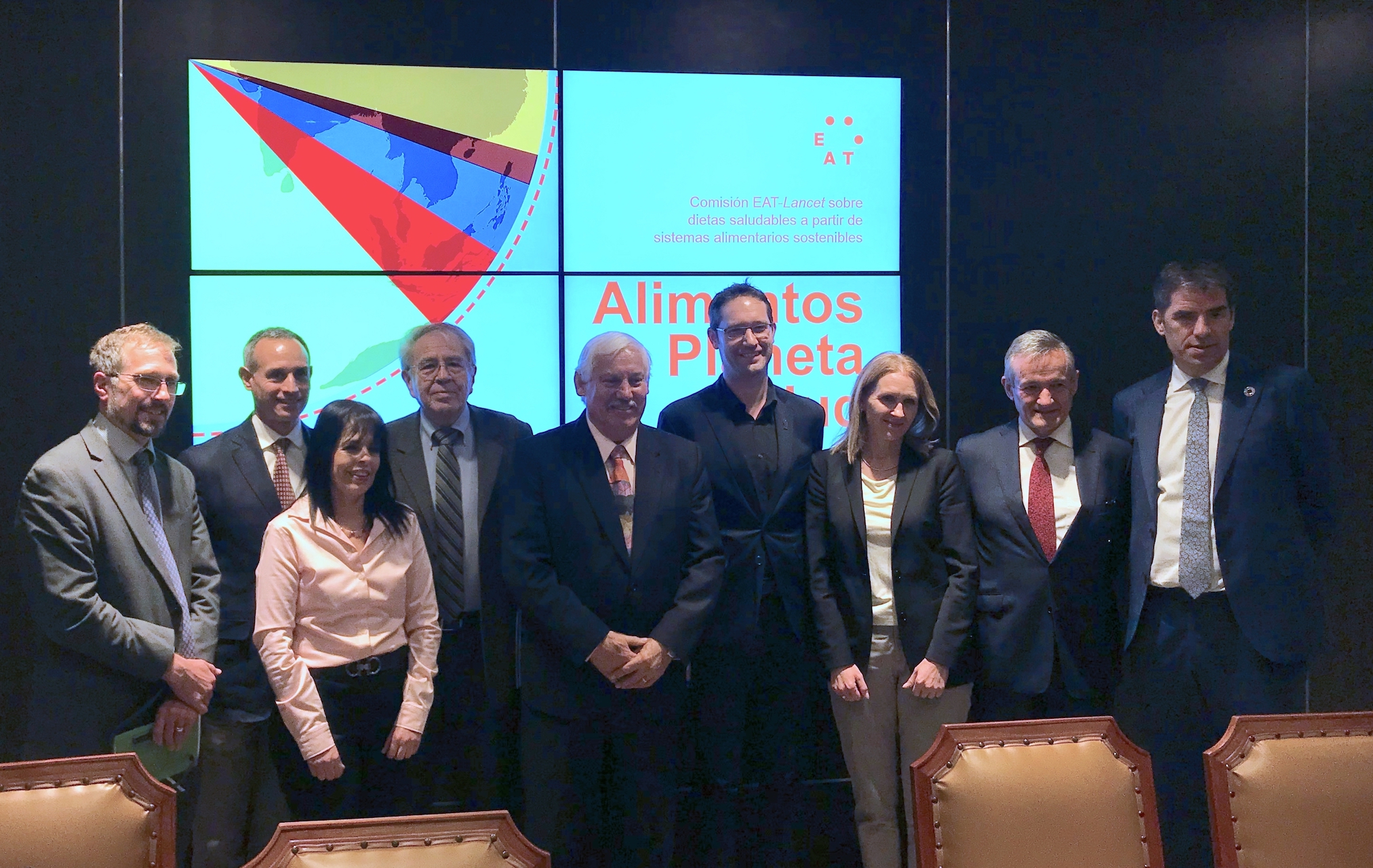
The 5-year Memorandum of Understanding was signed at the annual Borlaug Dialogue organized by the World Food Prize Foundation, which convenes international thought leaders, development specialists, researchers, farmers, practitioners and authorities from around the world to promote global food systems transformation and food security.
Under this year’s “Harnessing Change” theme, the Foundation presented the prestigious World Food Prize to Heidi Kühn from the United States for her farmer-focused development model that revitalizes farmland, food security, livelihoods and resilience in war-torn regions around the world as a way for restoring peace and prosperity through agriculture.
About GRP
Gorongosa Restoration Project is a poverty alleviation, sustainable development and conservation non-profit organization used by Gorongosa National Park as a development engine for the Sofala region. GRP is a unique organization, with a mission to advance an integrated, multi-partner approach to conservation and people-centered development. While GRP actively protects Gorongosa National Park’s biodiversity and ecosystems, it also strives to unlock its economic potential for the community inhabitants of the Park’s Buffer Zone, former hunting and forestry concessions, Sofala Province and further afield. GRPs dual mandate of biodiversity conservation and human development is undergirded by the principle that the quest for conservation is a human-nature dynamic that must be addressed holistically. This axiom is increasingly supported by conservation science as well as by GRP’s 15 years of experience in the field.
About CIMMYT
CIMMYT is a cutting edge, non-profit, international organization dedicated to solving tomorrow’s problems today. It is entrusted with fostering improved quantity, quality, and dependability of production systems and basic cereals such as maize, wheat, triticale, sorghum, millets, and associated crops through applied agricultural science, particularly in the Global South, through building strong partnerships. This combination enhances the livelihood trajectories and resilience of millions of resource-poor farmers, while working towards a more productive, inclusive, and resilient agrifood system within planetary boundaries.
CIMMYT is a core CGIAR Research Center, a global research partnership for a food-secure future, dedicated to reducing poverty, enhancing food and nutrition security and improving natural resources.
For more information, visit staging.cimmyt.org.
Press contact: Ricardo Curiel, Communications Manager to the Director General, CIMMYT, r.curiel@cgiar.org







 The 2021 Global Agricultural Productivity (GAP) Report warns that farmers and food workers globally face the intimidating challenge of producing food sustainably in a degrading environment. The global economic slowdown and climate change are making the situation even more difficult.
The 2021 Global Agricultural Productivity (GAP) Report warns that farmers and food workers globally face the intimidating challenge of producing food sustainably in a degrading environment. The global economic slowdown and climate change are making the situation even more difficult.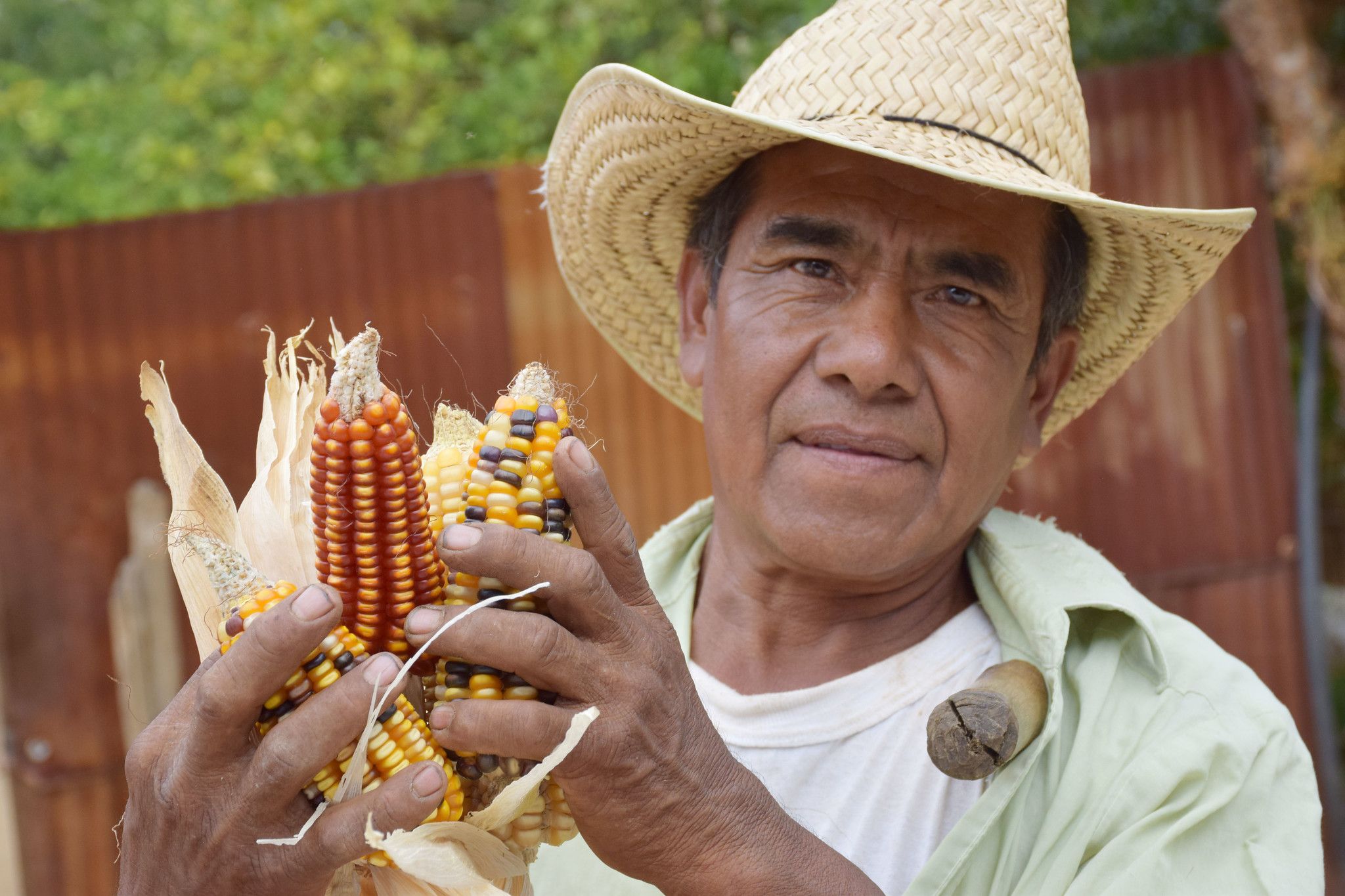
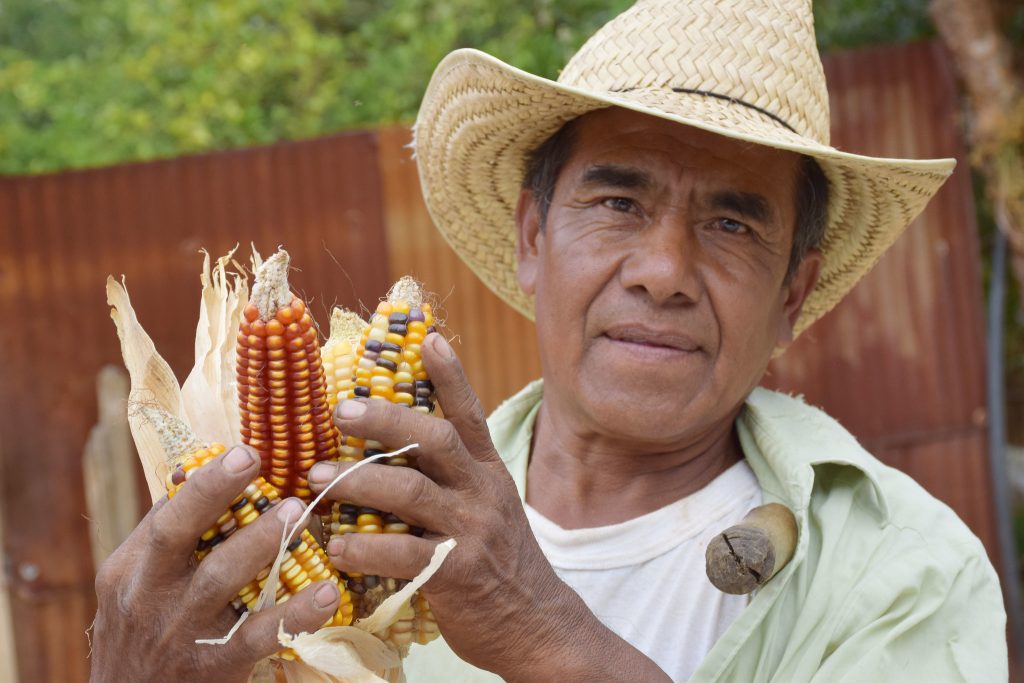
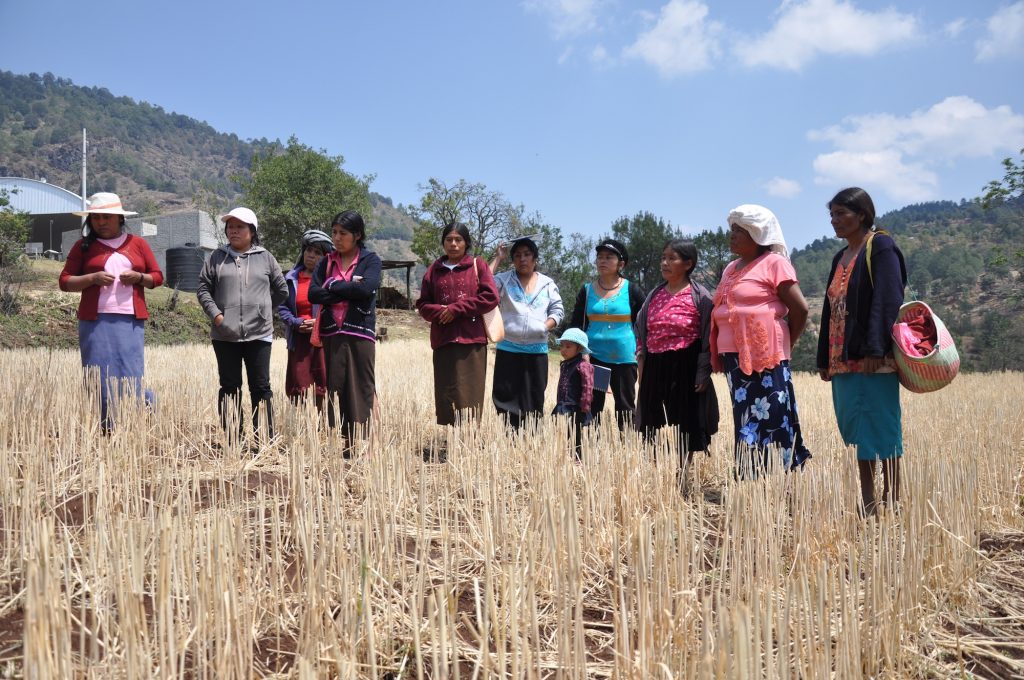


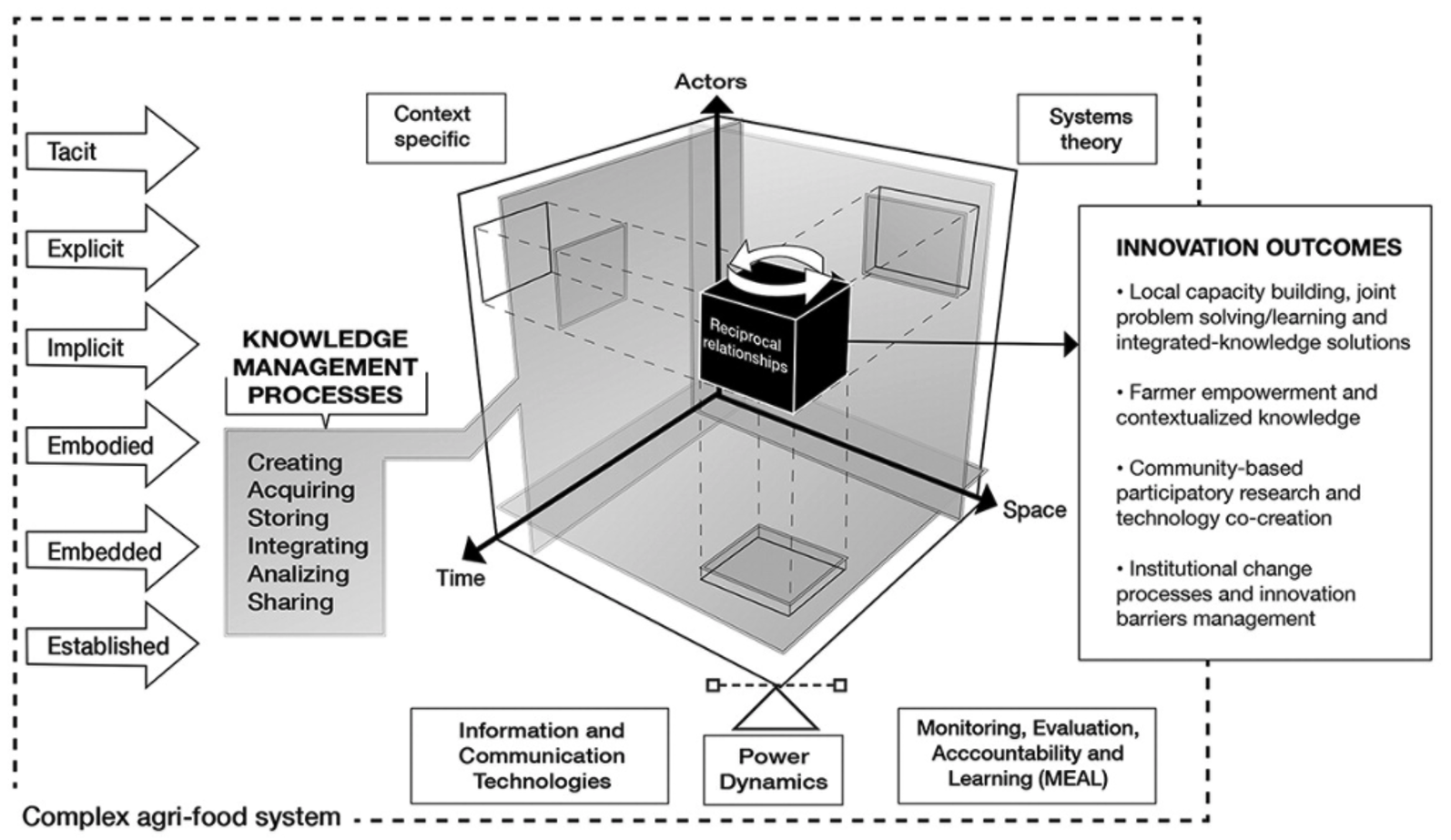
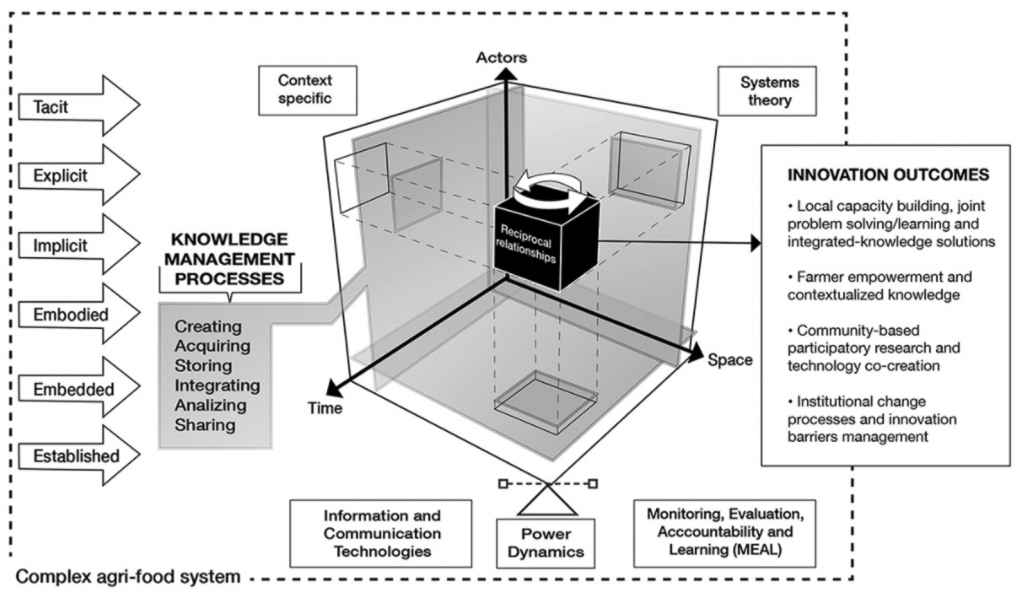
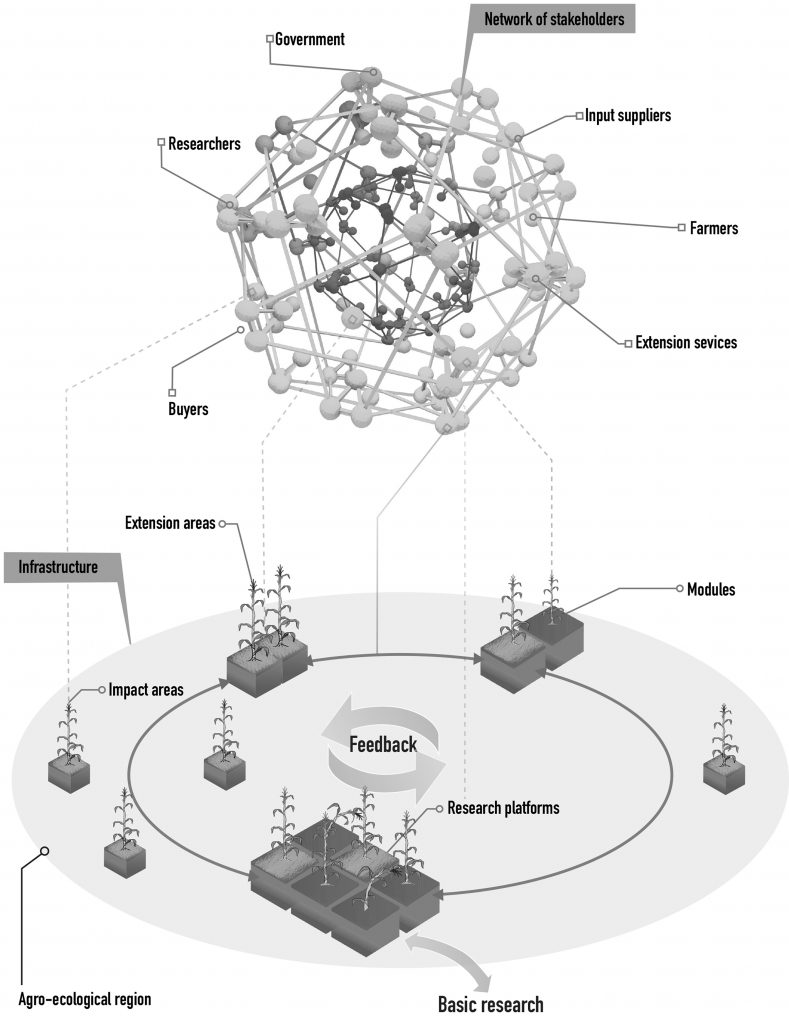




 The World Food Prize Foundation is honoring the work of Rattan Lal, who dedicated his life to study the effect of soil health in food production and climate change mitigation. On October 15 he will receive the 2020 World Food Prize, considered the “Nobel Prize” of agriculture.
The World Food Prize Foundation is honoring the work of Rattan Lal, who dedicated his life to study the effect of soil health in food production and climate change mitigation. On October 15 he will receive the 2020 World Food Prize, considered the “Nobel Prize” of agriculture.











