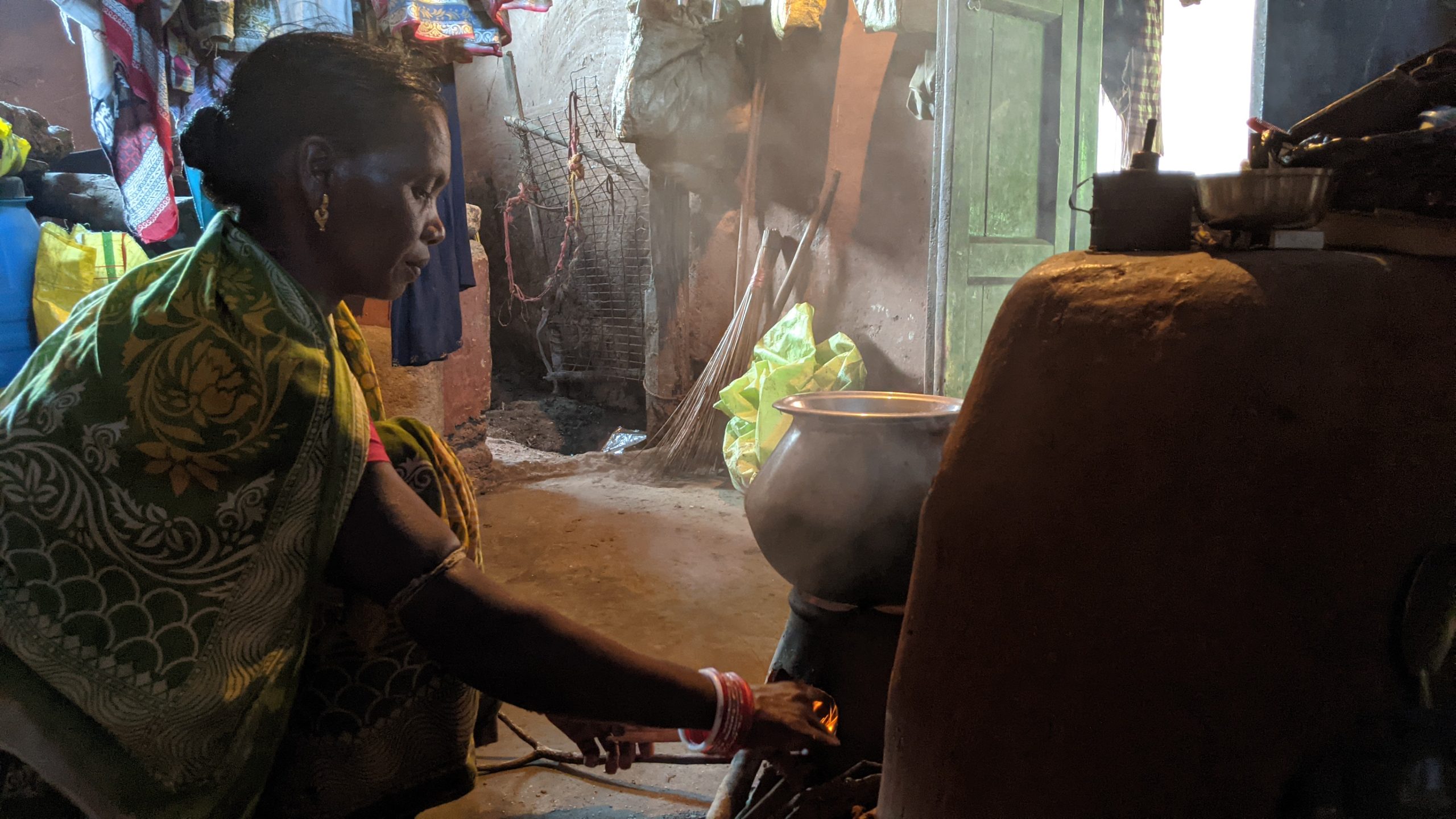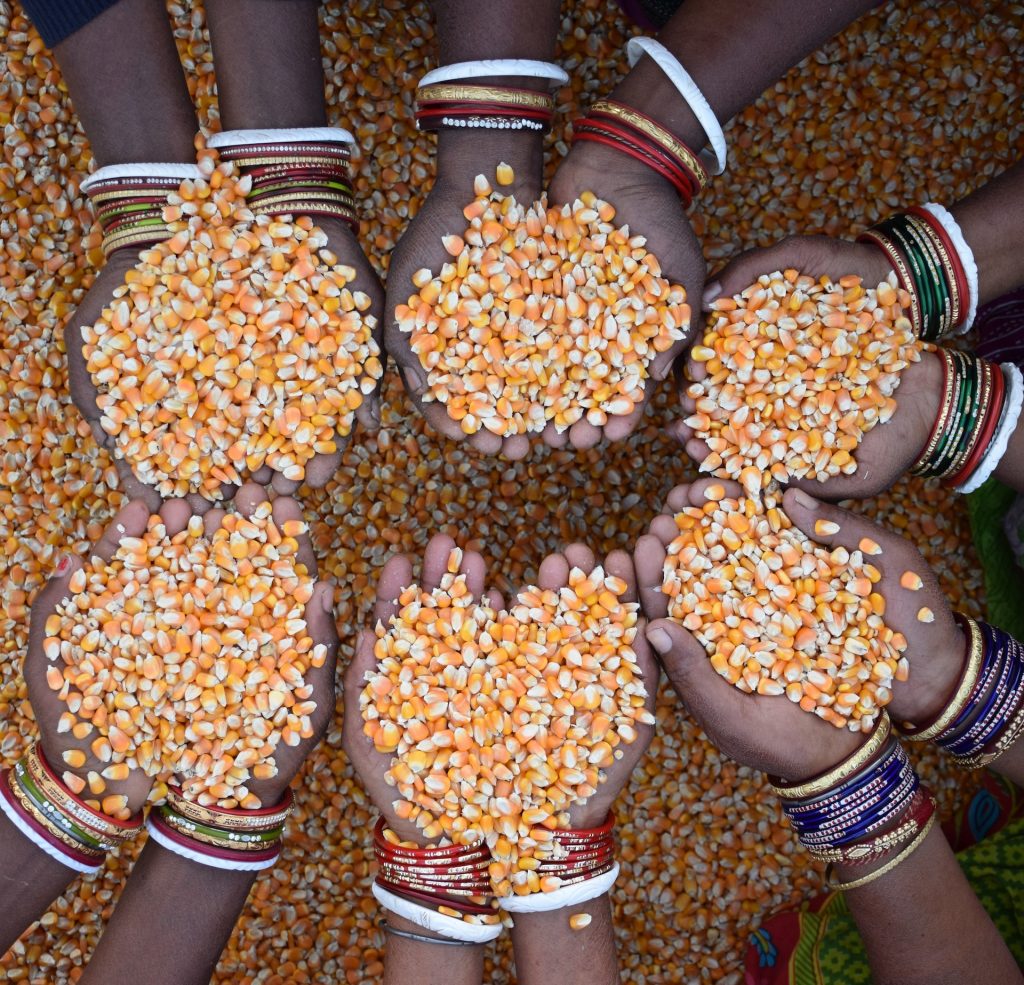Being the change you wanted to see as a young girl
In the traditional Indian society Madhulika Singh grew up in, girls choosing to study science, technology, engineering or mathematics (STEM) was as radical as choosing a life partner on their own.
“They say women hold up half the sky. I believe they should hold up as much and contribute equally in STEM too,” says Singh, now an agriculture specialist at the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT).
In her early teens she saw her mother, a school headmaster, comfortably navigate her career along with her domestic responsibilities without a sweat. She later saw a similar example in her sister-in-law. “I grew up thinking ‘there is so much that a woman is capable of,’ whether at home or her workplace,” Singh recalls.
This strong idea of women’s potential led her to pursue studies in science. “Many women before me, like my mother’s generation, were encouraged to take up [careers in] humanities — become a teacher, or pursue home management courses — to ensure a smooth transition once married,” Singh explains. She hoped this would change during her time and that following a career in STEM would be a matter of choice — not gender.
Singh’s goals and ambitions were very clear from the very beginning. In school, she was interested in biology, particularly plant studies and botany. Her inquisitive nature was reflected in her projects and presentations, scoring her high grades. She demonstrated a thorough understanding of plant physiology and her passion for the subject. The budding scientist always wanted to know more and to do more, which Singh feels resonates with her current research and publications.
A popular quote attributed to Mahatma Gandhi says “Be the change you want to see in the world.” When Singh chose to take up plant science in graduate school and then agriculture science for her doctorate, she became the change she had hoped to see in her home and society as a young girl. With the support from her family but a skeptical society, she went ahead and pursued a career in STEM, beginning her research on maize genotypes and conservation agriculture. In 2013 she joined CIMMYT as a physiologist.
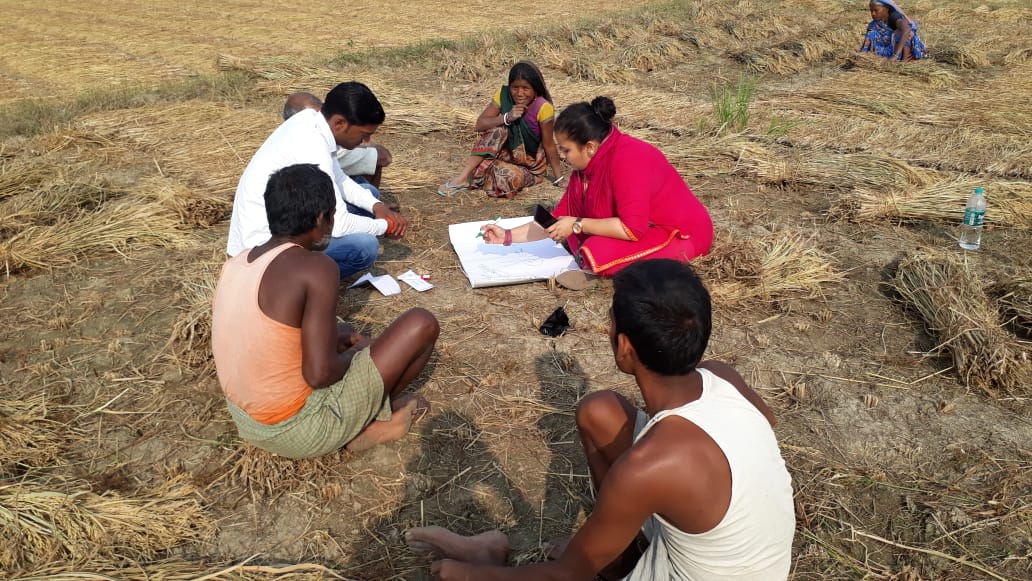

Helping farmers transition to conservation agriculture
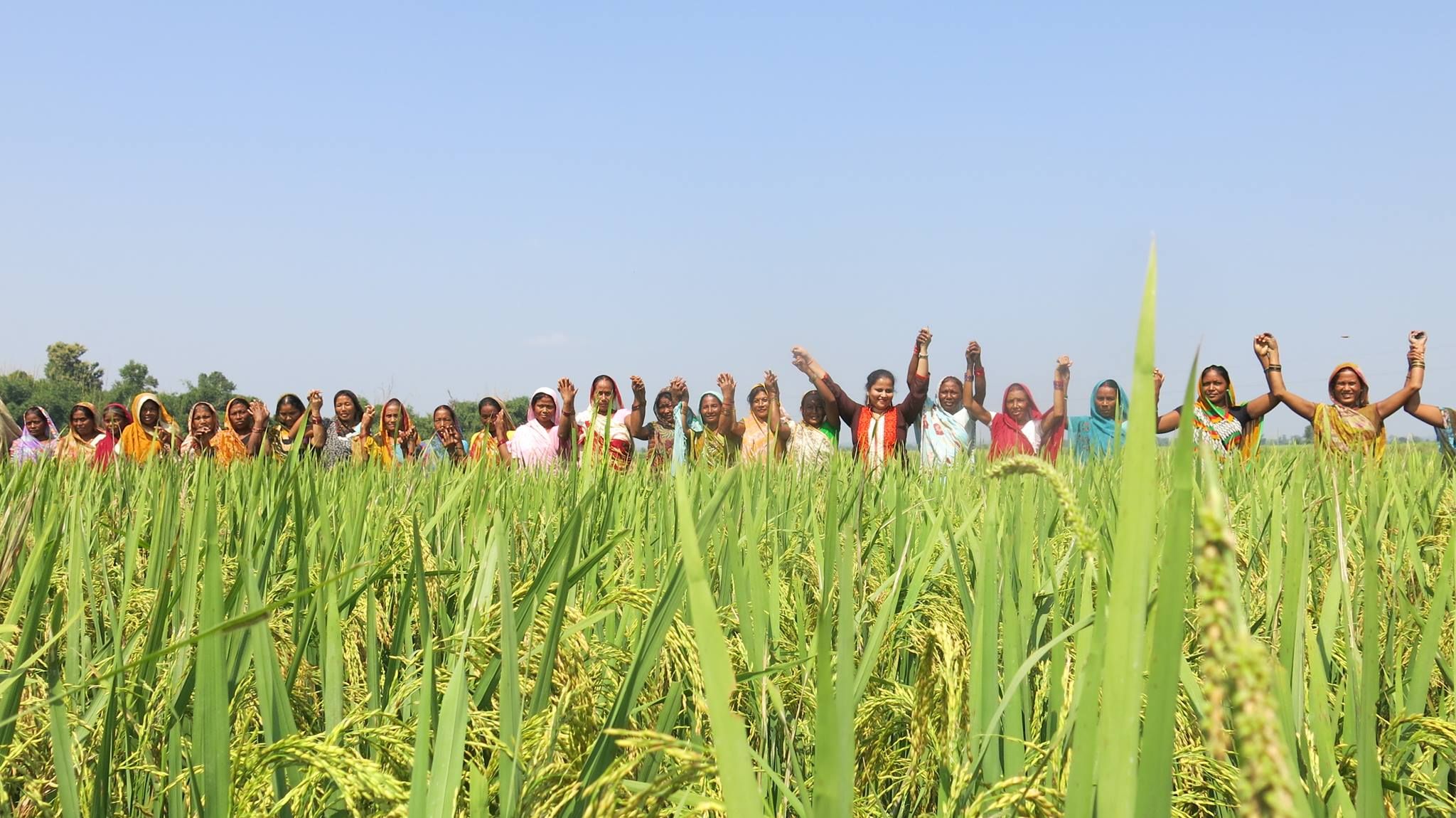
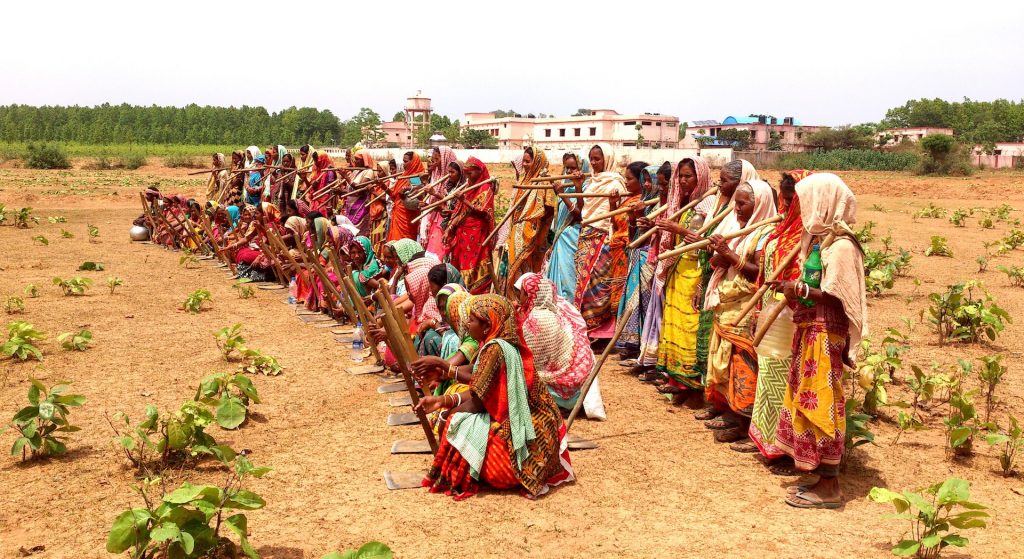
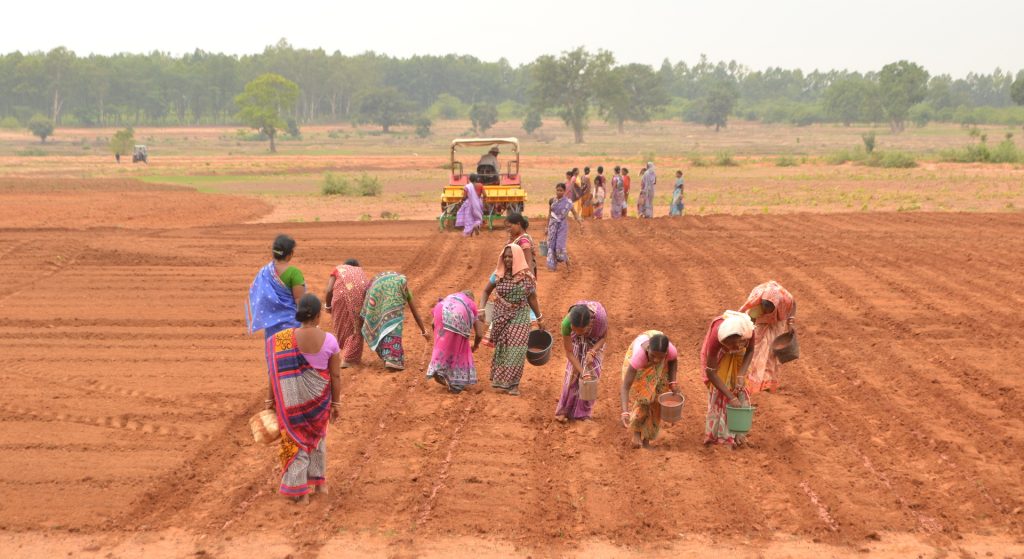
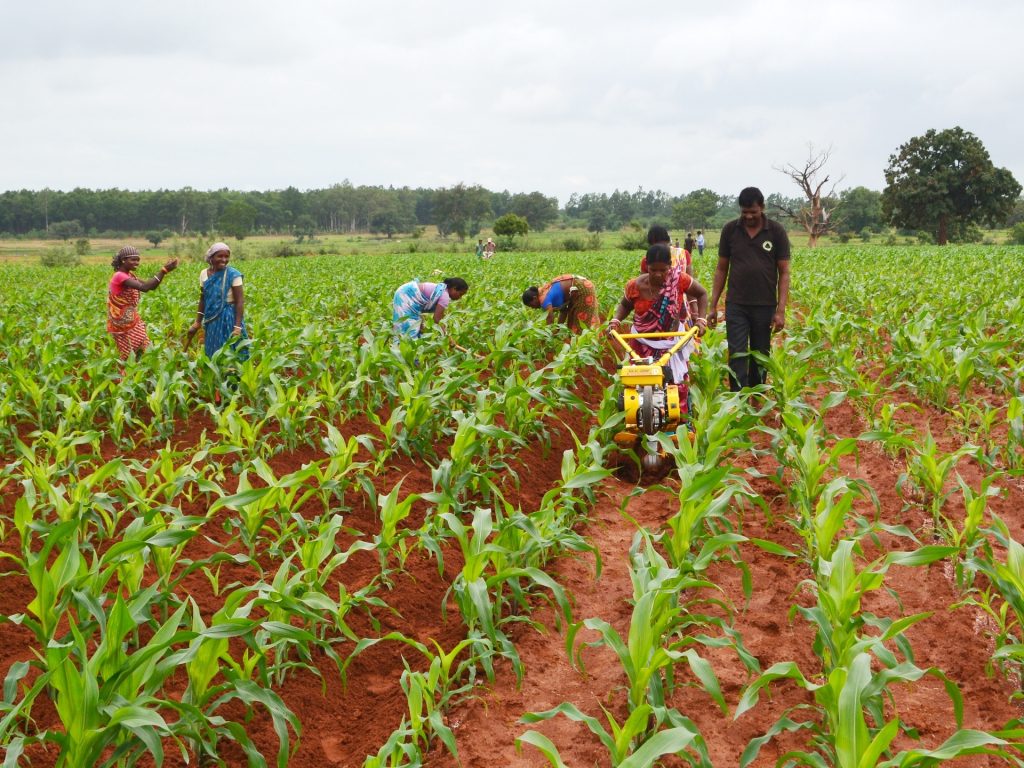
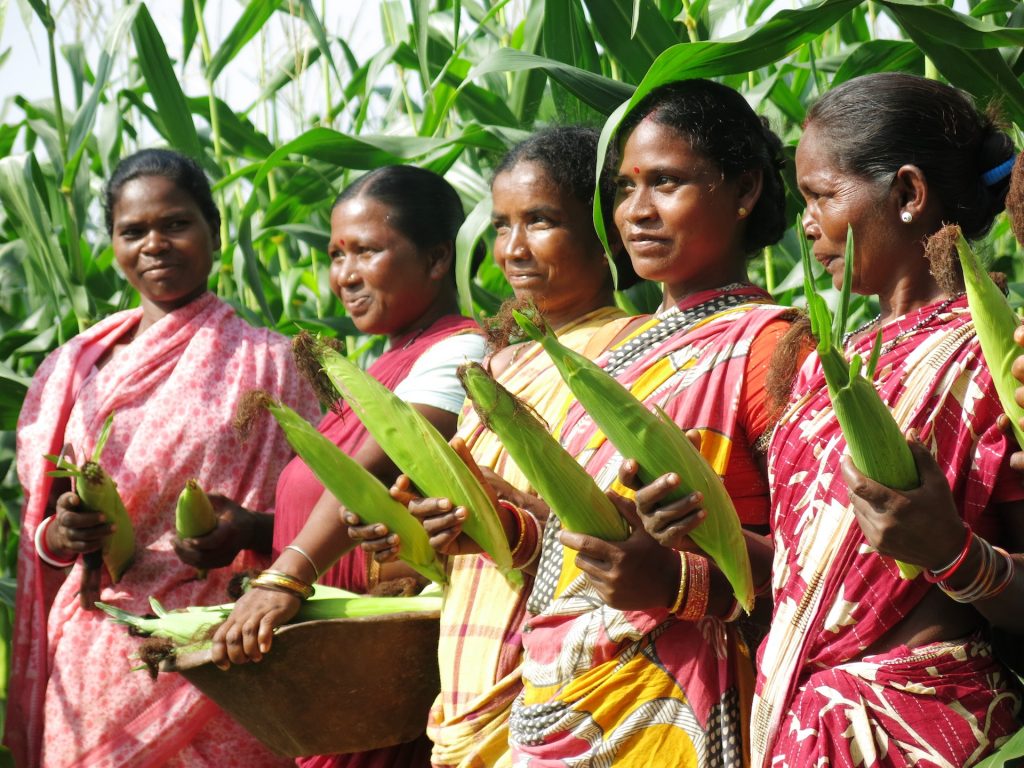
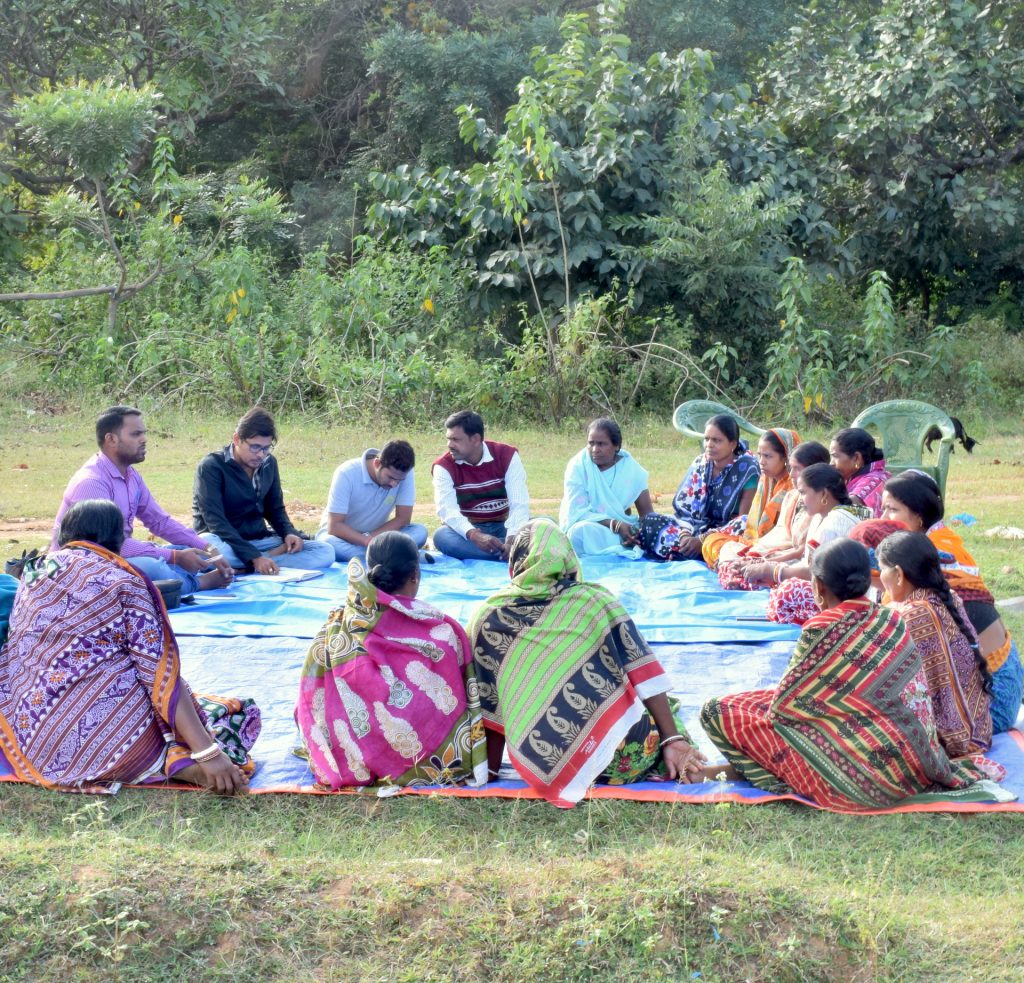
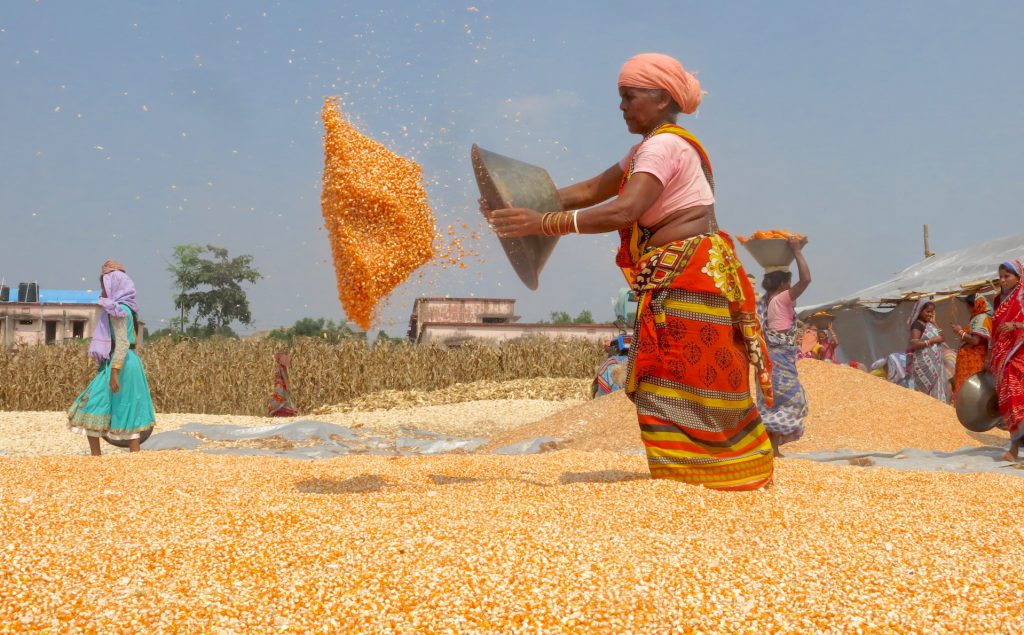
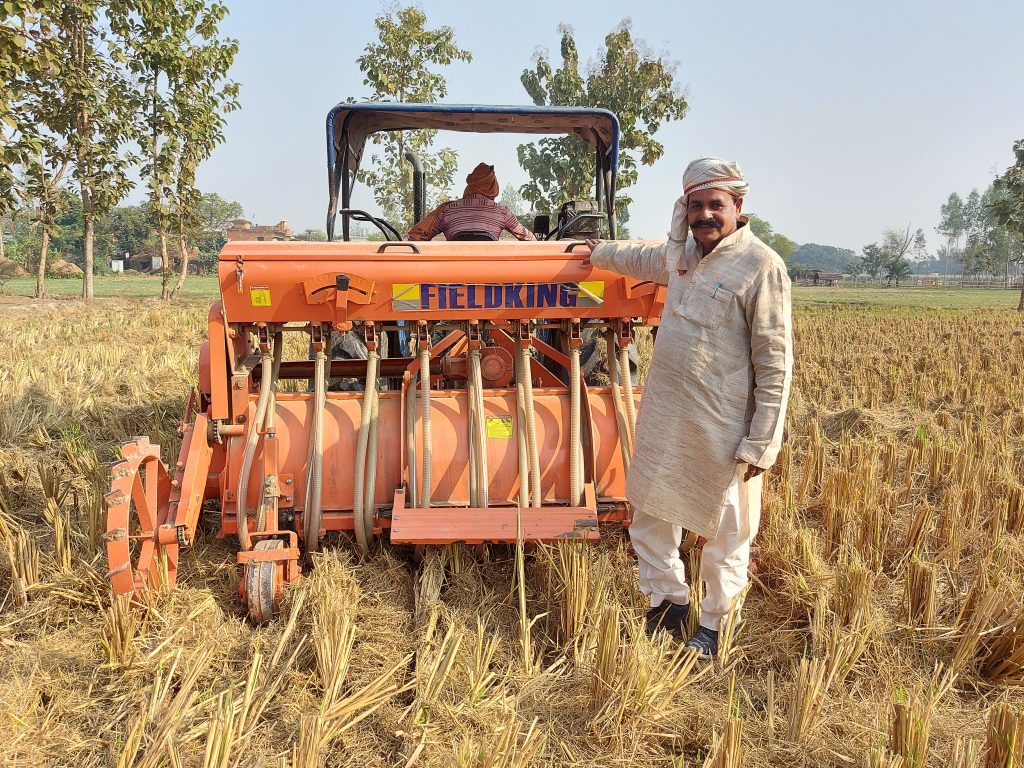
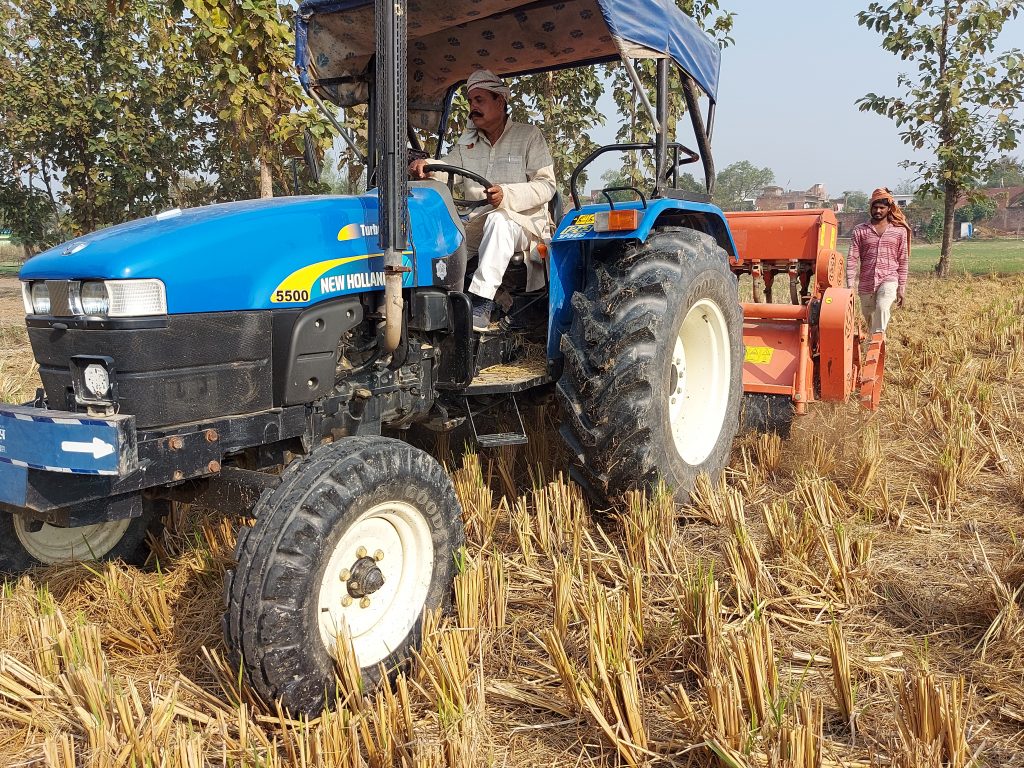
Singh currently works in her home state of Bihar for the Cereal Systems Initiative for South Asia (CSISA), led by CIMMYT. She is engaged with over ten thousand farmers from the states of Bihar and Uttar Pradesh, supporting the adoption of conservation agriculture practices.
Farming is vital for the region, as nearly 70% of the population is engaged in agriculture and extension services. However, food and livelihoods are threatened by the small size of farms, low incomes, and comparatively low levels of agricultural mechanization, irrigation and productivity.
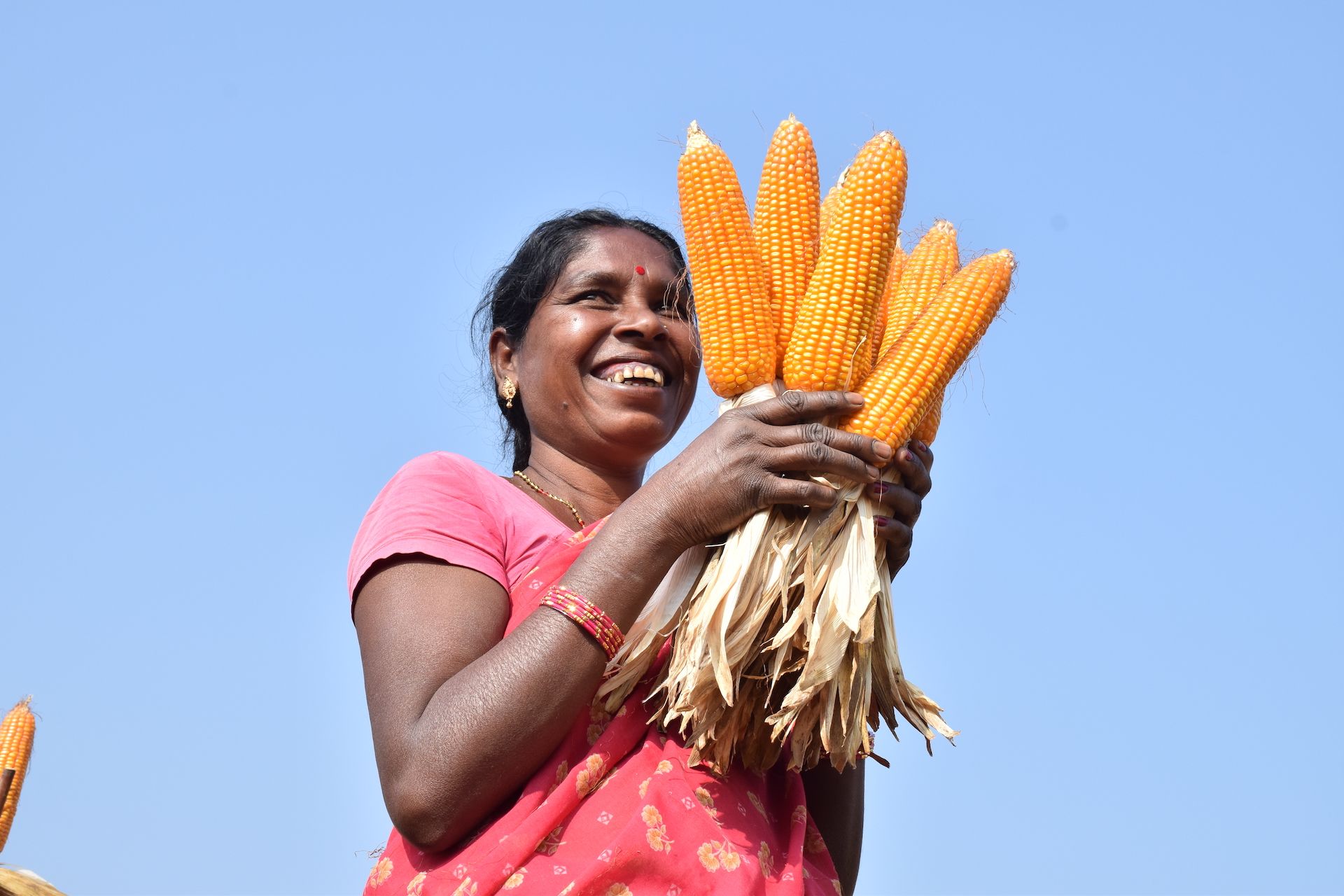
Singh and her colleagues have led the transition from traditional farming to sustainable intensification practices — like early wheat sowing, zero tillage and direct-seeded rice — which have helped smallholder farmers increase their yield potential substantially.
“We believe a project like CSISA, along with the government and partners, can help advance and support in realizing the full agriculture potential of these regions,” Singh explains.
Roots in the soil
Her grandparents were farmers. “To be able to care for the land that provided you nourishment and a living was always admired upon,” she says. As a crop scientist, Singh’s family acknowledges her work as an extension of the services her grandparents practiced.
Sustained by this motivation and encouragement, Singh feels reassured of her role: joining other scientists, partners and farmers to make agriculture sustainable and our communities food-secure.
“The fact that the data we generate from our experiments serve as building blocks in the generation of knowledge and help farmers optimize the cost of inputs and increase their productivity is fulfilling and enriching to me,” Singh expresses.
Apart from working to build the capacity of farmers and extension workers, Singh supports the implementation of field trials and community-based technology demonstrations. She also helps refine key agricultural innovations, through participatory testing, and optimizes cropping systems in the region.
Leading the way for for the next generation
A true representative of the STEM community, Singh is always learning and using her experience to give back to society. She has co-authored numerous books and contributed to journals, sharing her knowledge with others.
Other women leaders in STEM have inspired Singh in her professional life, including CIMMYT’s former deputy director general for research Marianne Banziger. Singh believes Banziger was trailblazing and that young girls today have many female role models in STEM that can serve as inspiration.
The change is already here and many more young women work in STEM, pursuing excellence in agriculture sciences, engineering and research studies contributing to as well as claiming “half the sky.”
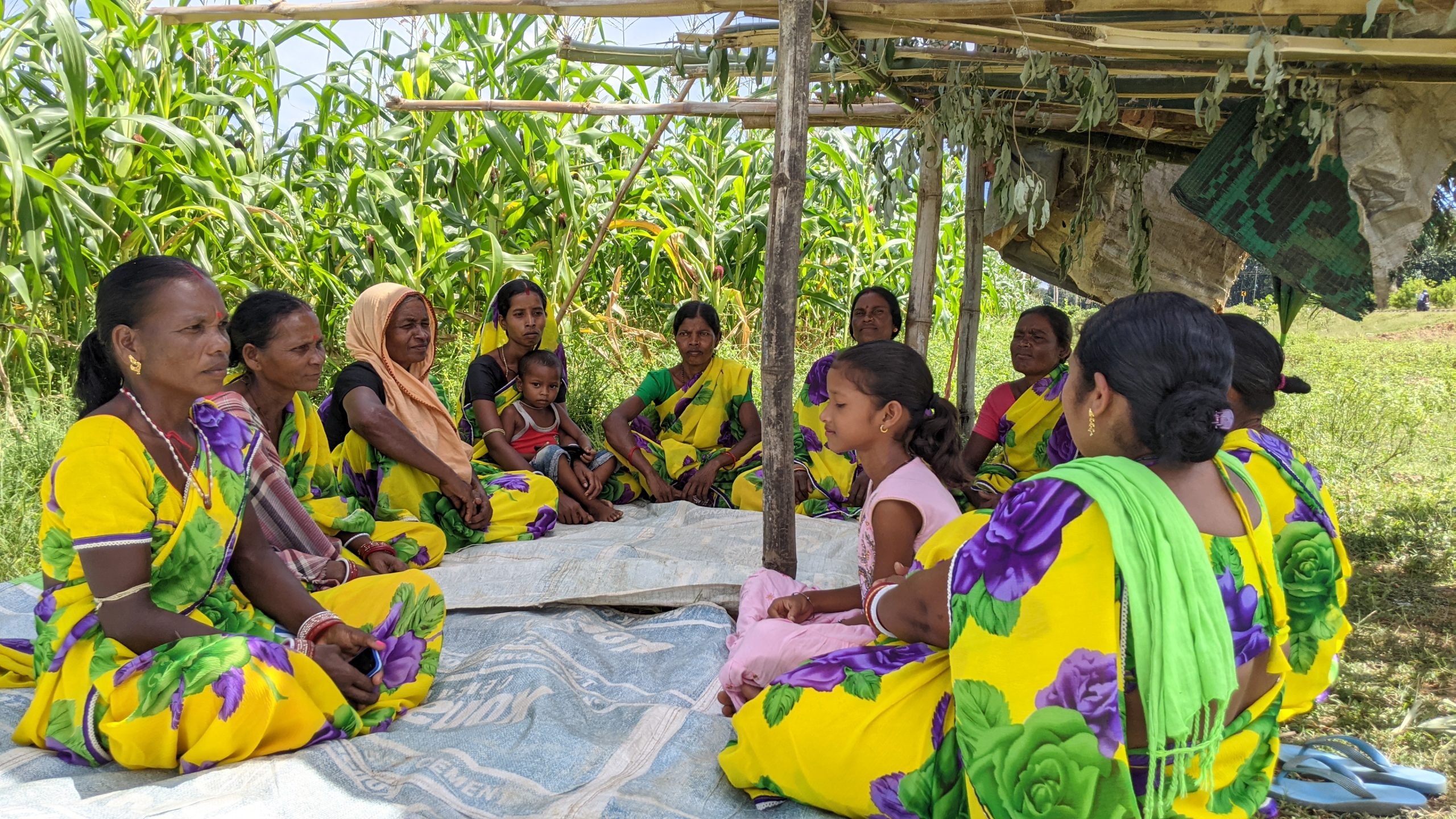
Cover photo: CIMMYT researcher Madhulika Singh (center-right) stands with farmers from self-help groups in the village of Nawtanwa, West Champaran, in India’s Bihar state. CIMMYT works on gender inclusion and participation through partnerships with other organizations and self-help groups. (Photo: CIMMYT)